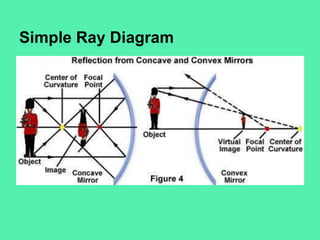
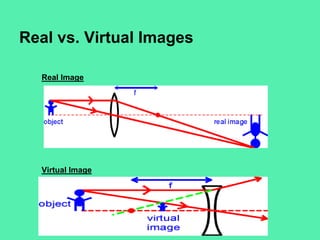
This document discusses different types of mirrors and their properties. It distinguishes between concave and convex mirrors. Concave mirrors curve inward and focus light, producing real or virtual images depending on the object's distance. Convex mirrors curve outward and always produce smaller, upright, virtual images. Examples of uses for each type of mirror are given, including car headlights, security mirrors, and makeup mirrors. Real images are described as inverted while virtual images are upright. A diagram is also included to illustrate ray diagrams and image formation using mirrors.