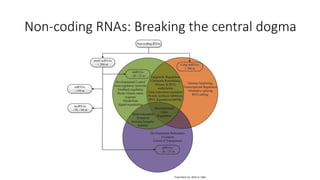
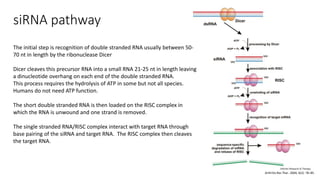
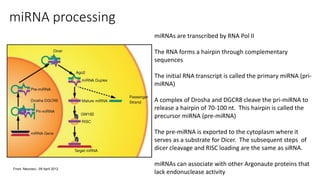
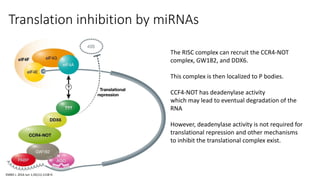
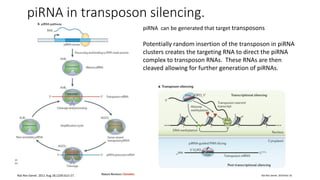
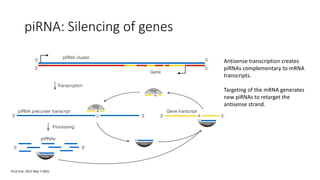
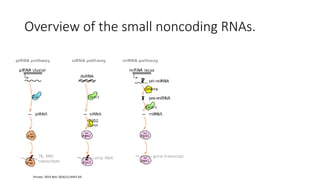
- Small noncoding RNAs include miRNAs, siRNAs, and piRNAs that are 20-33 nucleotides in length and regulate gene expression through RNA degradation or translation inhibition.
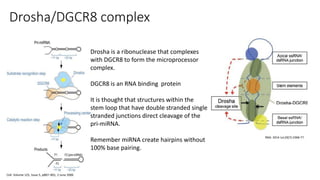
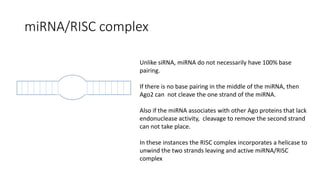
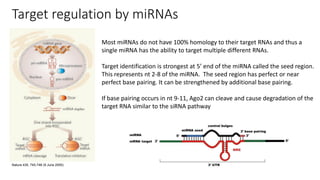
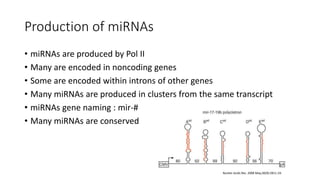
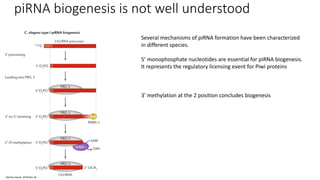
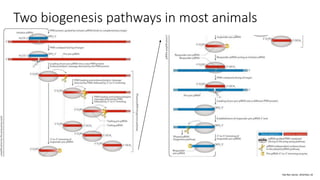
- miRNAs are derived from hairpin structures in RNA transcripts and regulate genes through partial base pairing, while siRNAs require perfect base pairing and are derived from double-stranded RNA. piRNAs are derived from single-stranded RNA and function in germ cells.
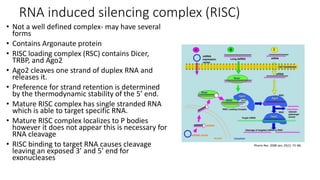
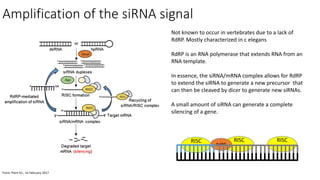
- These small RNAs are processed by Dicer and loaded into RISC complexes containing Argonaute proteins to target RNAs for cleavage or translational repression. Their biogenesis pathways differ but generally function to reduce expression of protein-coding or transposon genes.