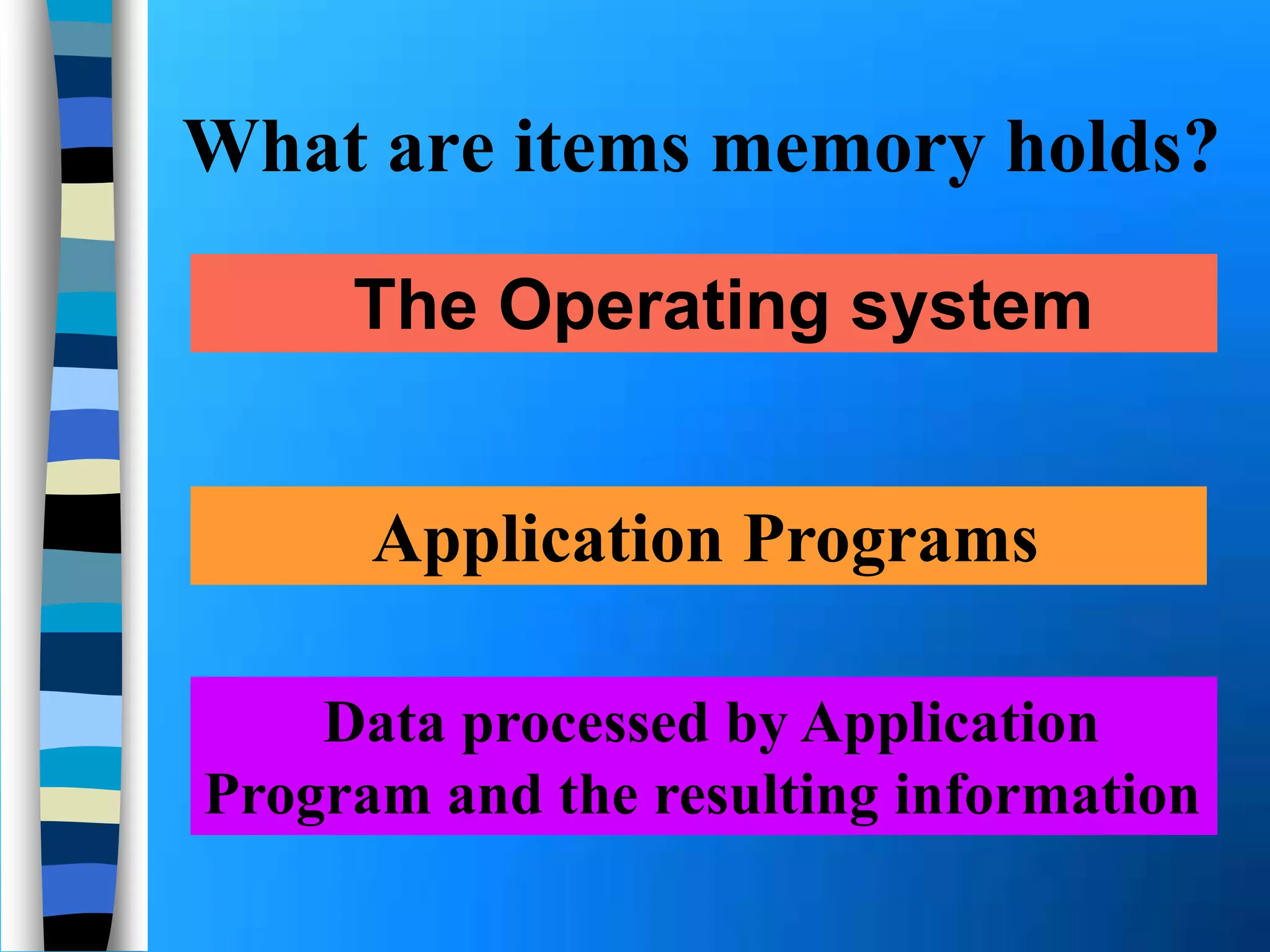
