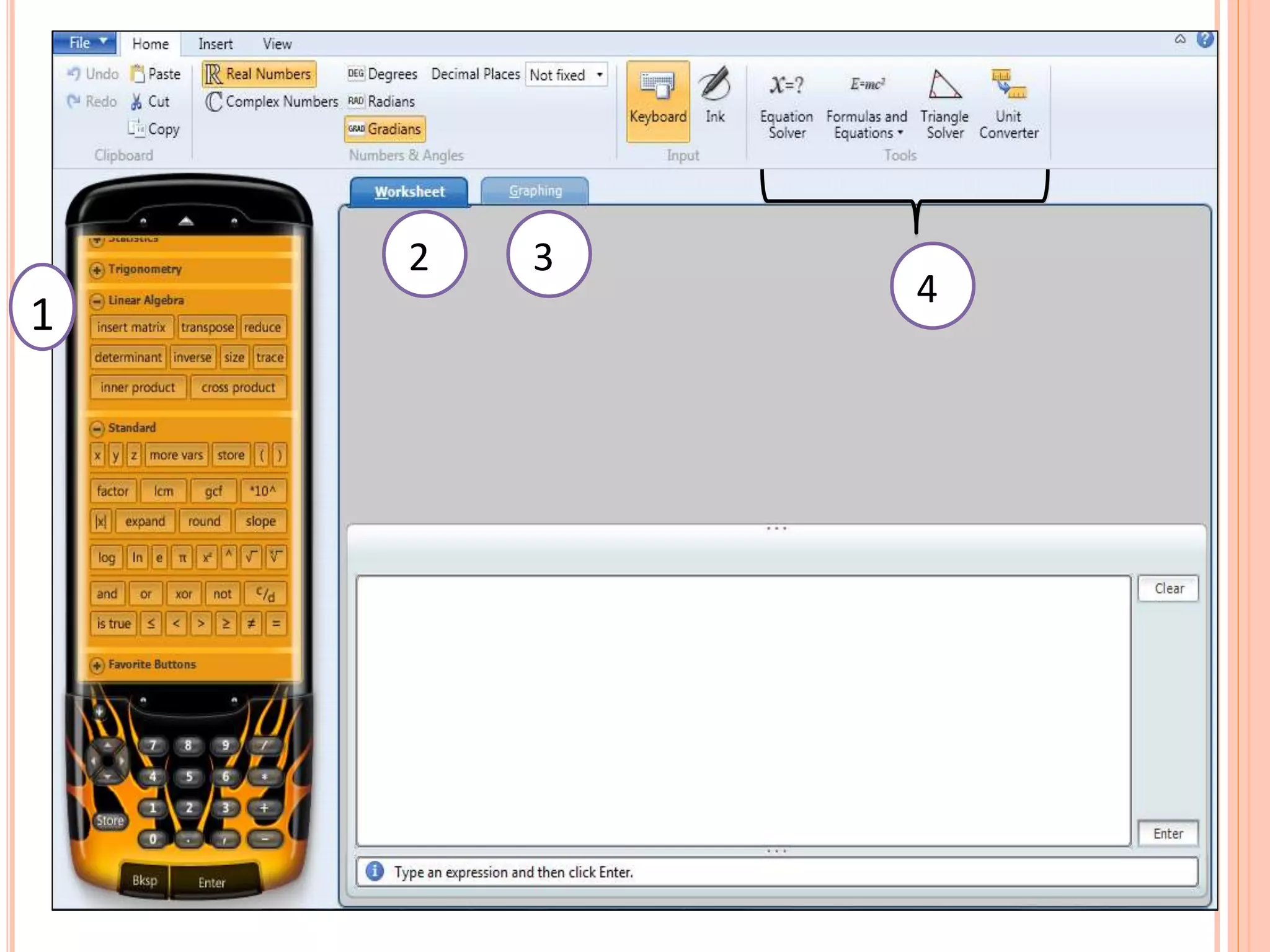
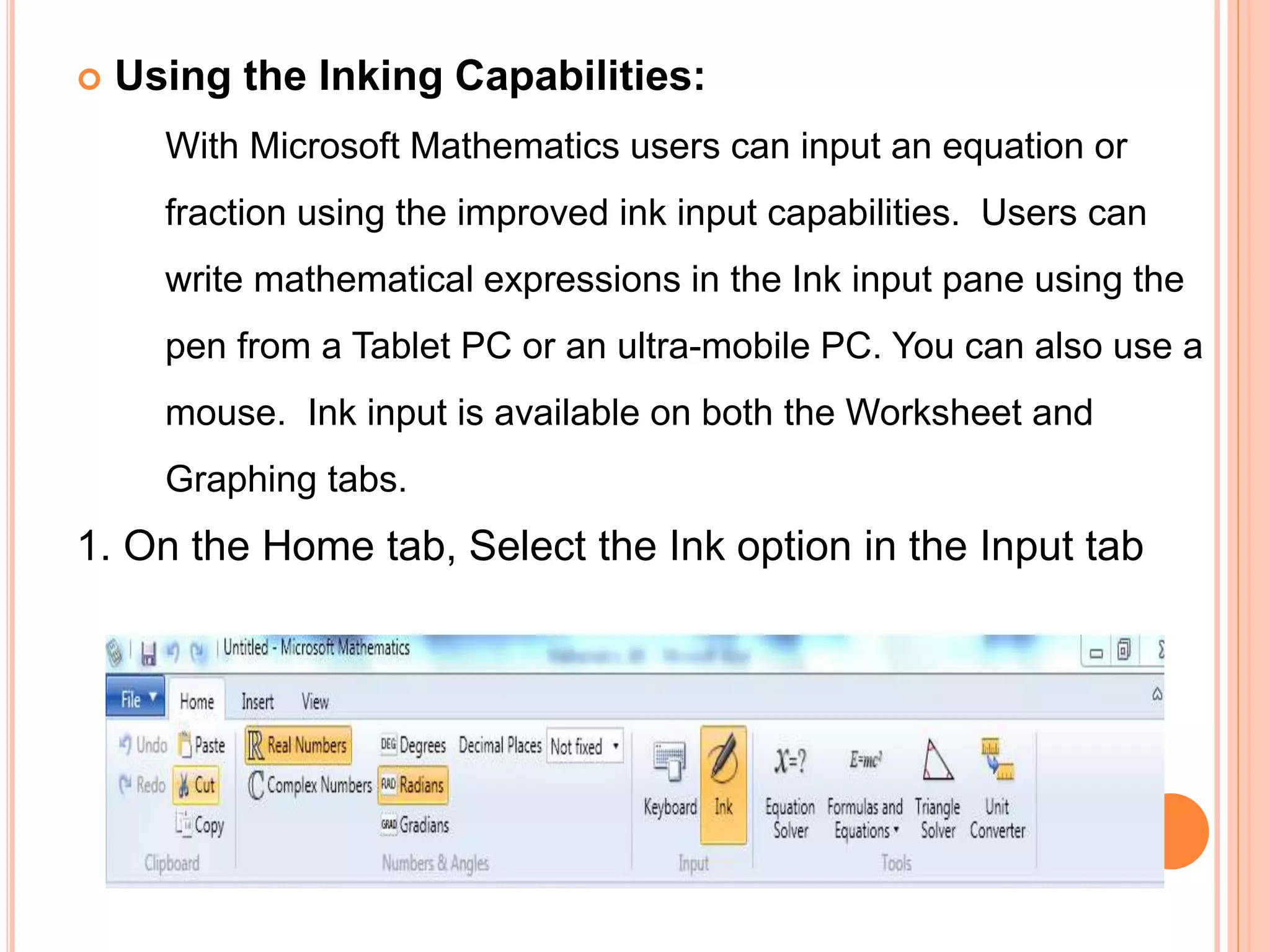
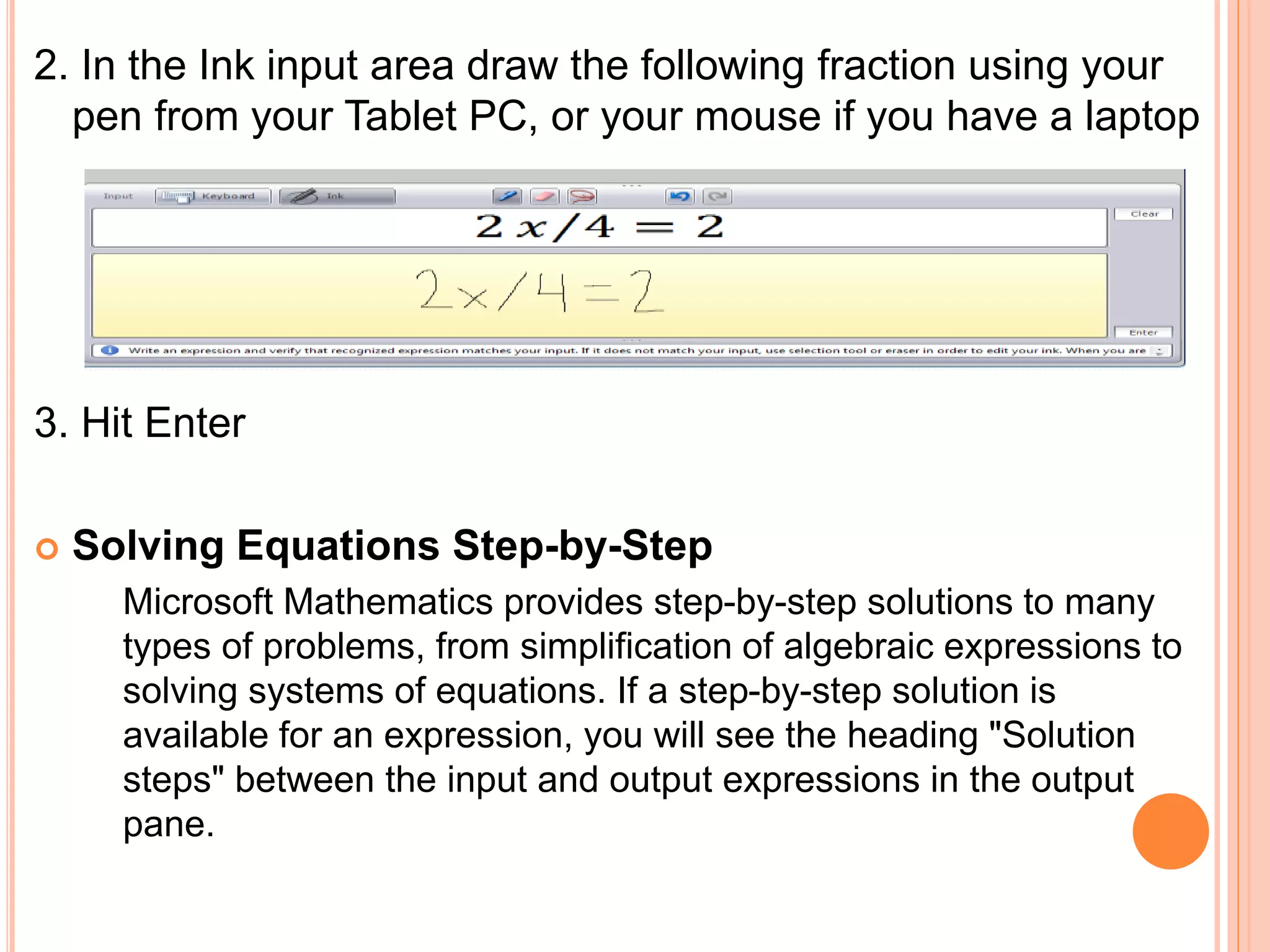
