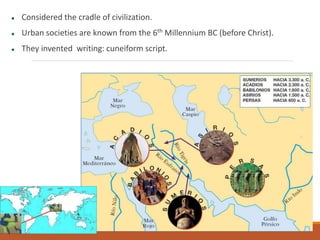
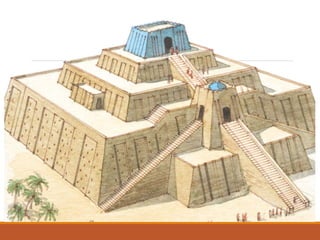
Mesopotamia, often referred to as the cradle of civilization, was home to early urban societies as early as the 6th millennium BC and is notable for the invention of writing through cuneiform script. The region's rich culture included significant architectural feats like ziggurats and notable literature such as the Epic of Gilgamesh, alongside a complex societal structure and religious practices centered around polytheism. Key historical figures, such as Gilgamesh and King Hammurabi, played crucial roles in the development of law and governance during this era.