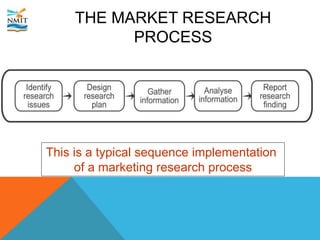
This document discusses market research and the market research process. It defines market research as collecting information to determine if there is a market for a new product or service. The market research process involves identifying research issues, designing a research plan such as exploratory, descriptive or causal research, gathering data through surveys, experiments or focus groups, analyzing the information, and reporting findings. Market research helps businesses understand customer needs, reduce risks of failure, and forecast trends.