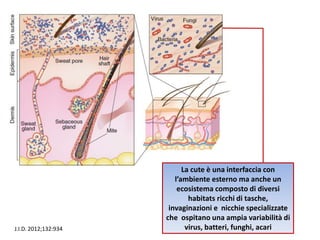
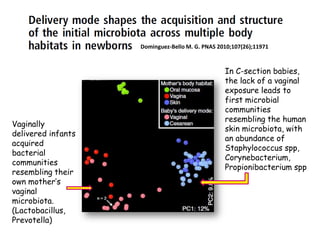
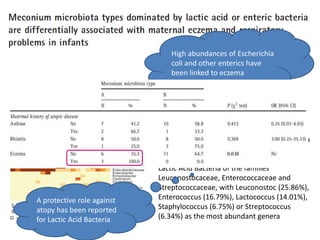
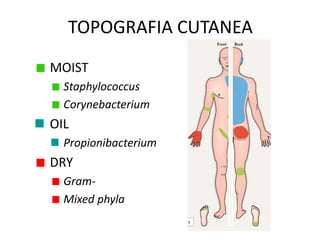
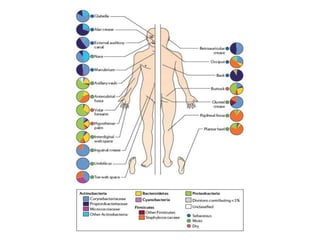
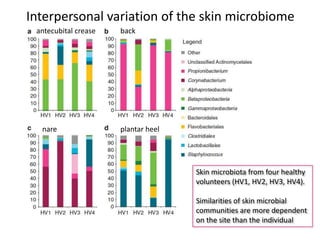
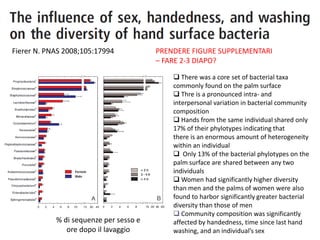
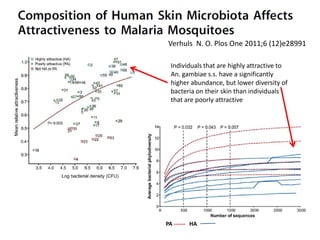
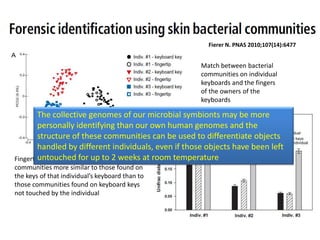
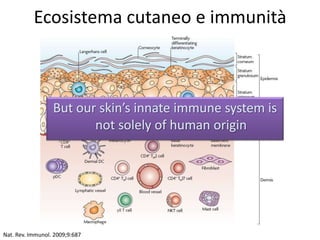
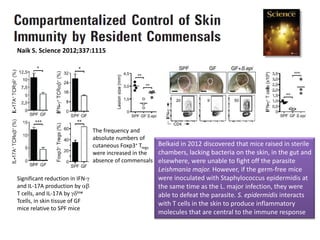
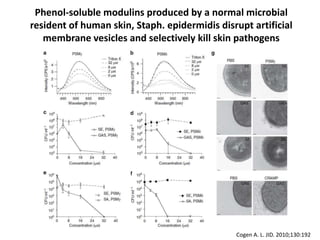
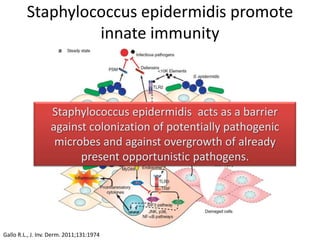
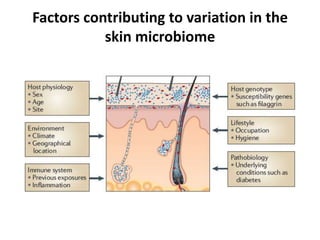
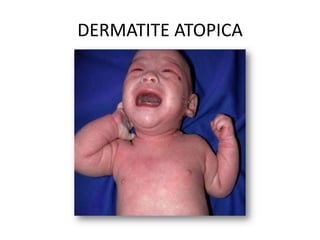
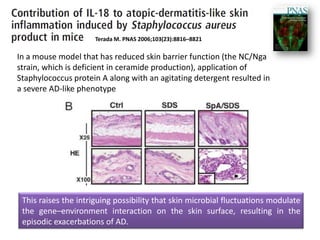
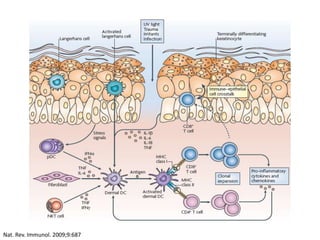
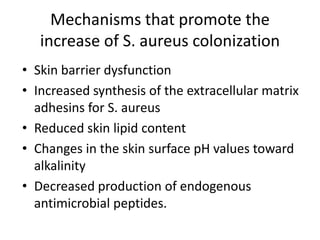
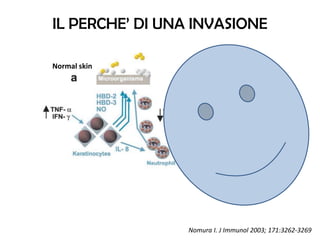
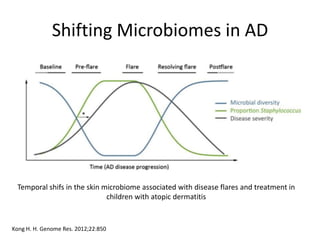
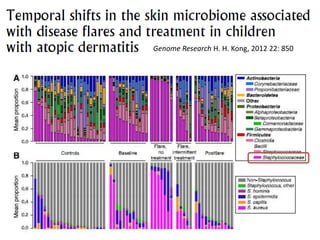
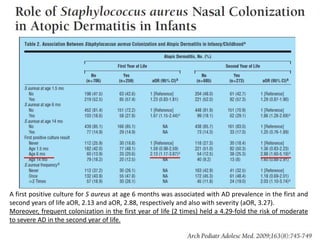
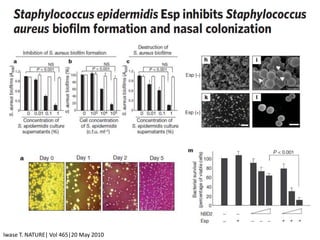
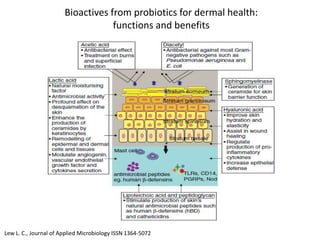
The document discusses the skin microbiome and its role in atopic dermatitis (eczema). It notes that the skin hosts trillions of bacteria that create an ecosystem. Factors like location on the body, moisture levels, and individual characteristics can influence the types of microbes present. In eczema, skin barrier defects allow overgrowth of bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus that secrete toxins exacerbating inflammation. Studies show shifts in skin microbiota during eczema flares and treatment. A healthy microbiome including species like Staphylococcus epidermidis promotes skin immunity, while dysbiosis may increase eczema risk.