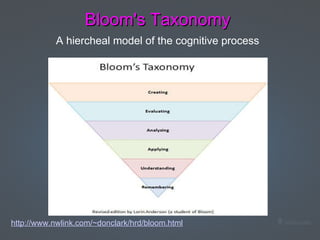
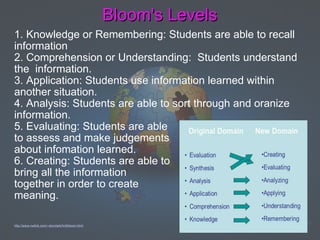
Constructivism is a theory of learning that states that individuals construct their own understanding and knowledge of the world through experiences and reflecting on those experiences. According to constructivism, learning is an active process where students learn by linking new information to previous knowledge and exploring ideas on their own. Key principles of constructivism include students learning through problem solving and incorporating new experiences into their existing understanding. In the classroom, constructivist teaching strategies include hands-on activities, collaborative learning, and using students' multiple intelligences. Constructivism aligns with critical thinking skills as defined in Bloom's Taxonomy, where students analyze, evaluate, and create new understanding.