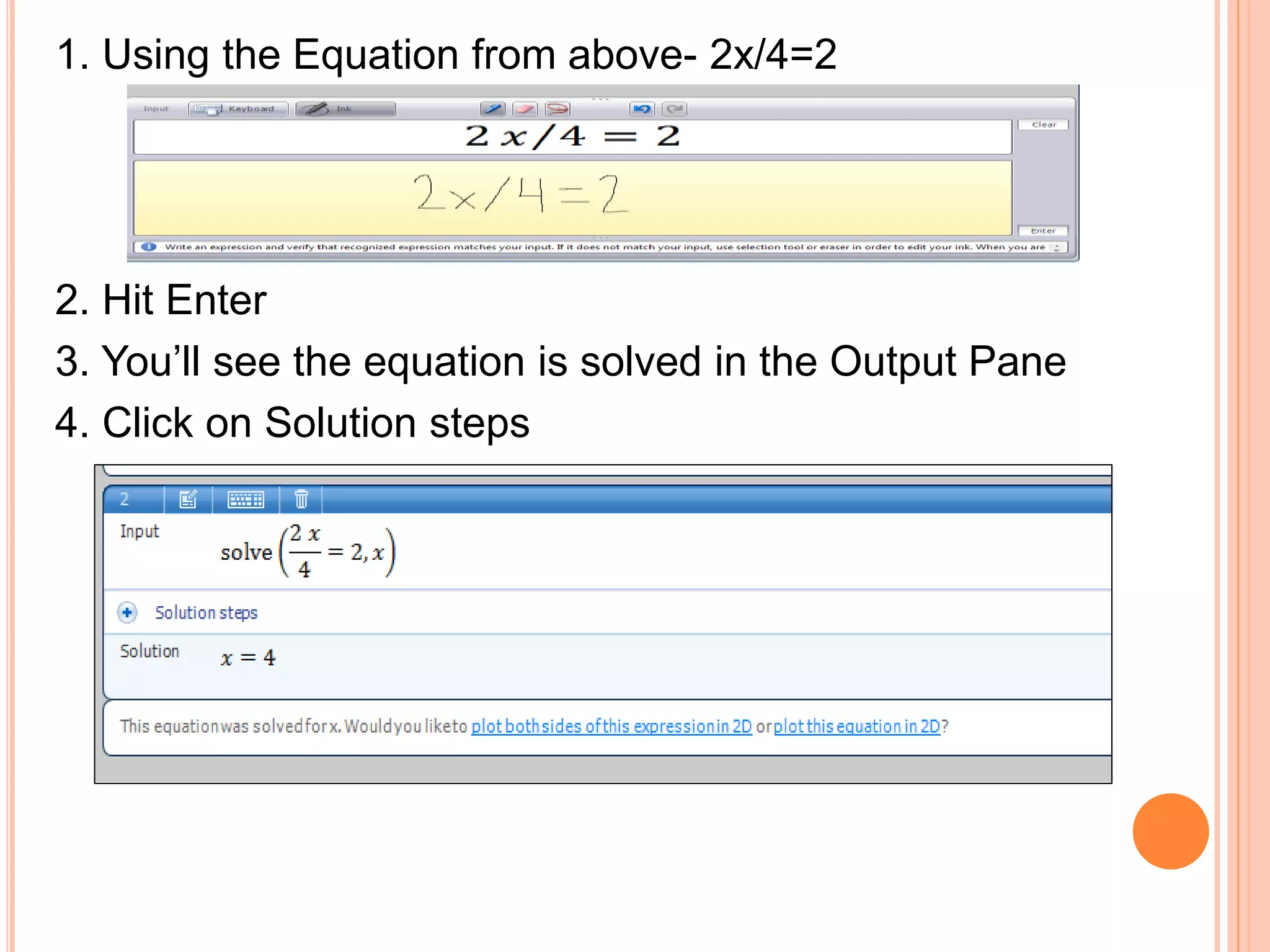
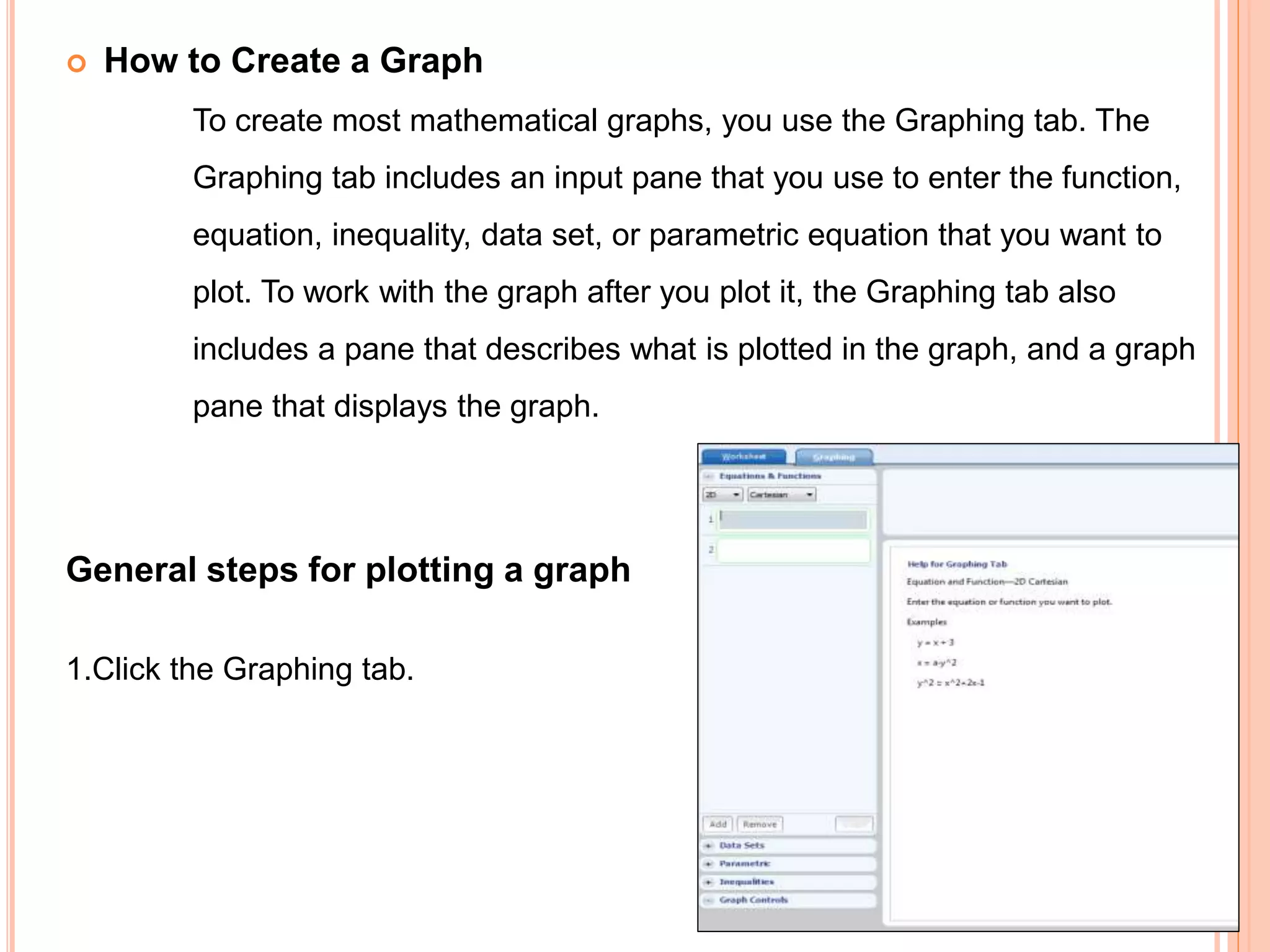
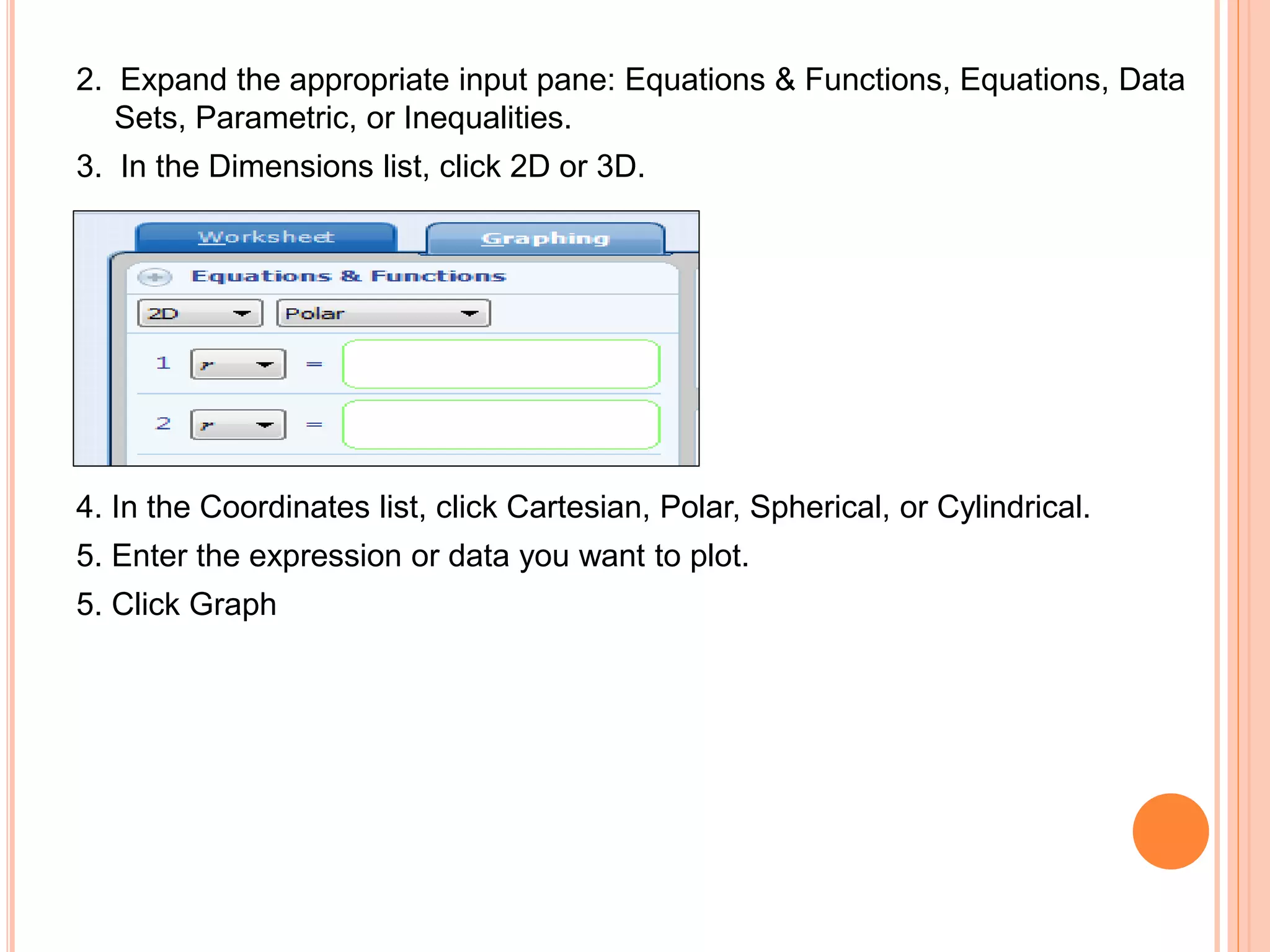
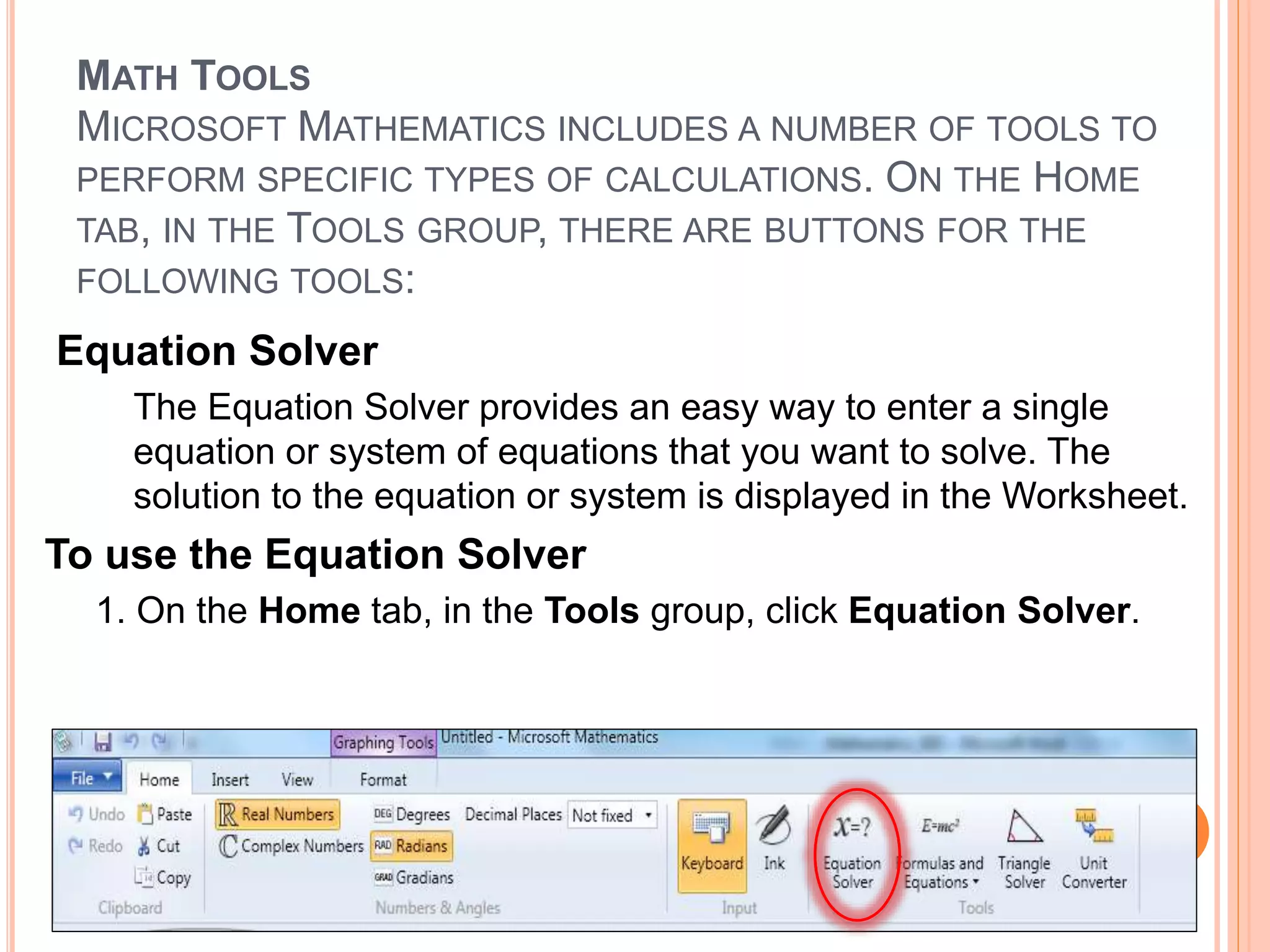
