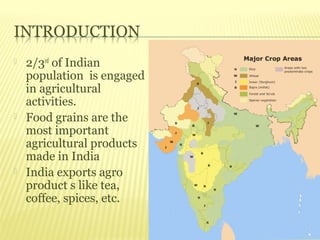
2/3 of India's population is engaged in agriculture, with food grains and exports like tea, coffee and spices being important agricultural products. There are three main types of farming practiced in India - primitive subsistence farming on small plots using basic tools, intensive subsistence farming in high population areas using fertilizers and irrigation, and commercial farming using high-yielding seeds and chemicals. Crops are grown in different seasons - rabi in winter, kharif in monsoon, and zaid in between. Key crops include rice, wheat, millets, maize, pulses, sugarcane, oilseeds, tea, coffee, fruits and vegetables, rubber, cotton, jute, and silk. The government has