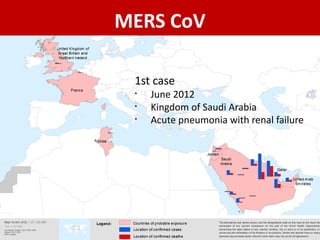
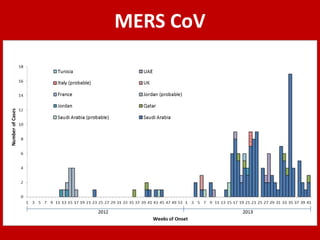
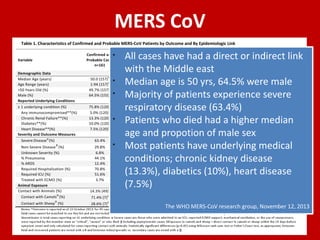
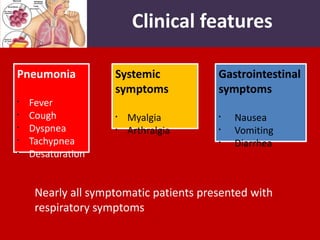
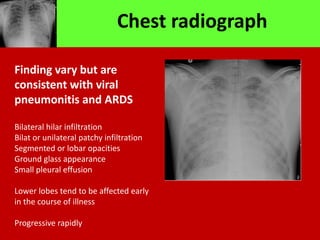
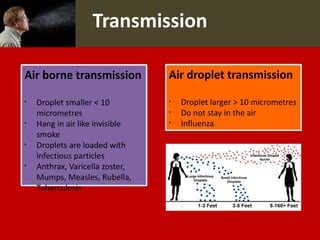
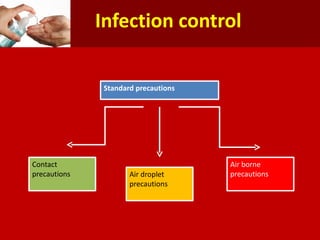
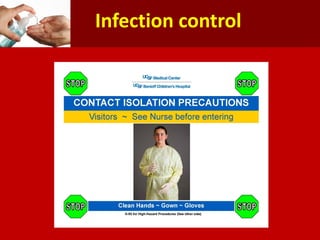
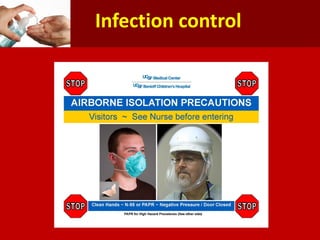
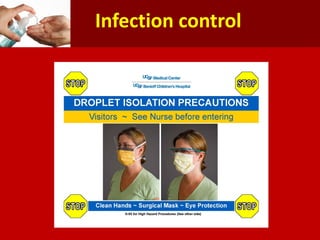
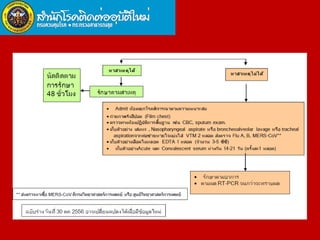
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) was first identified in Saudi Arabia in June 2012 and is associated with severe respiratory illness, often linked to underlying medical conditions. The disease has a median incubation period of 5-14 days, with symptoms ranging from asymptomatic to severe pneumonia and gastrointestinal issues. Transmission occurs primarily through close contact and healthcare settings, and while no specific treatment exists, management focuses on organ support and infection control.