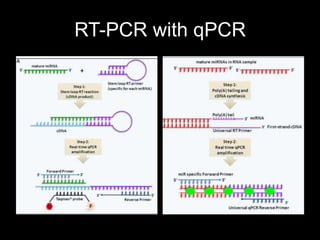
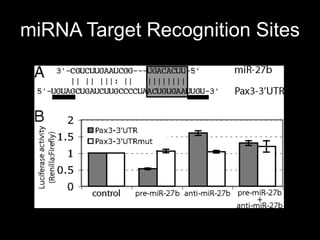
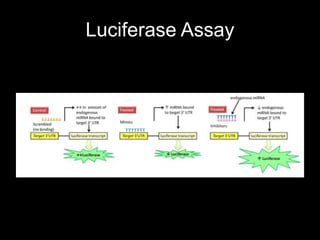
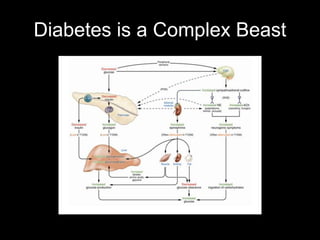
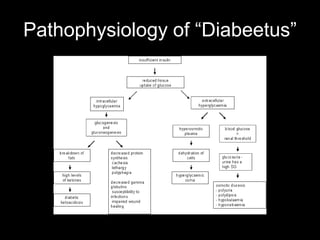
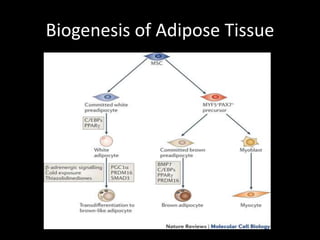
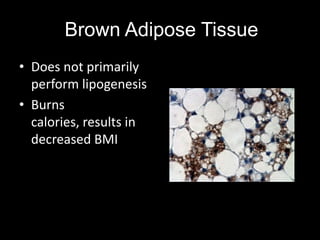
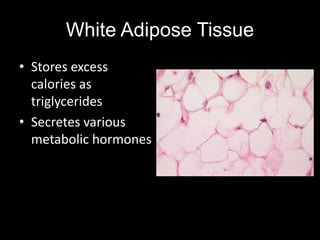
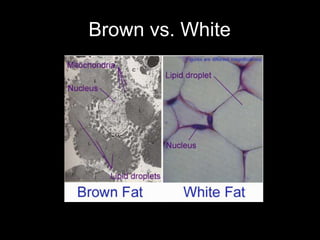
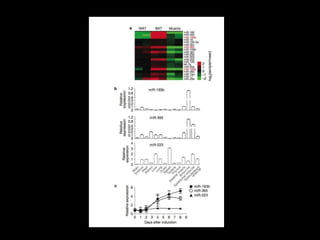
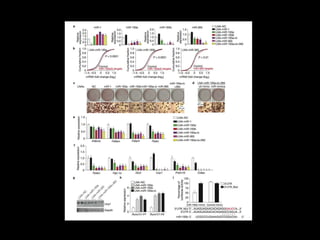
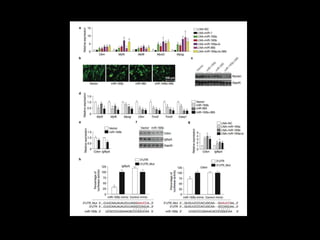
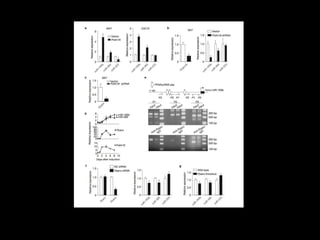
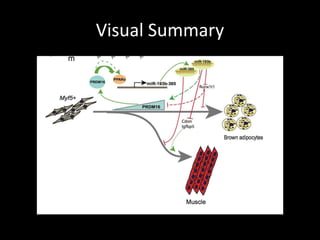
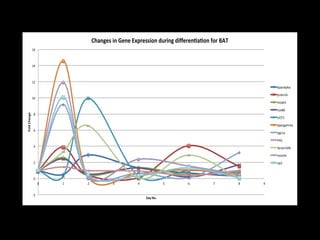
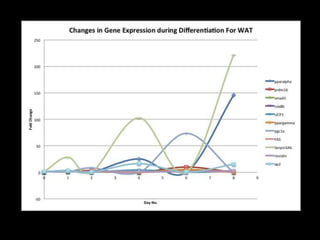
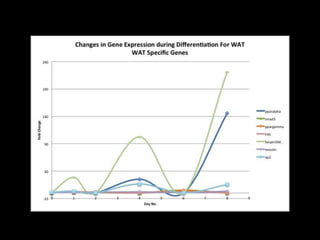
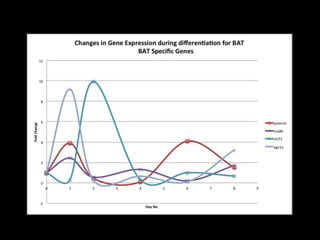
Mir193b–365 is essential for brown fat differentiation by regulating genes involved in adipogenesis. The study identified Mir193b-365 as a microRNA complex necessary for brown adipose tissue differentiation. Blocking Mir193b expression inhibited brown fat marker genes, pointing to its critical role in brown fat development. Mir193b-365 associates closely with mRNAs like Prdm16 and Pparα that help upregulate it during differentiation, inducing adipogenic factors while suppressing myogenic factors.