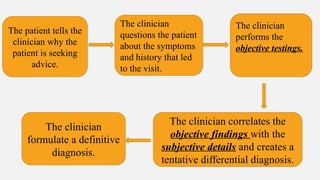
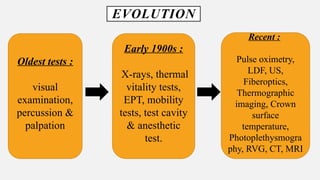
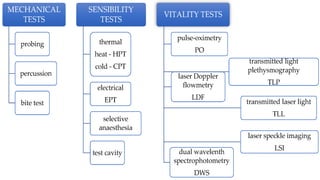
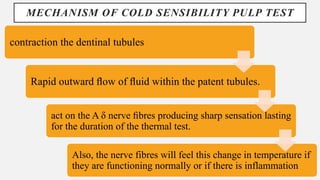
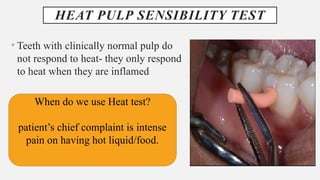
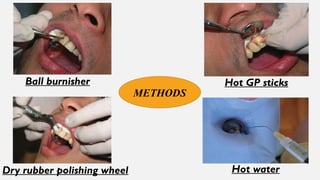
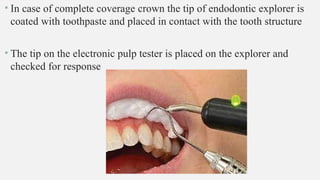
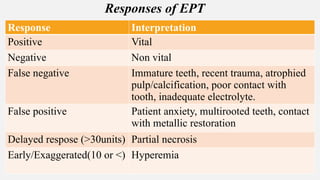
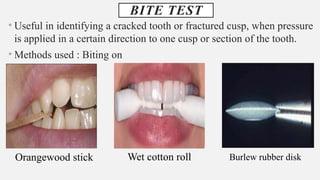
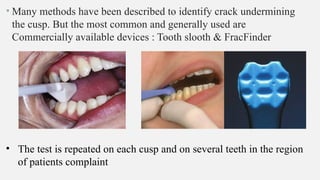
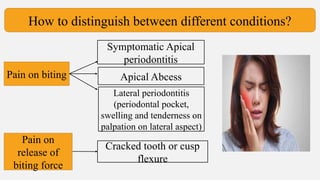
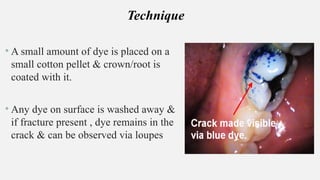
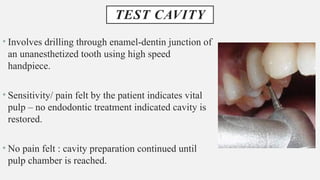
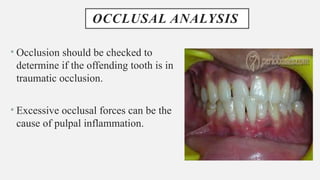
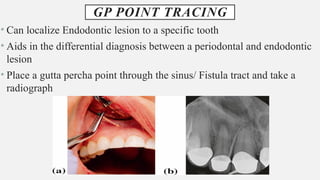
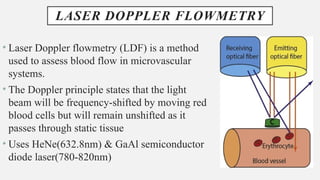
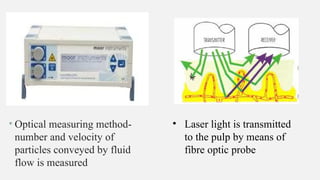
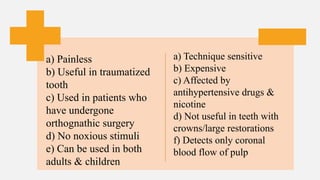
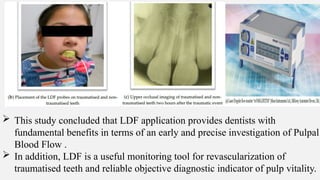
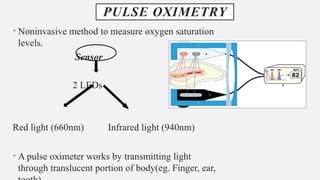
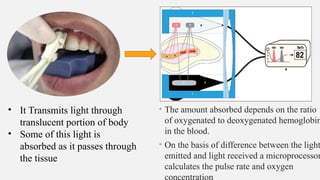
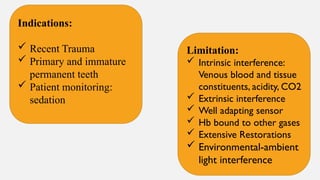
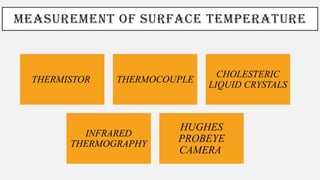
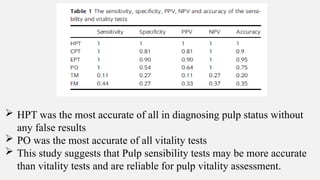
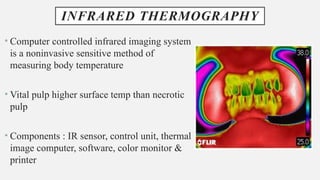
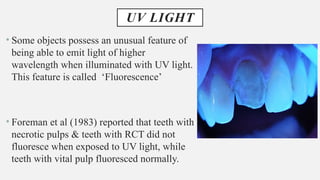
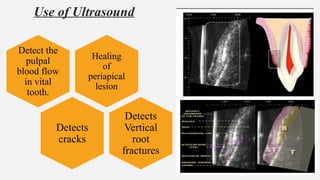
