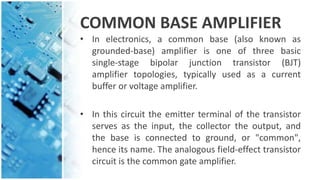
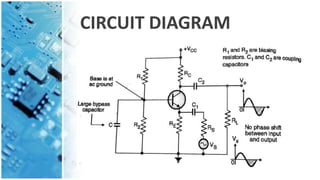
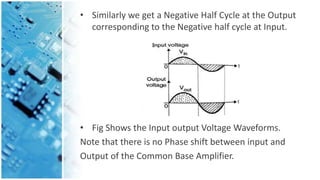
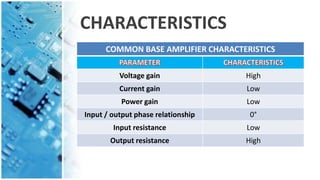
The document explains the common base amplifier, a basic amplifier topology used as a current buffer or voltage amplifier, and its operation. It discusses the types of amplifiers, features, characteristics, and applications, highlighting its low input resistance and high voltage gain. Common base amplifiers are particularly useful for impedance matching and wideband applications.