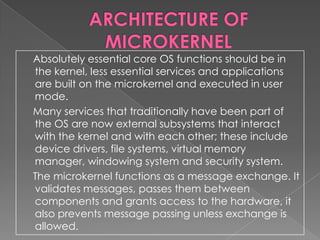
- An operating system consists of kernel mode and user mode. A microkernel breaks the kernel into separate processes called servers that run in either kernel or user space and communicate via message passing.
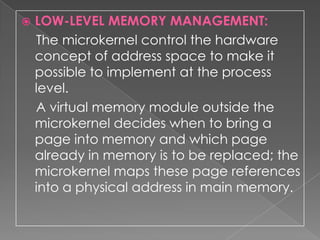
- The microkernel only includes essential functions for memory management, IPC, and I/O interrupt handling while less critical services are built as external subsystems that interact with the microkernel through message passing.
- A potential disadvantage is performance, as message passing takes longer than direct calls, but this can be improved by minimizing the microkernel size.