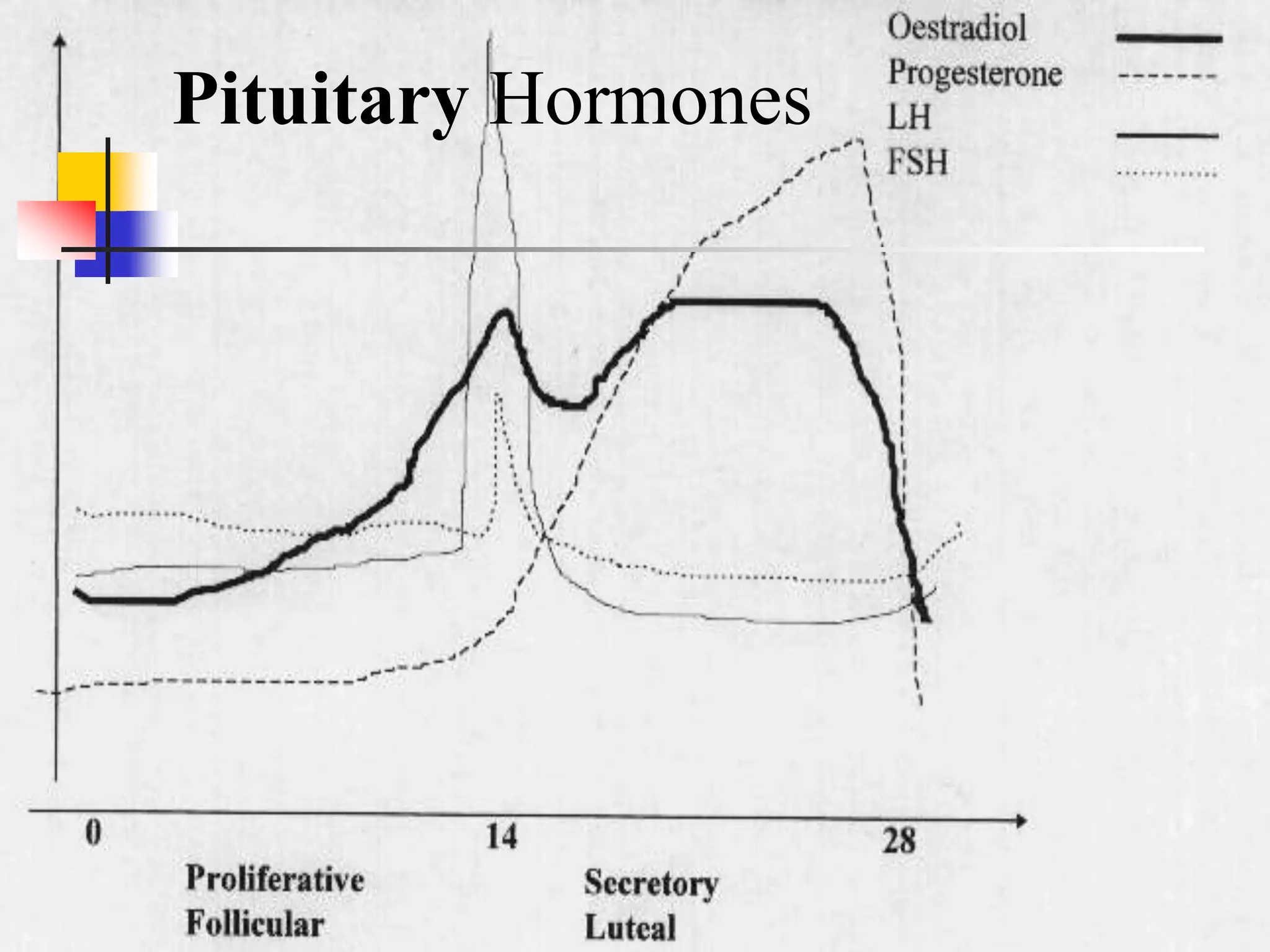
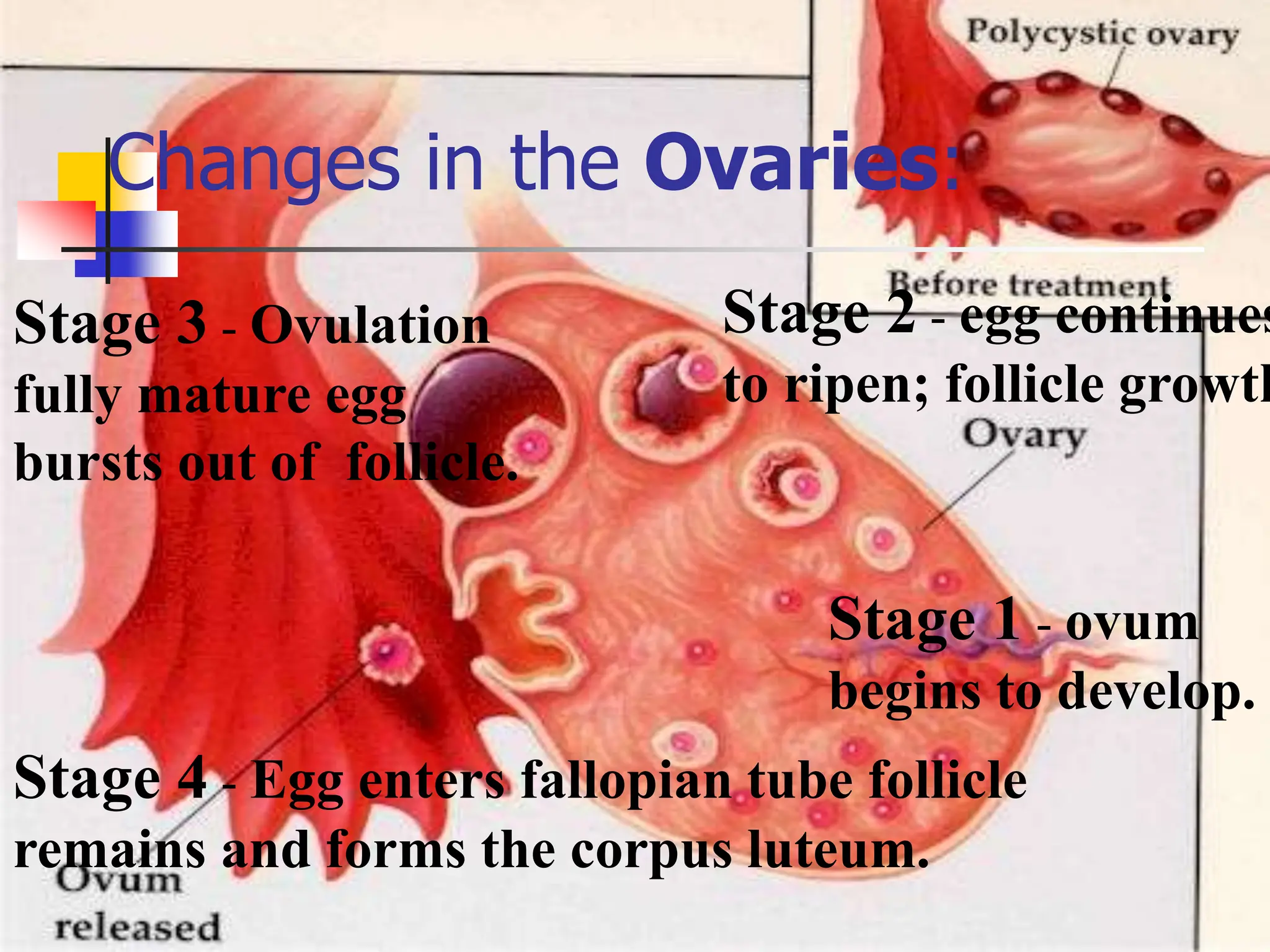
