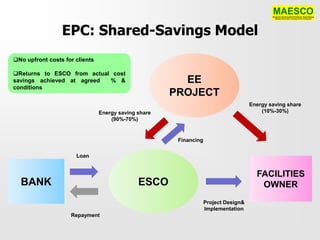
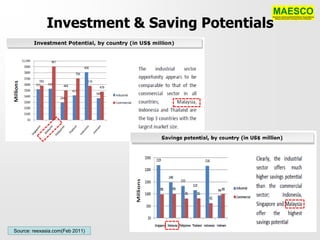
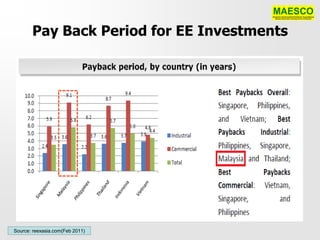
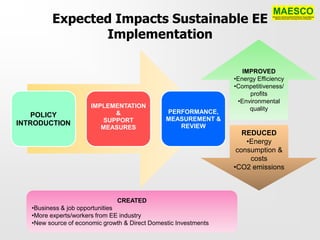
The document discusses a networking session focused on the potentials of energy efficiency (EE) in Malaysia, organized by Maesco. It highlights the role of Energy Service Companies (ESCOs) in implementing EE projects, identifies barriers to EE implementation, and proposes measures for sustainable development in the sector. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for a national EE policy, a centralized agency, and funding mechanisms to overcome existing challenges and promote energy efficiency across various sectors.