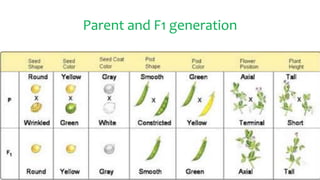
- Gregor Johann Mendel conducted experiments with pea plants in the 1850s and discovered the principles of heredity, but his work went largely unnoticed.
- He studied seven traits in pea plants and found consistent inheritance patterns that could be explained by discrete units (now known as genes) being passed from parents to offspring.
- His work was rediscovered in 1900 by three botanists, De Vries, Correns, and Tschermak, and his principles of heredity and inheritance ratios were confirmed to be valid.