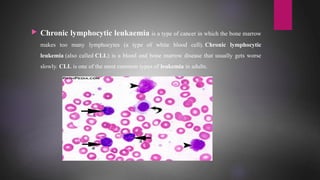
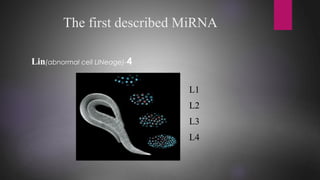
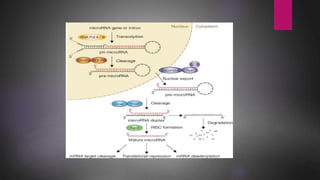
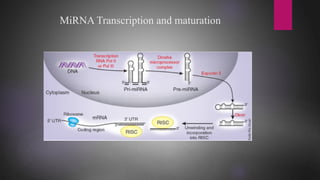
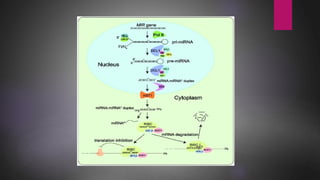
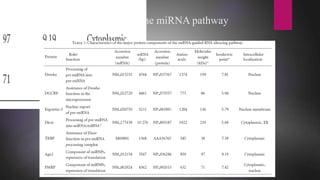
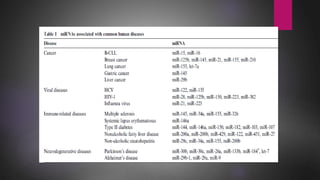
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNA molecules that play important gene regulatory roles. The first miRNA, lin-4, was discovered in C. elegans in 1993. MiRNAs are transcribed and then undergo a multi-step maturation process involving cleavage by Drosha and Dicer enzymes to produce the mature miRNA which is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) and guides it to target mRNAs. Deregulation of miRNAs has been associated with diseases like chronic lymphocytic leukemia.