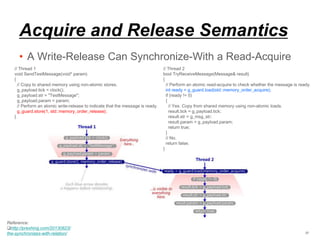
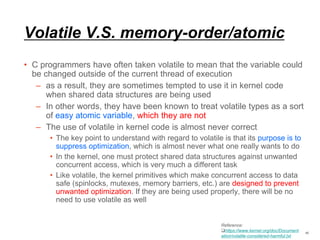
This document discusses memory ordering and synchronization in multithreaded programs. It begins with background on mutexes, semaphores, and their differences. It then discusses problems that can occur with locking-based synchronization methods like mutexes, such as deadlocks, priority inversion, and performance issues. Alternative lock-free programming techniques using atomic operations are presented as a way to synchronize access without locks. Finally, memory ordering, consistency models, barriers, and their implementations in compilers, Linux kernels, and ARM architectures are covered in detail.




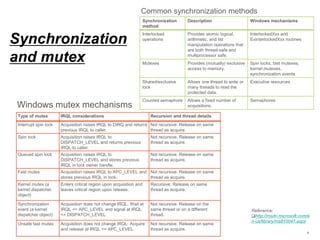




![Atomic operation
• Load-Link/Store-Conditional
– The LDREX and STREX instructions in ARM split the operation of
atomically updating memory into two separate steps. Together, they provide
atomic updates in conjunction with exclusive monitors that track exclusive
memory accesses. Load-Exclusive and Store-Exclusive must only access
memory regions marked as Normal
– For example
» LDREX R1, [R0] performs a Load-Exclusive from the address in R0, places the value into
R1 and updates the exclusive monitor(s).
» STREX R2, R1, [R0] performs a Store-Exclusive operation to the address in R0,
conditionally storing the value from R1 and indicating success or failure in R2.
10
Reference:
http://infocenter.arm.com/help/topic/co
m.arm.doc.dht0008a/ch01s02s01.html
http://infocenter.arm.com/help/topic/co
m.arm.doc.dht0008a/CJAGCFAF.html
Exclusive accesses to memory locations
marked as Non-shareable are checked
only against this local monitor. Exclusive
accesses to memory locations marked as
Shareable are checked against both the
local monitor and the global monitor.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memorymodel-pub-151021125202-lva1-app6892/85/Memory-model-10-320.jpg)

![Atomic operation
• Is atomic operation enough?
• Linux-v3.7.8/arch/arm/include/asm/atomic.h
12
static inline int atomic_cmpxchg(atomic_t *ptr, int old, int new)
{
unsigned long oldval, res;
smp_mb();
do {
__asm__ __volatile__("@ atomic_cmpxchgn"
"ldrex %1, [%3]n"
"mov %0, #0n"
"teq %1, %4n"
"strexeq %0, %5, [%3]n"
: "=&r" (res), "=&r" (oldval), "+Qo" (ptr->counter)
: "r" (&ptr->counter), "Ir" (old), "r" (new)
: "cc");
} while (res);
smp_mb();
return oldval;
}
Reference:
http://lxr.linux.no/#linux+v3.7.8/arch/ar
m/include/asm/atomic.h#L115
Before talking about memory
barrier, let’s see memory ordering
first.
Memory barrier](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memorymodel-pub-151021125202-lva1-app6892/85/Memory-model-12-320.jpg)

























![Usage of memory barrier
instructions
• In what situations might I need to insert memory barrier instructions?
– Mutexes
43
Reference:
http://infocenter.arm.com/help/topic/
com.arm.doc.genc007826/Barrier_Lit
mus_Tests_and_Cookbook_A08.pdf
http://infocenter.arm.com/help/topic/
com.arm.doc.faqs/ka14041.html
LOCKED EQU 1
UNLOCKED EQU 0
lock_mutex
; Is mutex locked?
LDREX r1, [r0] ; Check if locked
CMP r1, #LOCKED ; Compare with "locked"
WFEEQ ; Mutex is locked, go into standby
BEQ lock_mutex ; On waking re-check the mutex
; Attempt to lock mutex
MOV r1, #LOCKED
STREX r2, r1, [r0] ; Attempt to lock mutex
CMP r2, #0x0 ; Check whether store completed
BNE lock_mutex ; If store failed, try again
DMB ; Required before accessing protected resource
BX lr
unlock_mutex
DMB ; Ensure accesses to protected resource have completed
MOV r1, #UNLOCKED ; Write "unlocked" into lock field
STR r1, [r0]
DSB ; Ensure update of the mutex occurs before other CPUs wake
SEV ; Send event to other CPUs, wakes any CPU waiting on using WFE
BX lr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memorymodel-pub-151021125202-lva1-app6892/85/Memory-model-43-320.jpg)
![Usage of memory barrier instructions
– Memory Remapping
• Consider a situation where your reset handler/boot code lives in Flash memory (ROM),
which is aliased to address 0x0 to ensure that your program boots correctly from the vector
table, which normally resides at the bottom of memory (see left-hand-side memory map).
• After you have initialized your system, you may wish to turn off the Flash memory alias so
that you can use the bottom portion of memory for RAM (see right-hand-side memory
map). The following code (running from the permanent Flash memory region) disables the
Flash alias, before calling a memory block copying routine (e.g., memcpy) to copy some
data from to the bottom portion of memory (RAM).
44
MOV r0, #0
MOV r1, #REMAP_REG
STR r0, [r1] ; Disable Flash alias
BL block_copy_routine() ; Block copy code into RAM
BL copied_routine() ; Execute copied routine (now in RAM)
DMB ; Ensure above str completion with DMB
DSB ; Ensure block copy is completed with DSB
ISB ; Ensure pipeline flush with ISB
Question](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memorymodel-pub-151021125202-lva1-app6892/85/Memory-model-44-320.jpg)
