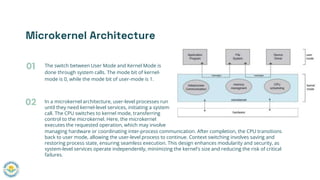
The document discusses microkernels in operating systems, highlighting their architecture, advantages, and disadvantages. Microkernels streamline the OS by removing non-essential components, enhancing modularity and security while posing challenges like increased resource usage and complexity. They are particularly useful in systems prioritizing scalability and security, as seen in platforms like Apple's macOS and iOS.