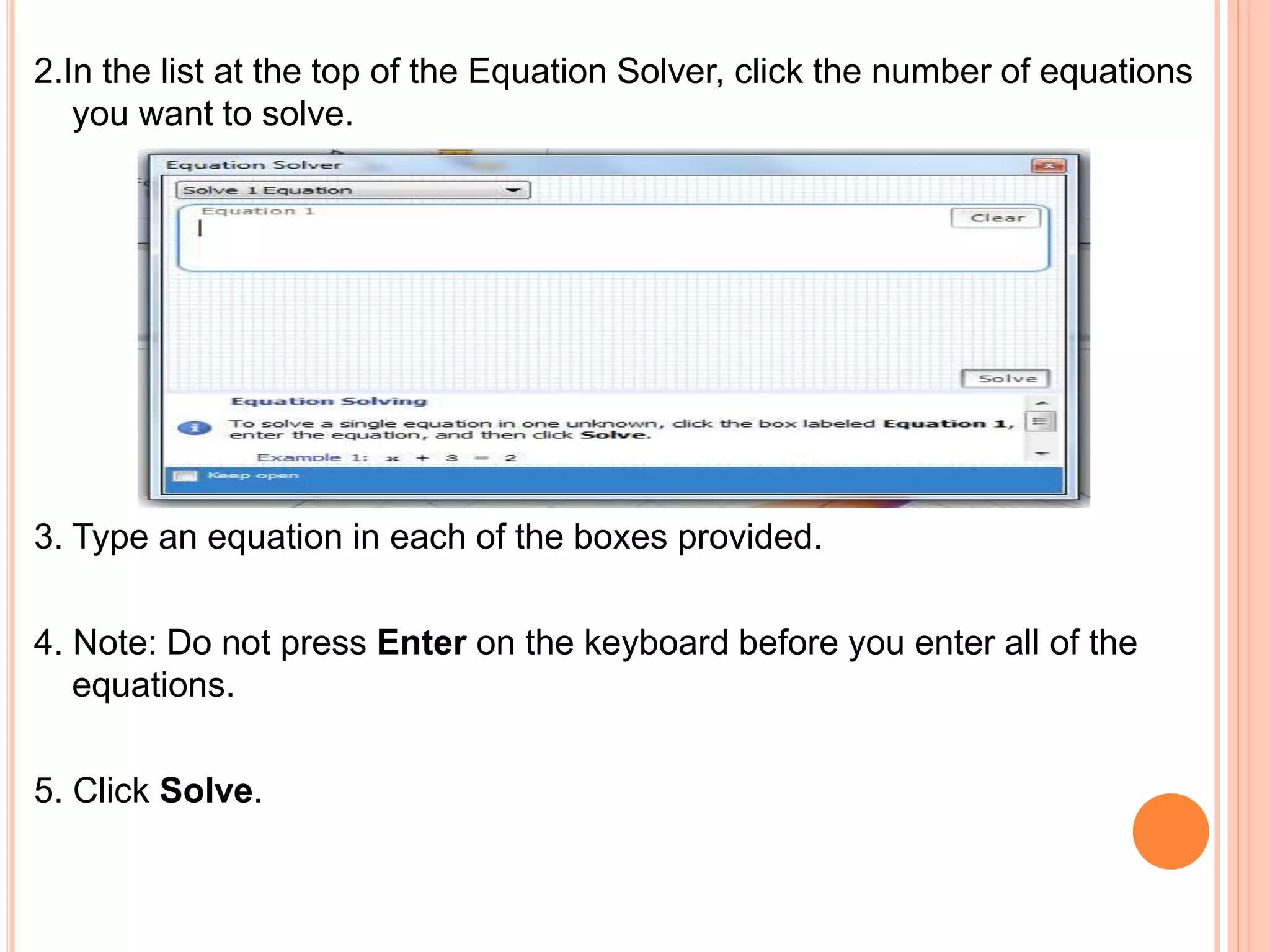
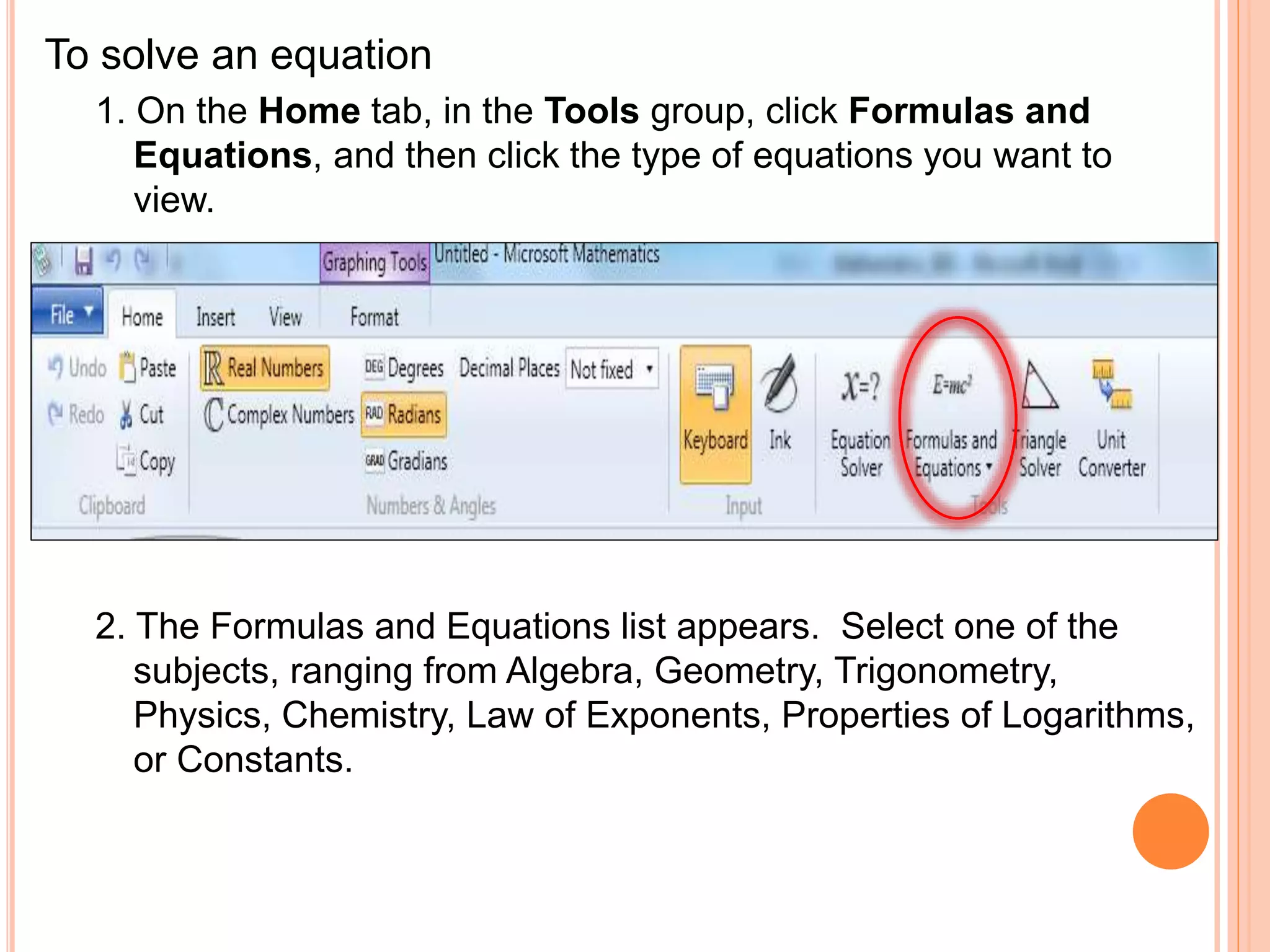
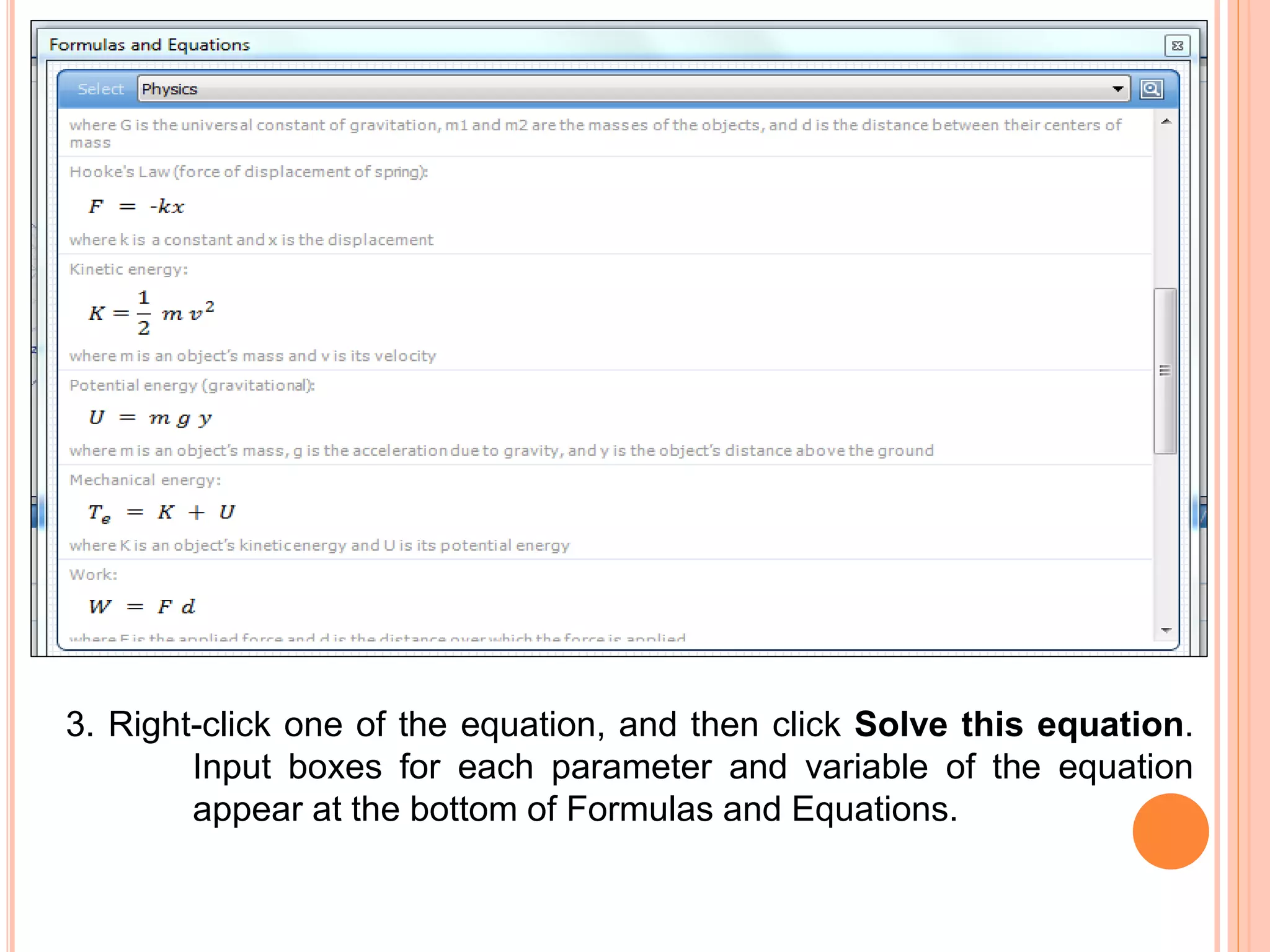
