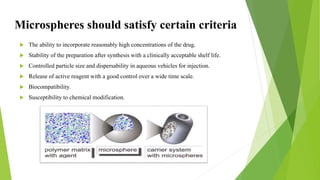
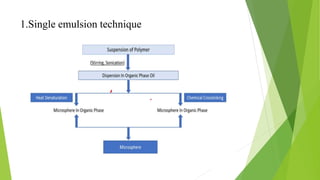
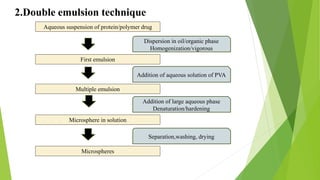
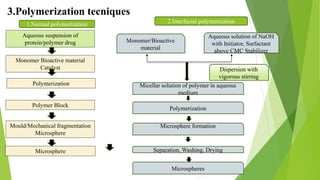
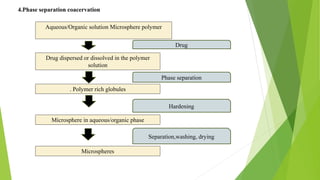
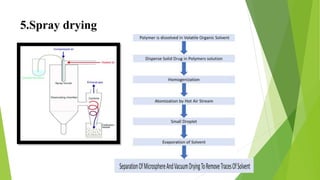
Microspheres are solid biodegradable polymer particles that are typically less than 200 μm in size. They can incorporate drugs throughout their matrix and provide controlled release of medications over extended periods of time. Microspheres are prepared using various techniques including single emulsion, double emulsion, and polymerization. They are evaluated based on parameters such as particle size, shape, drug content, degradation, and release kinetics. Microspheres show potential for a variety of pharmaceutical applications due to their biodegradability and ability to prolong drug delivery.