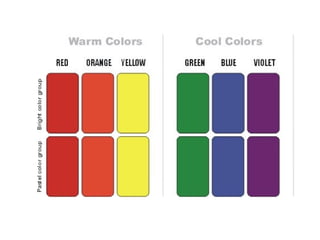
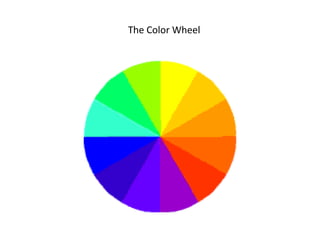
The document discusses color concepts and their use in merchandise development. It describes the physical and psychological reactions people have to different colors, and how colors can influence moods and shopping behaviors. It then provides details on the color wheel, including primary, secondary, tertiary, warm, cool, complementary, analogous, and other color schemes. The last parts discuss how color harmony is created and factors like context, dimensions, and cycles that are considered in developing an effective color story for merchandise.