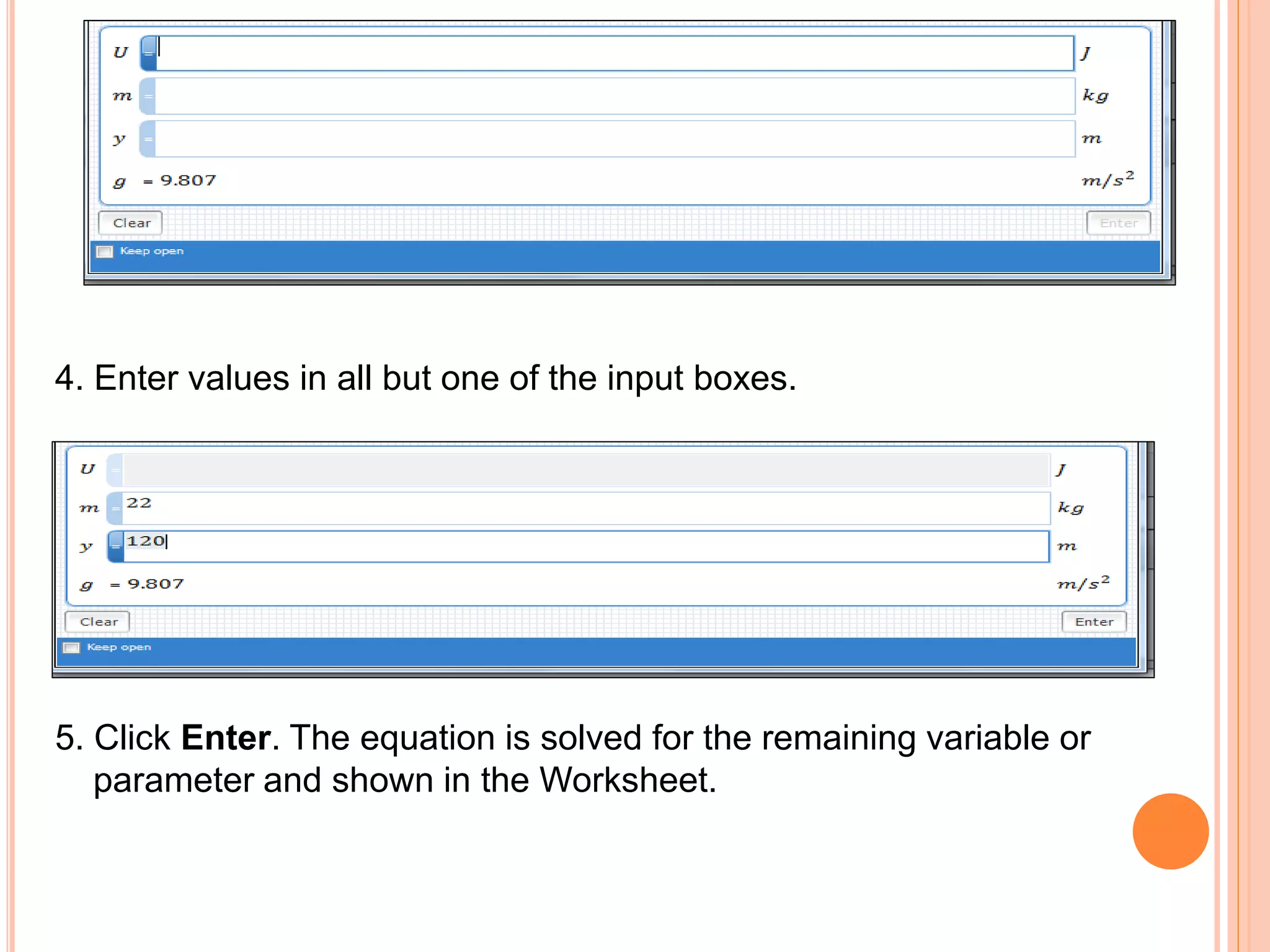
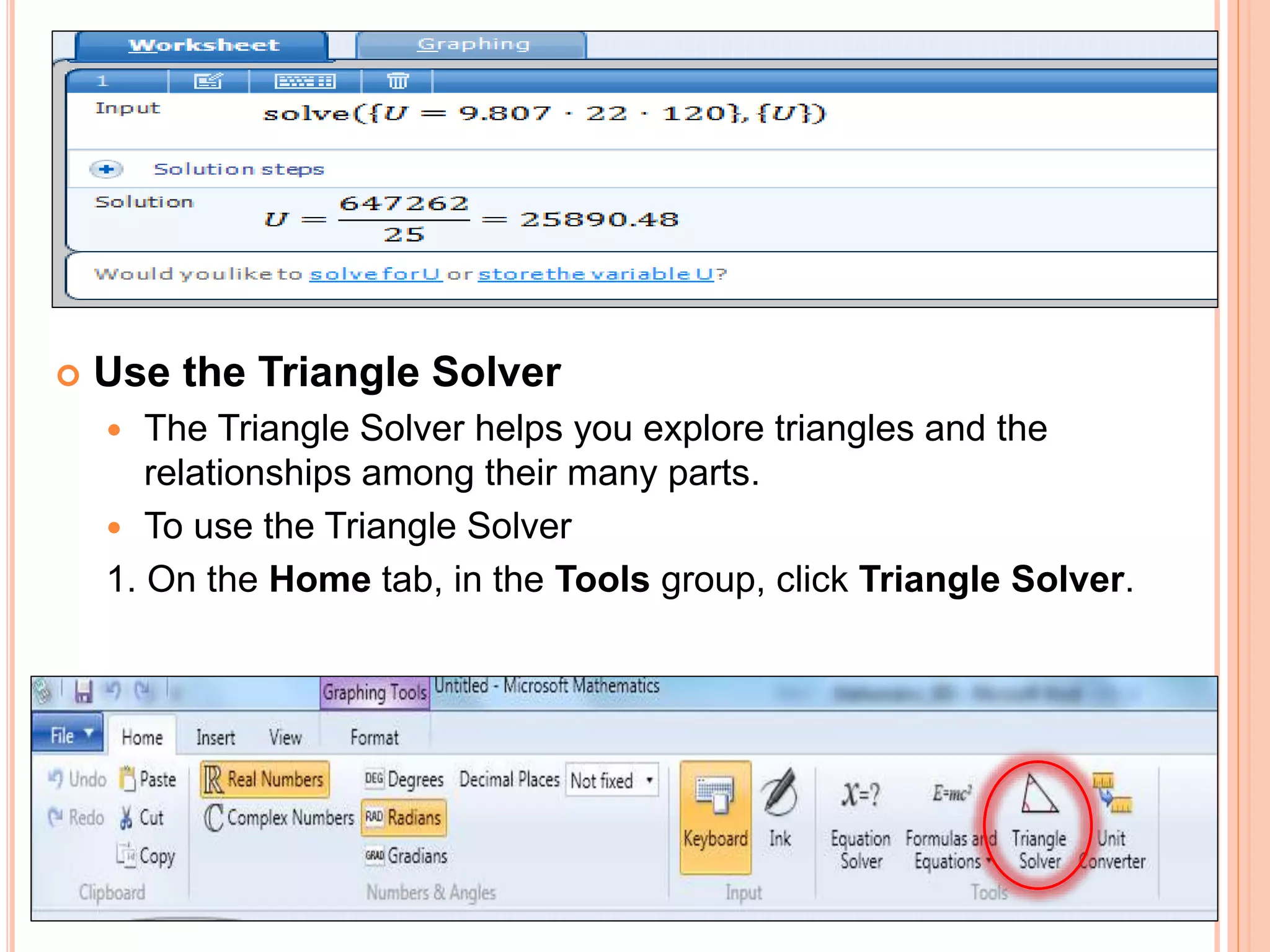
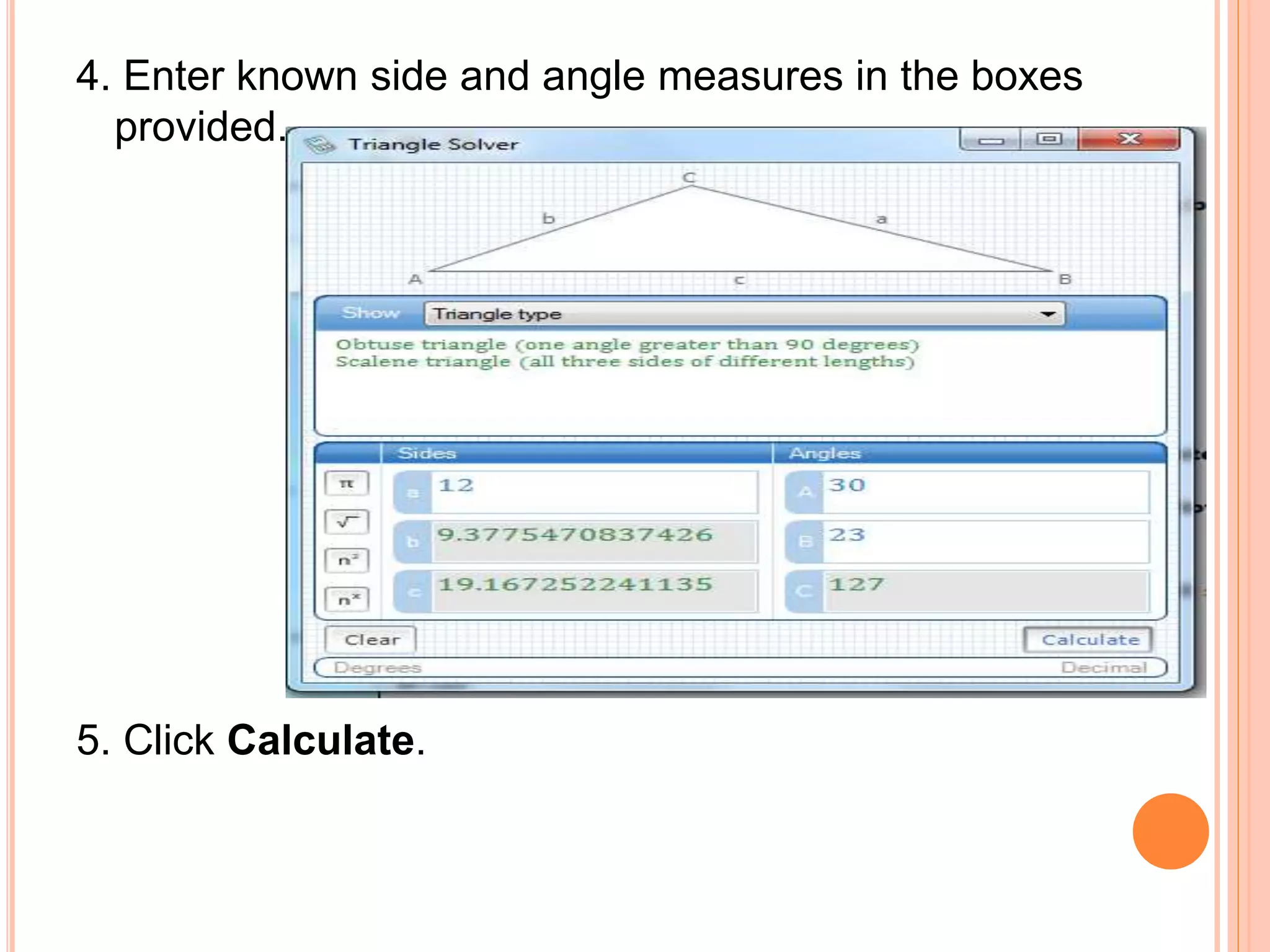
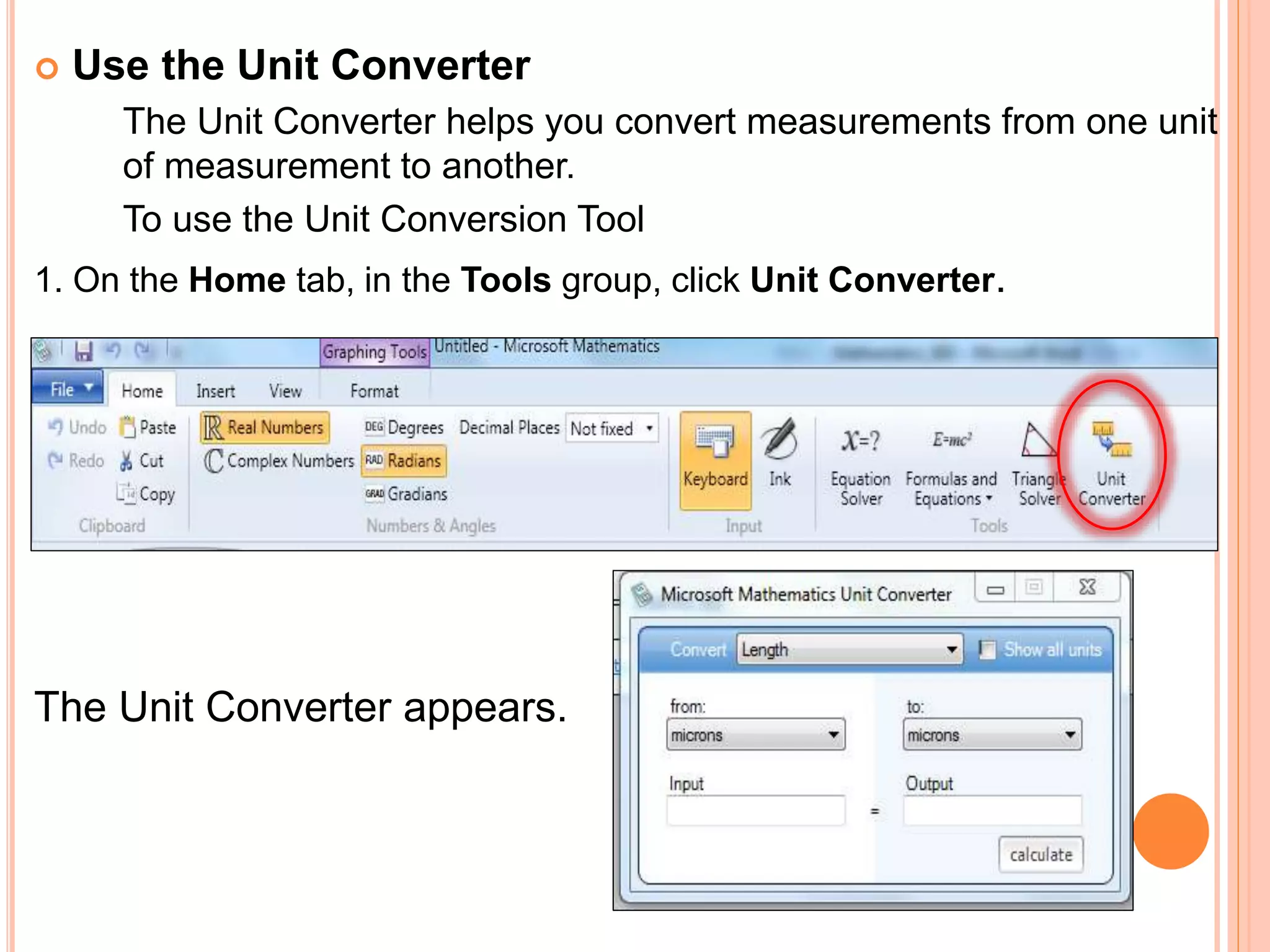