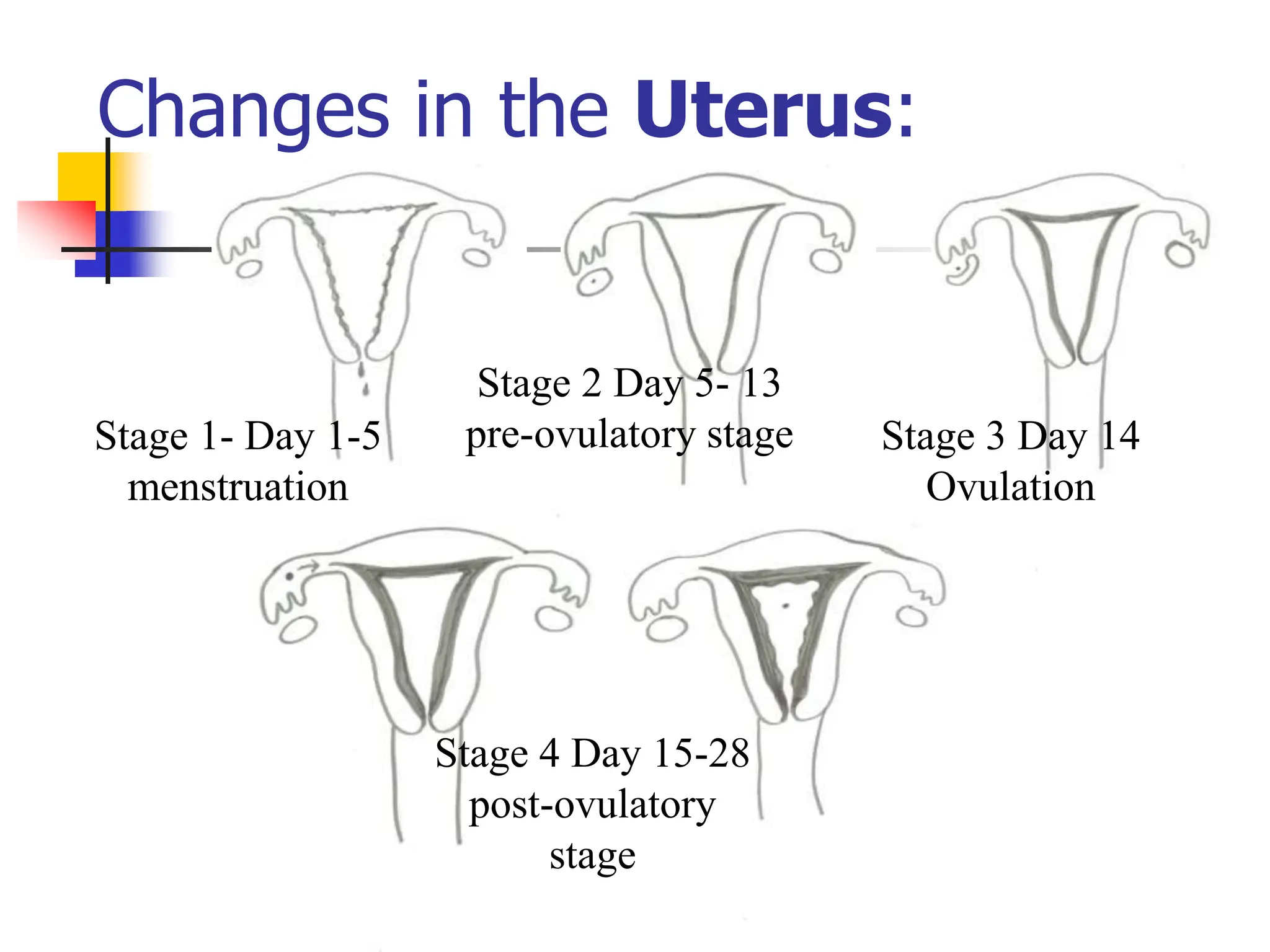
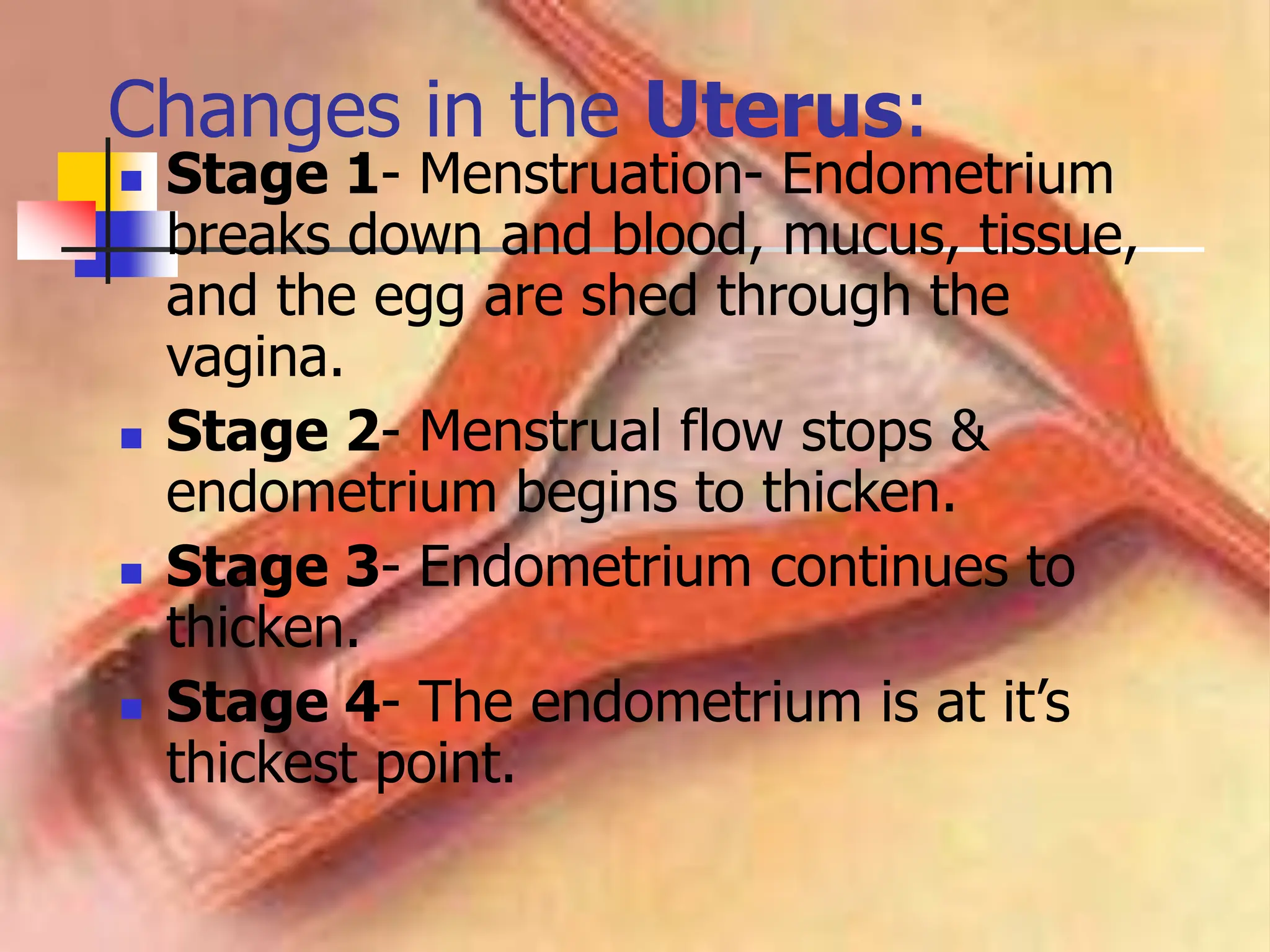
