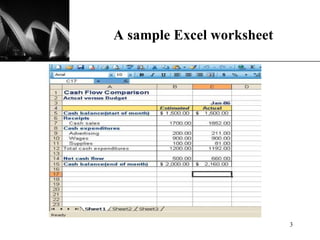
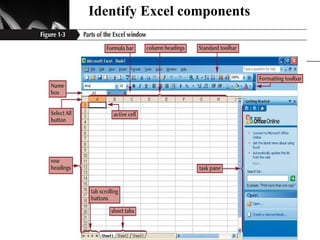
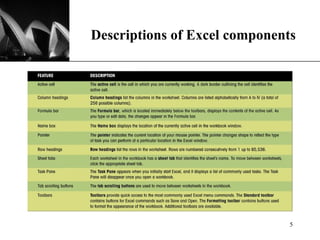
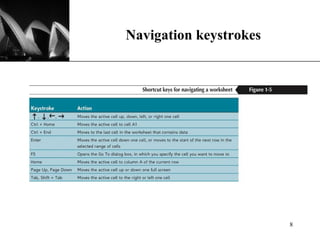
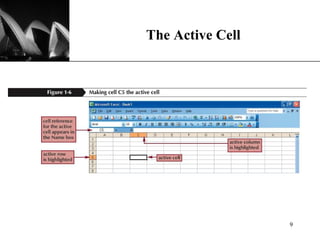
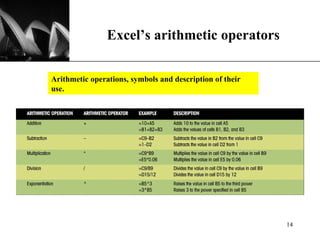
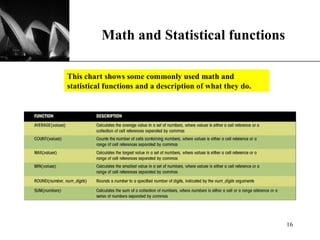
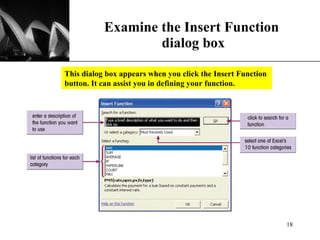
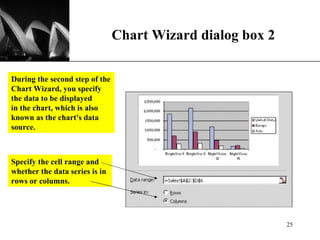
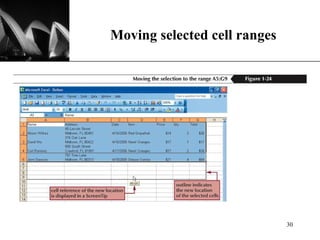
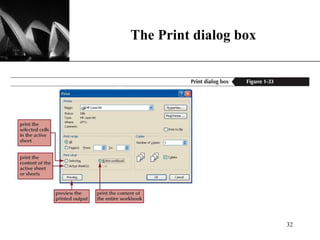
The document discusses the key components of Microsoft Excel, including worksheets, cells, formulas, functions, charts, and printing. It describes how to enter and format data, use formulas and functions, navigate between sheets, resize rows and columns, and create basic charts using the Chart Wizard. Key components of the Excel window include the worksheet, formula bar, row and column headings, and sheet tabs. Formulas in Excel always begin with an equal sign and can include arithmetic operators. Functions like SUM can be used to calculate values across ranges of cells.