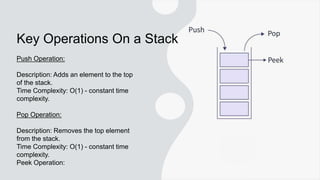
The document provides an overview of the stack data structure, emphasizing its last in, first out (LIFO) principle and key operations such as push, pop, and peek, all of which have constant time complexity. It discusses array-based and linked list-based implementations, common use cases like arithmetic expression evaluation and function calls, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of using stacks. Overall, it highlights the simplicity and efficiency of stacks while noting their limitations regarding element access and fixed sizes in some implementations.