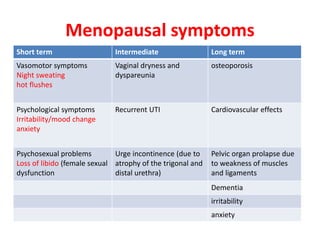
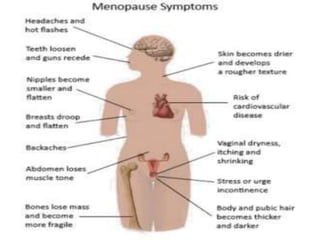
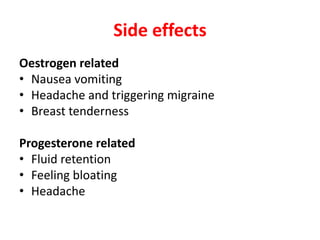
Menopause typically occurs between ages 50-52 as ovaries stop producing eggs and estrogen levels decline. Symptoms include hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. Management includes lifestyle changes and various hormonal and non-hormonal treatments to relieve symptoms and prevent long-term issues like osteoporosis and heart disease. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) effectively treats short-term menopausal issues but carries risks if used long-term like an increased risk of breast cancer. Careful screening and use of the lowest effective dose for the shortest time is recommended for HRT.