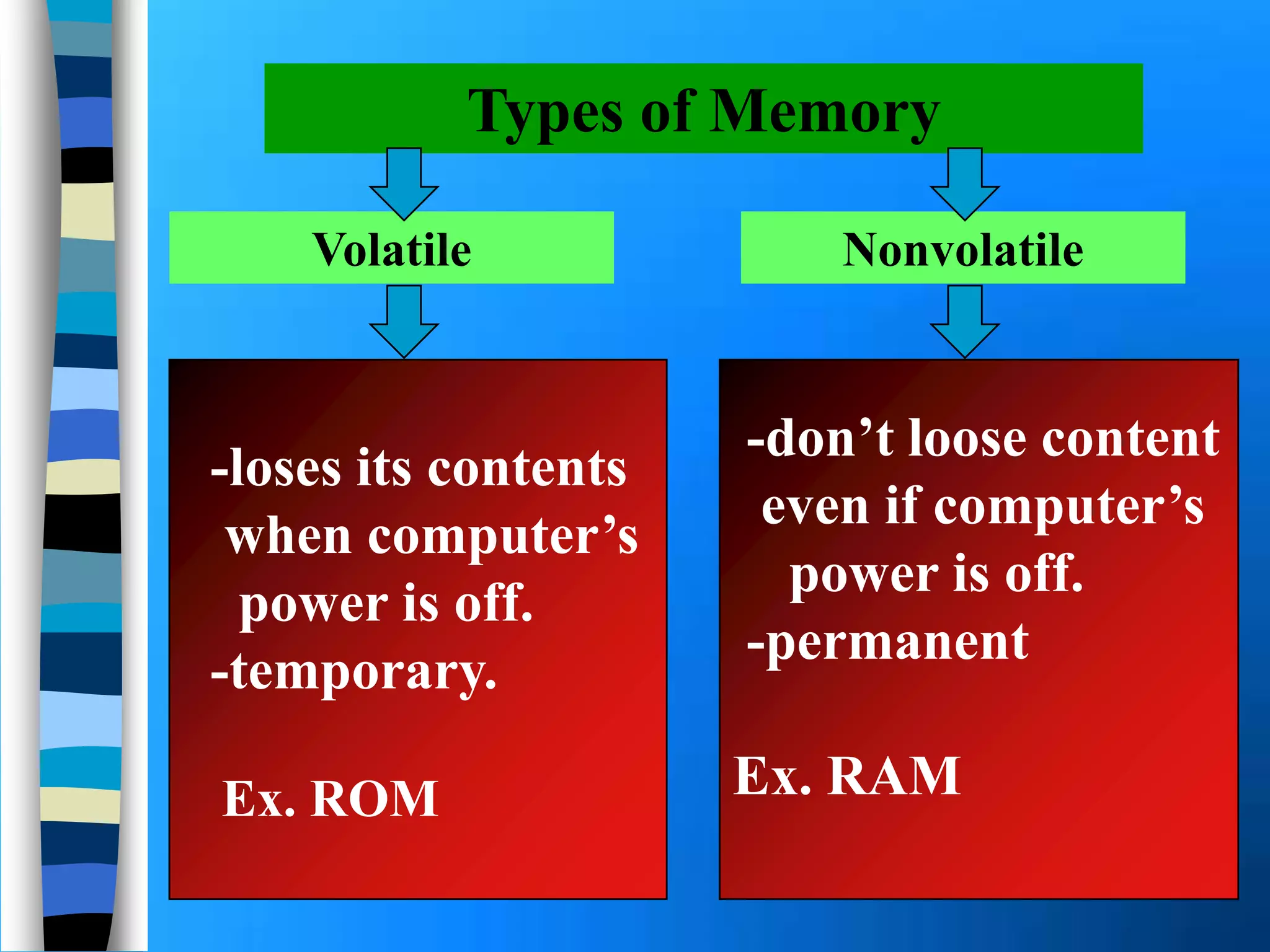