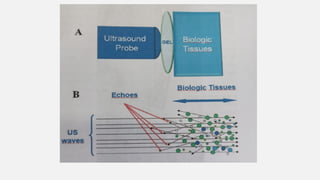
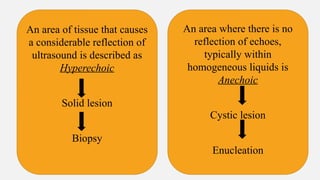
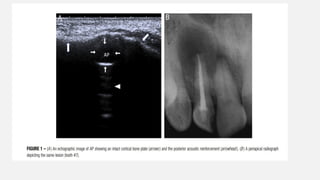
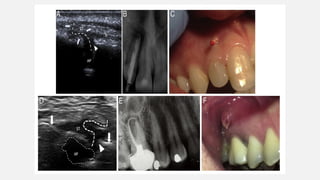
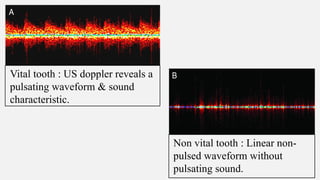
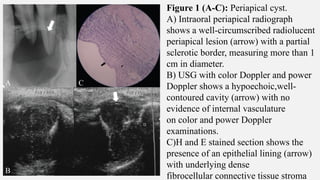
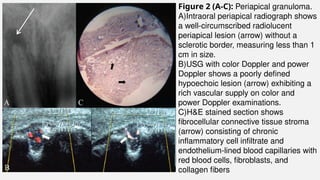
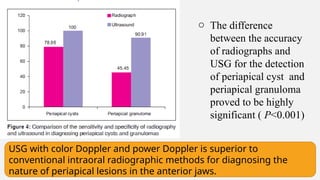
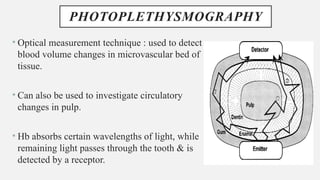
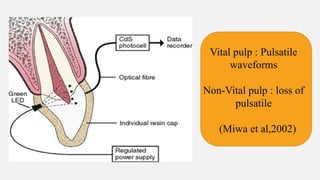
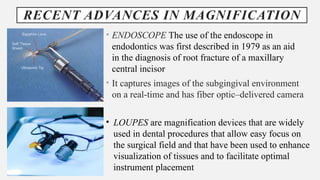
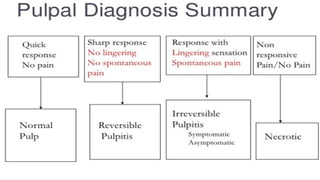
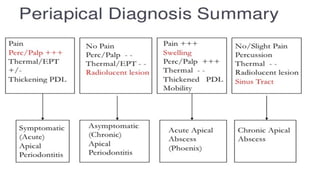
The document provides a comprehensive overview of endodontic diagnosis, detailing various diagnostic methods and their applications in determining pulp health. It explains traditional and modern techniques such as thermal tests, electric pulp testing, and advanced methods like laser doppler flowmetry and infrared thermography, along with their respective advantages and limitations. Key findings indicate a comparison of the sensitivity and specificity of different tests, identifying the most effective methods for assessing pulp vitality and diagnosing dental conditions.