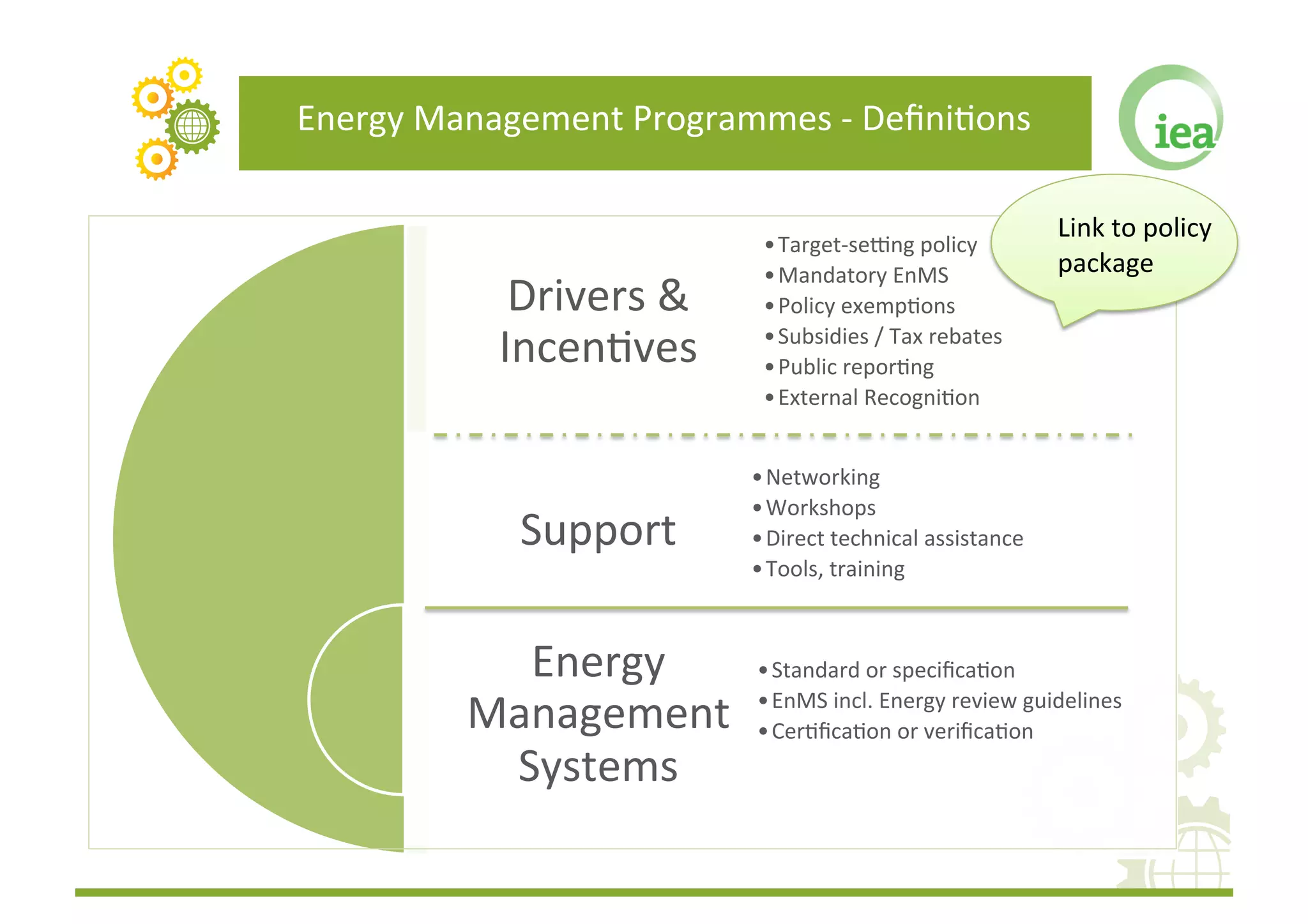
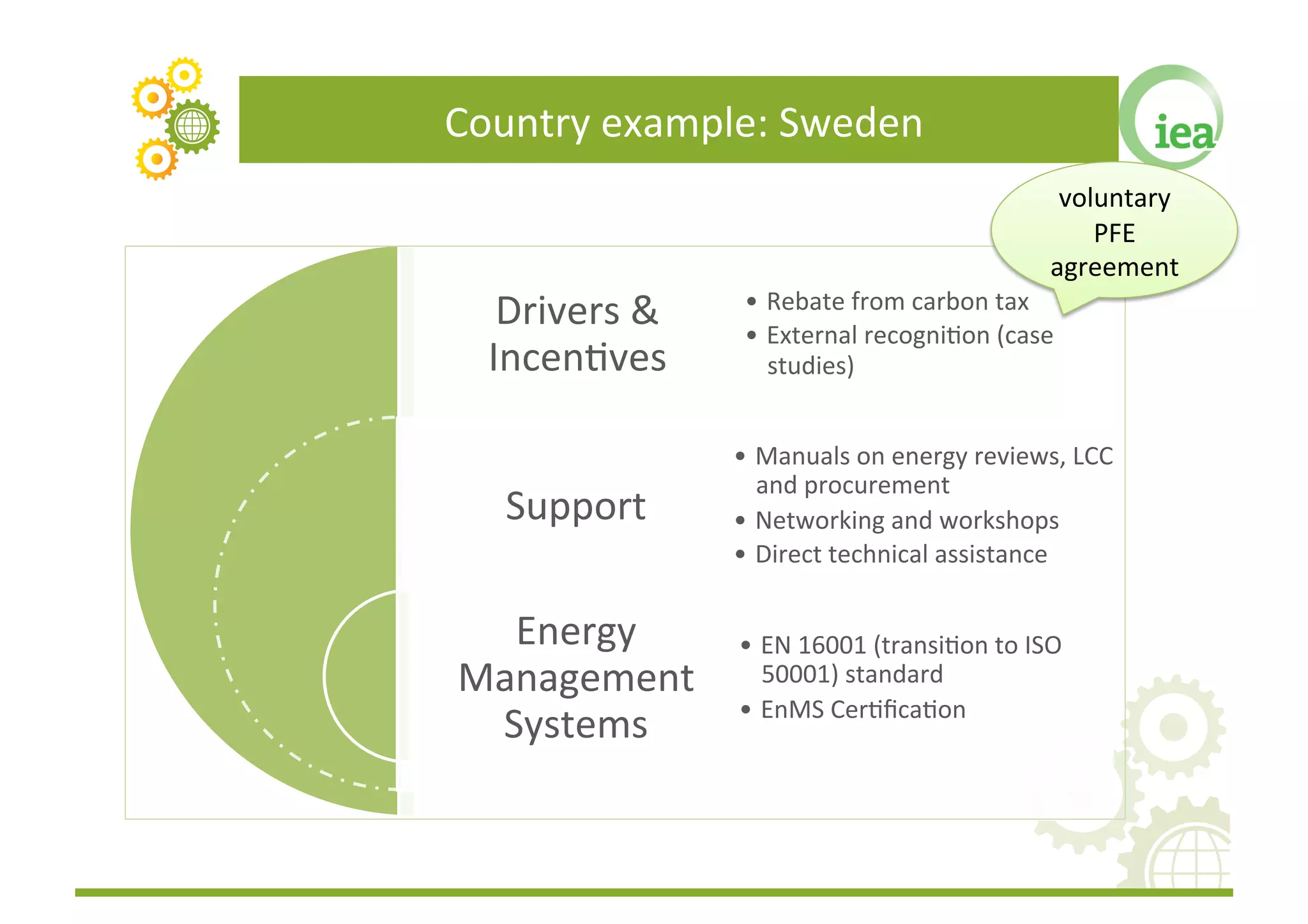
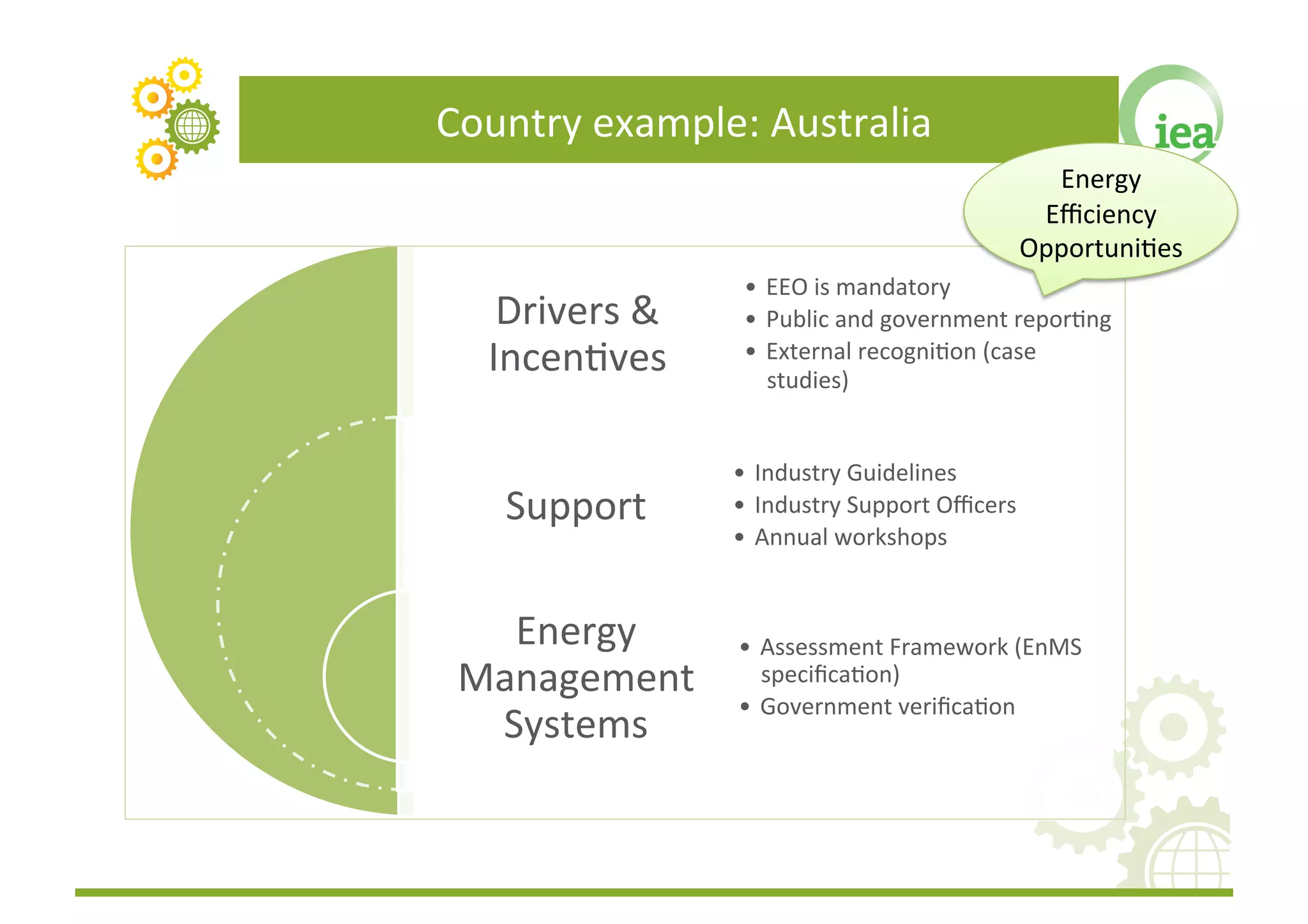
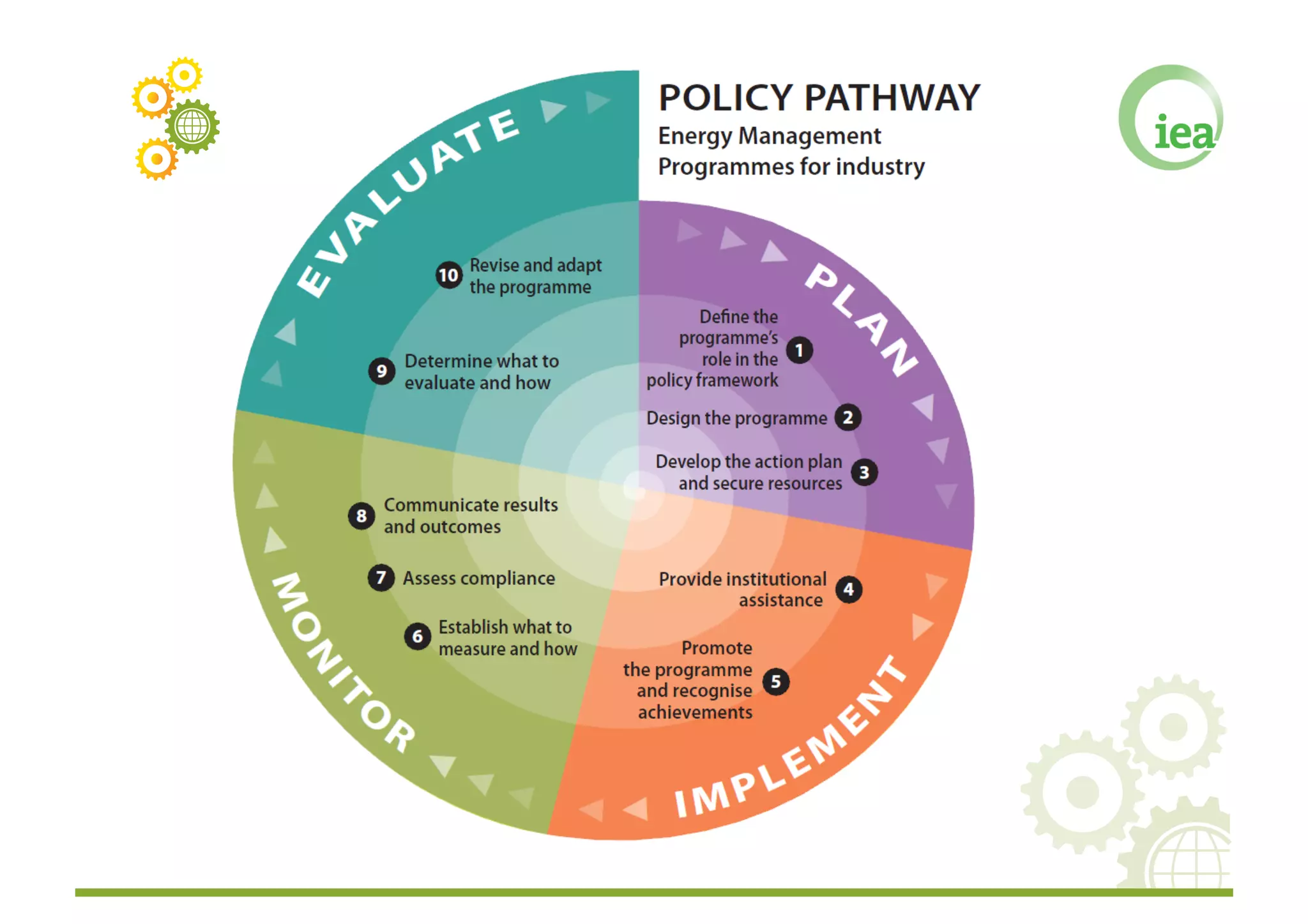
The document discusses energy management programs (EnMPs) and their importance for reducing energy use and costs in industry. It provides an overview of the Institute for Industrial Productivity's relevant research on EnMPs, including case studies of programs in various countries and guidelines for designing and implementing effective EnMPs. The key components of successful EnMPs are establishing energy management