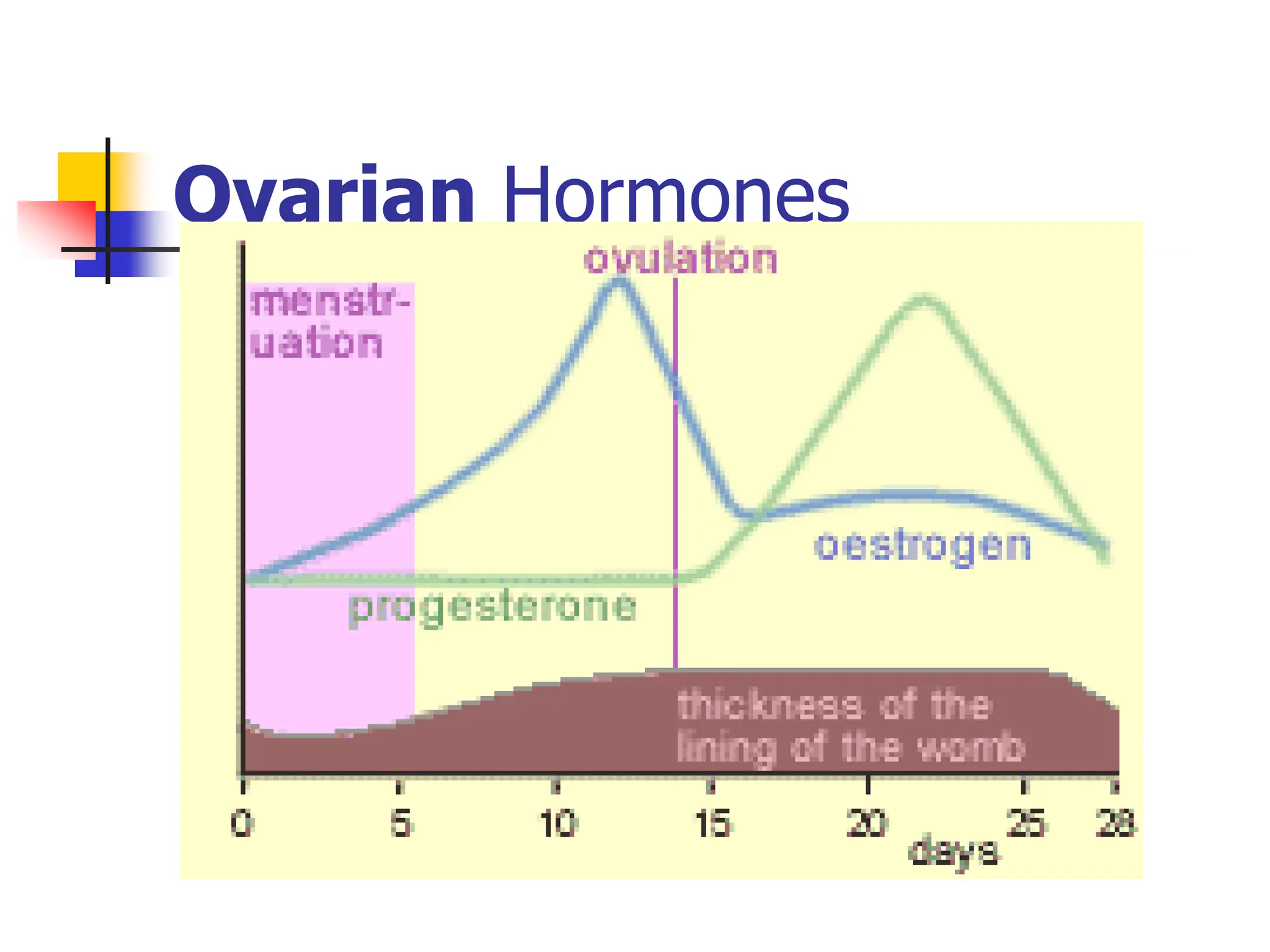
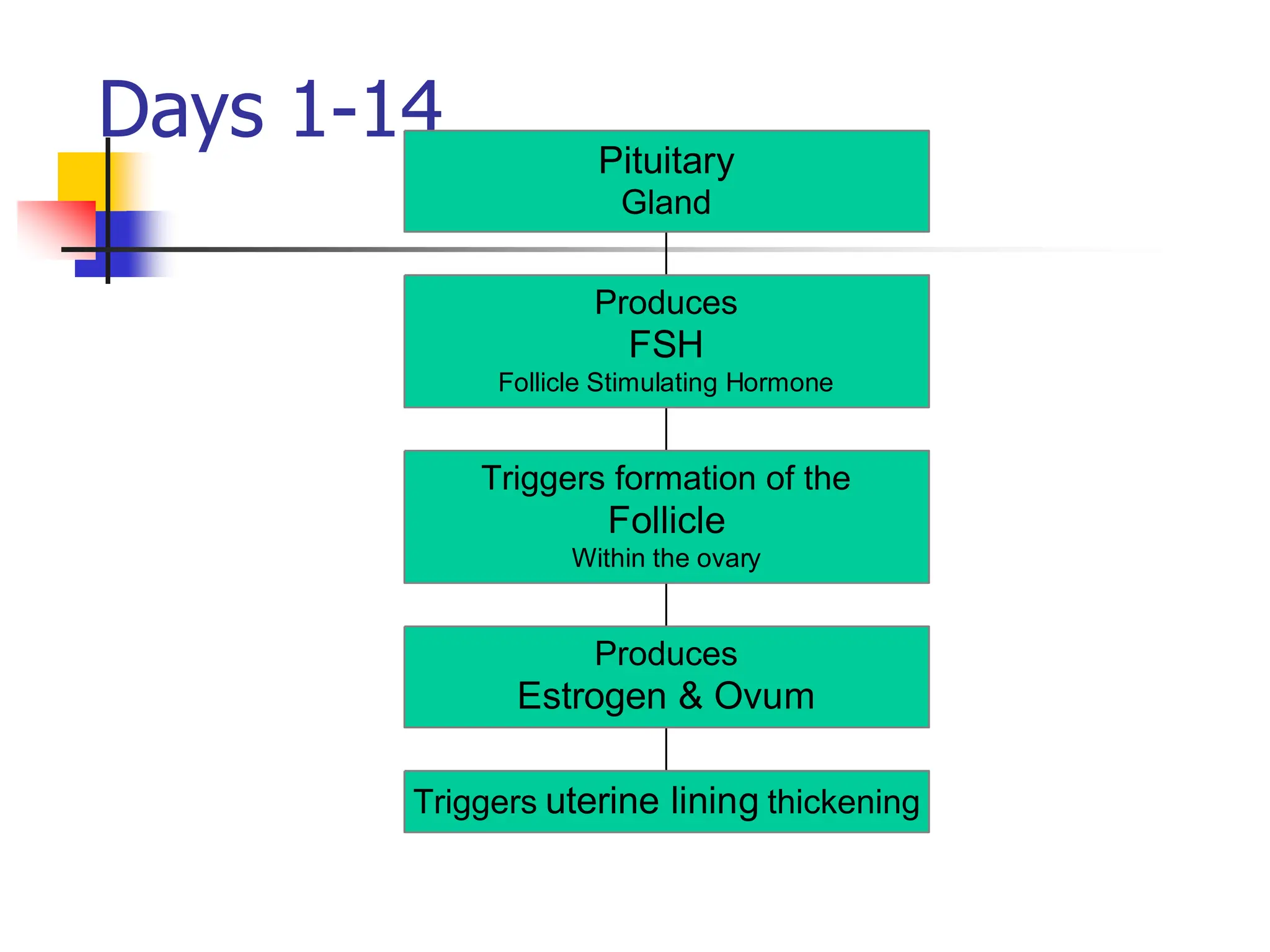
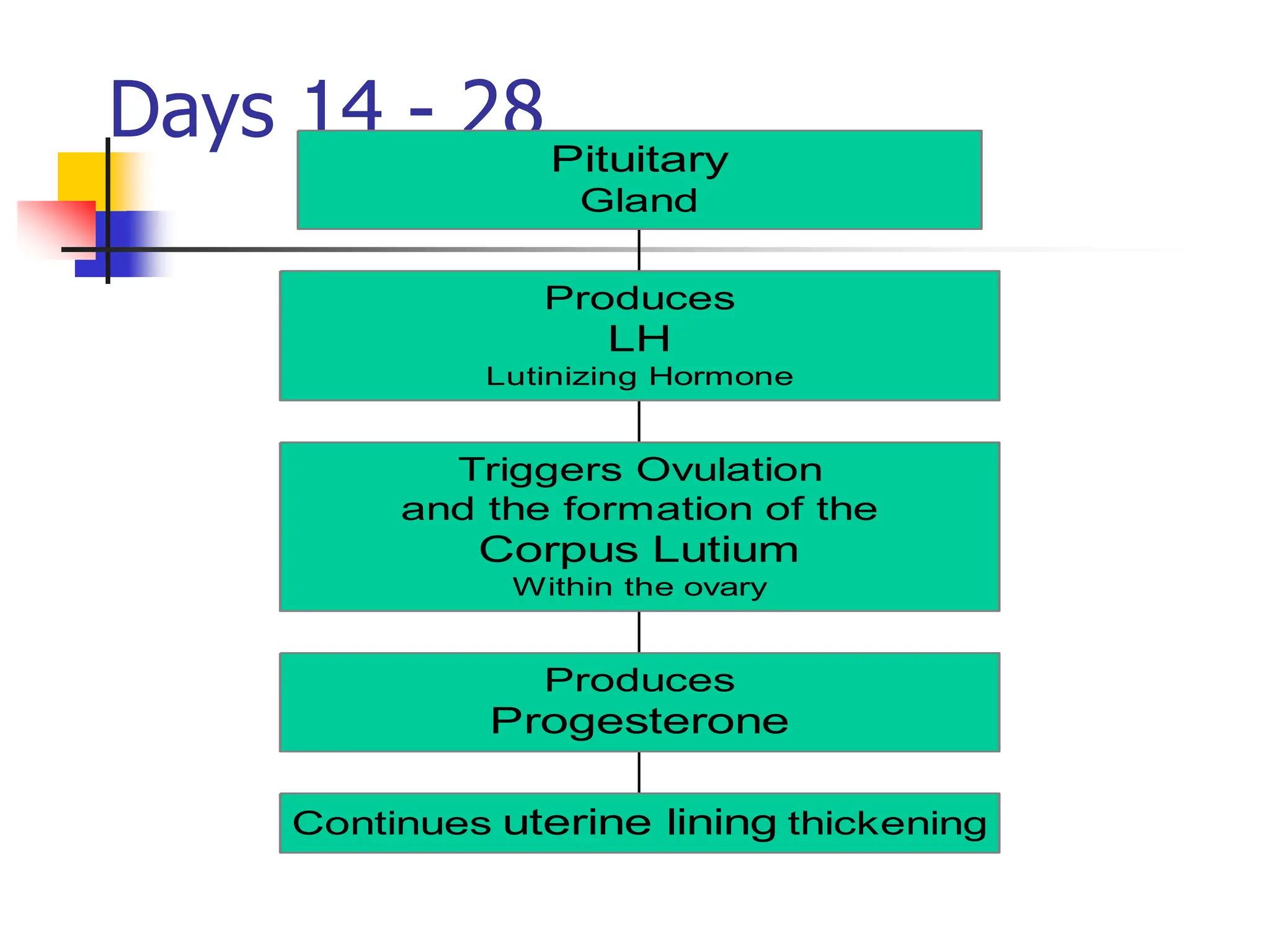
