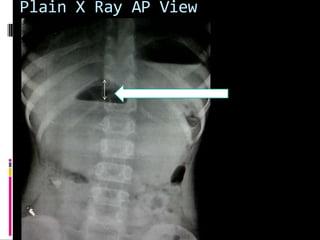
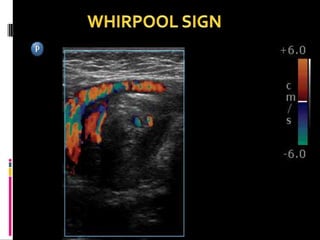
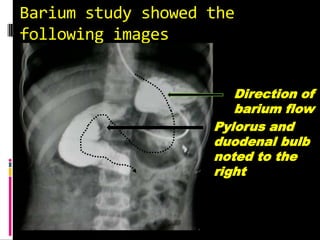
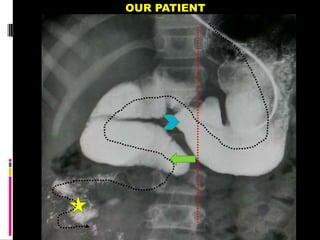
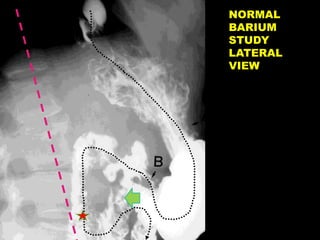
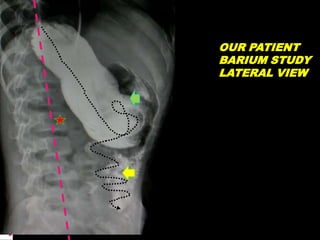
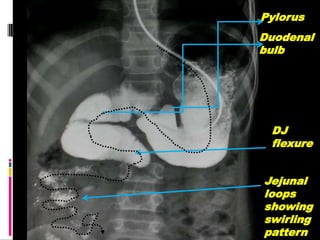
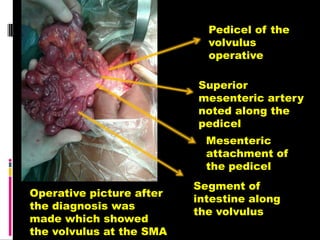
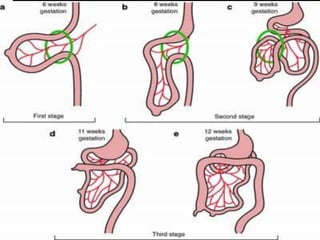
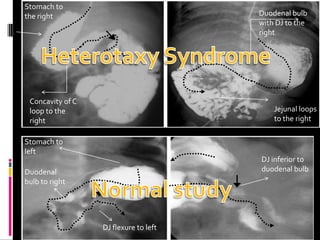
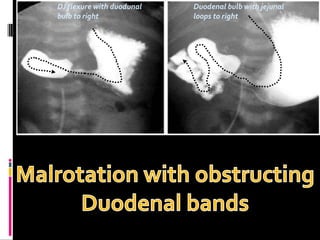
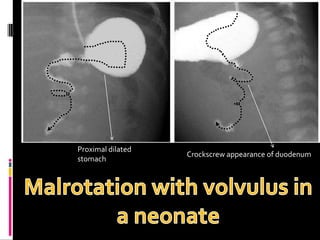
A 10-year old female presented with abdominal pain, bilious vomiting, and an epigastric lump. Imaging studies including ultrasound, barium study, and surgery revealed malrotation of the gut with midgut volvulus. Normally during fetal development the gut rotates to position the duodenojejunal flexure on the left, but in this patient malrotation left the bowel susceptible to twisting around the superior mesenteric artery, known as midgut volvulus. The barium study and ultrasound were able to diagnose malrotation and volvulus without other tests.