systems, while also providing drivers, incentives, and implementation support for companies.



![Decision-‐makers
Ma]er!
Need
to
make
a
compelling
business
case
to
the
board
Produc(vity
gains
“sell”
Chief Technology Officer
“Do we know what energy efficiency
practices and technologies are
available?” Financial Director
Driver: knowledge Do we have the money to invest
and are we willing to spend it on
EE?
Driver: Financials
CEO
Are we committed to prioritize EE
above other investments?
Driver: Commitment
Source:
Ecofys
in
Reinaud
and
Goldberg,
2011
Marketing Director
Do the public and market demand
us taking EE measures?
Driver: Public and market Regulatory Affairs Officer
demand Does this government policy
require us to take EE measures?
Driver: Policy obligation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eeglobalmar2012pres-120426082602-phpapp02/75/Pathways-to-Energy-Management-Programmes-Gaining-through-Saving-Amelie-Goldberg-5-2048.jpg)
![EnMS
in
the
Supply
Chain
What
is
the
role
of
EnMS
in
supply
chain
ini(a(ves?
• Successful
examples
of
large
buyers/retailers
engaging
their
manufacturing
base
in
energy
or
GHG
saving
acFviFes,
e.g.:
• Ikea
audits
and
capacity
building
with
its
manufacturing
suppliers
(partnership
with
WWF
Climate
PosiFve
OpportuniFes
for
Suppliers)
• Ford
and
SKF
require
suppliers
to
be
ISO
14001
cerFfied
• IIP
Database
on
Supply
Chain
IniFaFves
for
Industry
(April)
• ISO
50001
–
an
internaFonally
recognised
a
framework
for
organisaFons
to
encourage
suppliers
to
be]er
manage
energy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eeglobalmar2012pres-120426082602-phpapp02/75/Pathways-to-Energy-Management-Programmes-Gaining-through-Saving-Amelie-Goldberg-14-2048.jpg)