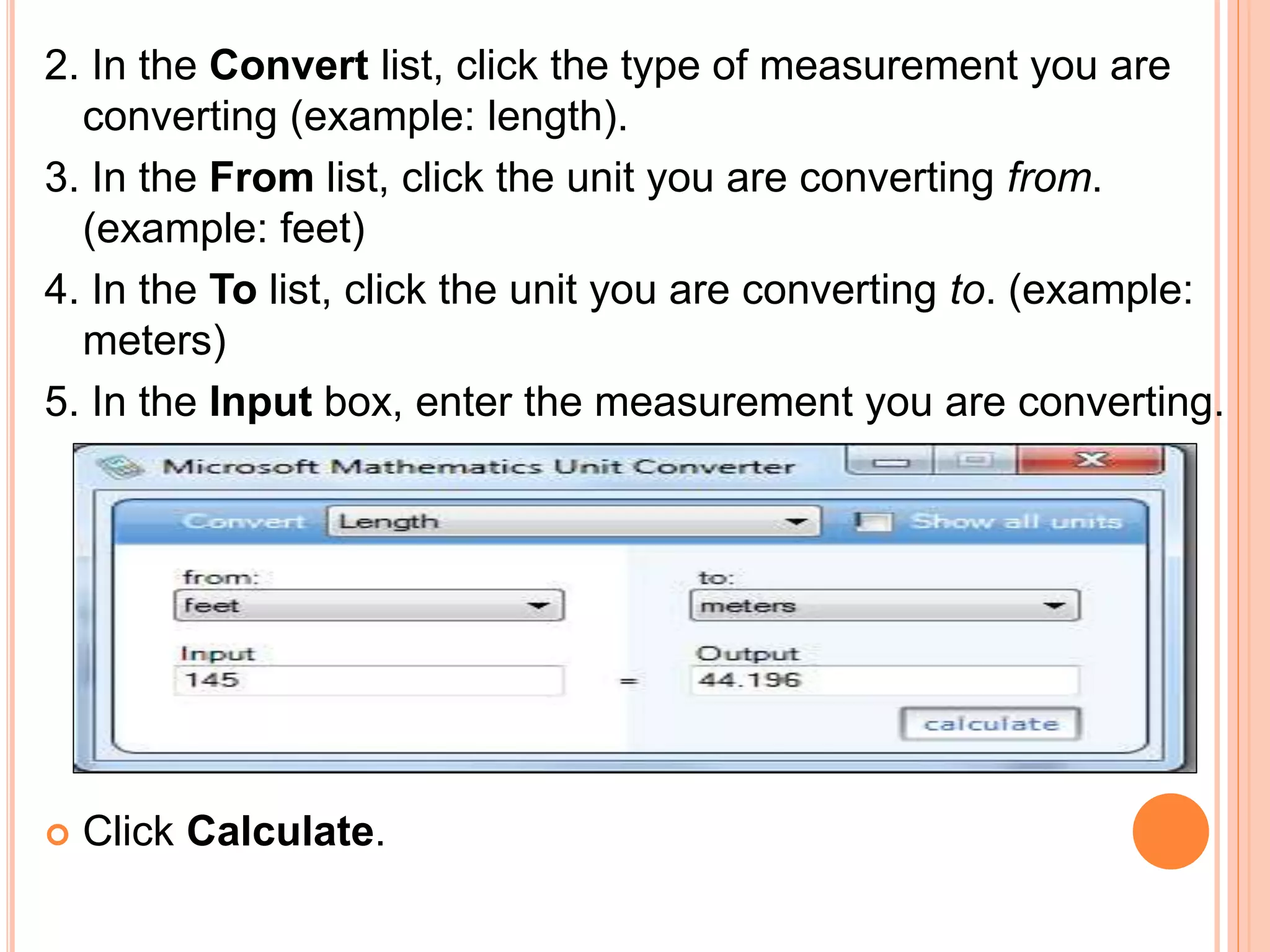
This document provides an overview of the Microsoft Mathematics application, including its objectives, introduction, and key features. It describes the elements displayed in the app's calculator pad, worksheet, and graphing tabs. It also summarizes the app's math tools for solving equations, working with formulas and equations, using the triangle solver, and converting units. The document explains how to create graphs, solve equations step-by-step, and use the inking capabilities within Microsoft Mathematics.