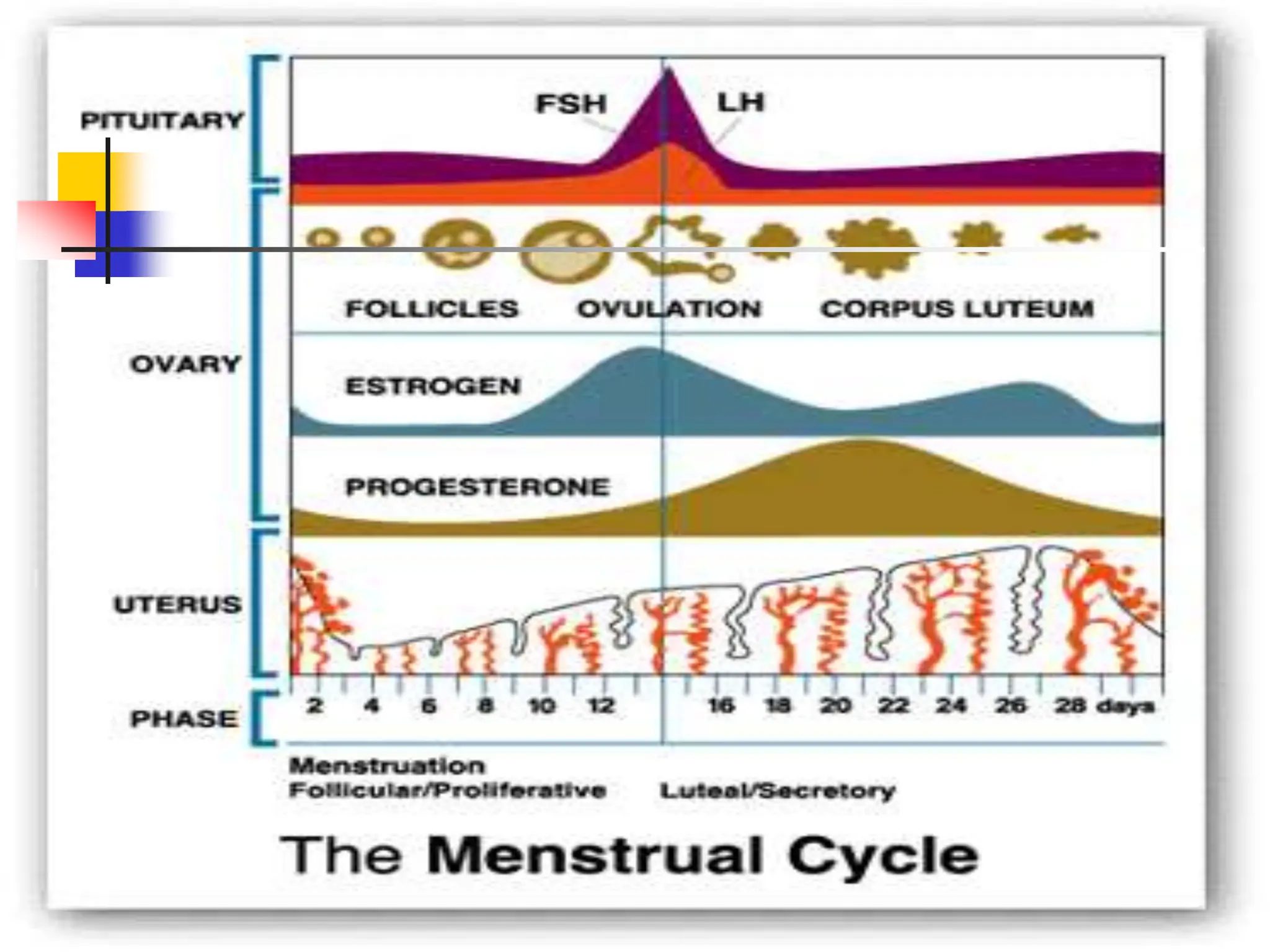
The menstrual cycle is a monthly process where females release a mature egg, typically every 28 days, influenced by hormonal changes from the pituitary gland. It consists of four main stages in the ovaries and uterus, involving the maturation of the egg, ovulation, and the thickening of the uterine lining. If the egg is not fertilized, hormonal changes trigger menstruation and the cycle begins anew.