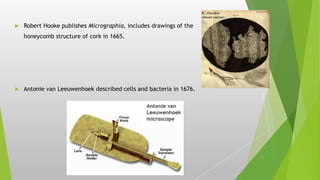
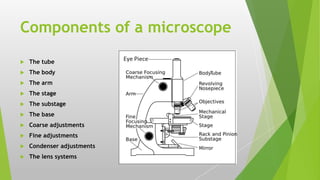
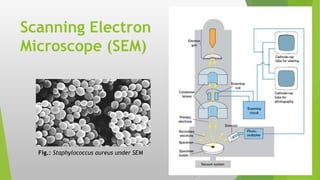
The document provides an overview of microscopy, detailing its history, components, types, and usage. It outlines the development of various microscopes, including light microscopes (such as brightfield, darkfield, phase-contrast, and fluorescence) and electron microscopes (transmission and scanning). Key care instructions for microscopes are also highlighted, ensuring proper maintenance and optimal functionality.