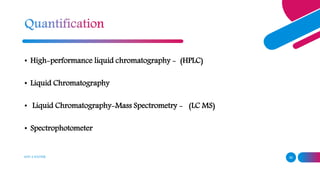
This document discusses natural dyes and their extraction process. It provides information on various plants used for natural dye extraction in India and the colors they produce. It also describes different extraction methods like aqueous, alkali, acid, microwave and ultrasonic assisted, solvent and supercritical fluid extraction. Key steps involved in natural dye production include collecting plant materials, testing for color content, drying, size reduction, extraction of coloring components, drying of dye obtained, and packing. Analytical techniques mentioned for identification of dyes include HPLC, LC-MS and spectrophotometry.
























![ADD A FOOTER 26
• Powder is initially defatted with petroleum benzene [60-80 degree] by required
amount of ethanol by using an extractor for 72 hours.
• Extract is filtered by using filter paper and dry at 45 degree .
• Extract is kept in sterile bottle under refrigerated condition until use.
• METHANOL METHOD:
• Powder is taken and extracted by 20% aq.methanol using Soxhlet extraction
method.
• Dye powder is slightly soluble in hot water and completely soluble in alkaline
material.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecno-201212051754/85/Methods-of-dye-extraction-from-flower-crops-26-320.jpg)






![ADD A FOOTER 34
DRYING OF COLOURING MATTER[DYE] IN SPRAY DRYER](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecno-201212051754/85/Methods-of-dye-extraction-from-flower-crops-34-320.jpg)