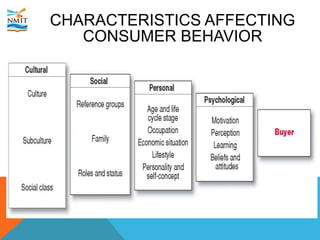
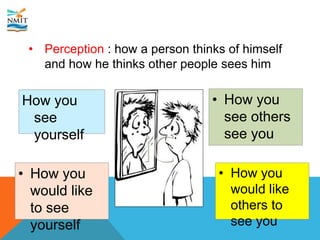
The document discusses consumer behavior and the factors influencing buying decisions in consumer markets. It explores cultural influences, social classes, reference groups, age, personal attributes, economic situations, lifestyle, self-concept, perception, learning, and beliefs. Various examples, particularly related to food and purchasing decisions, illustrate the differences in consumer behavior among diverse cultural groups.