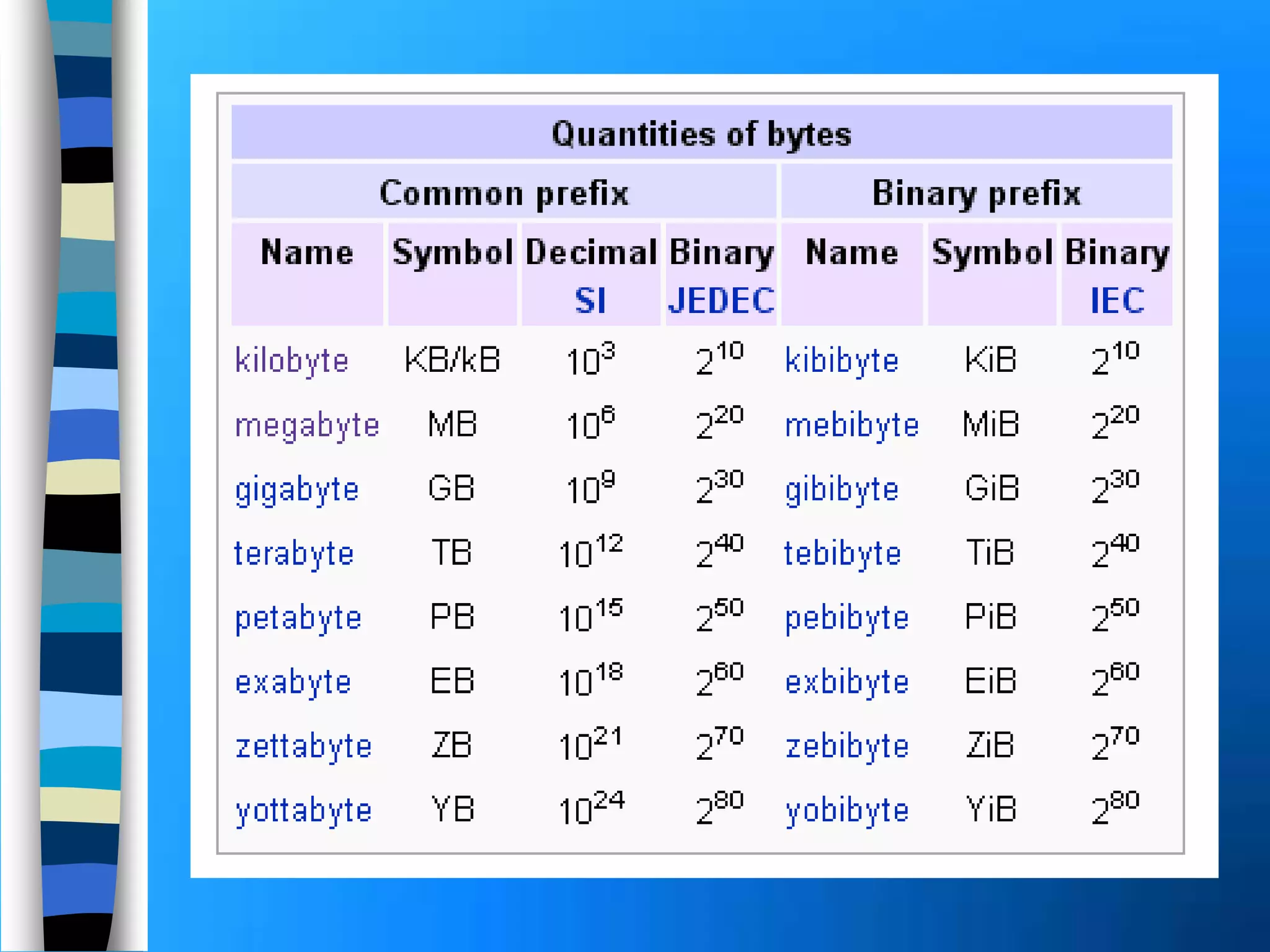
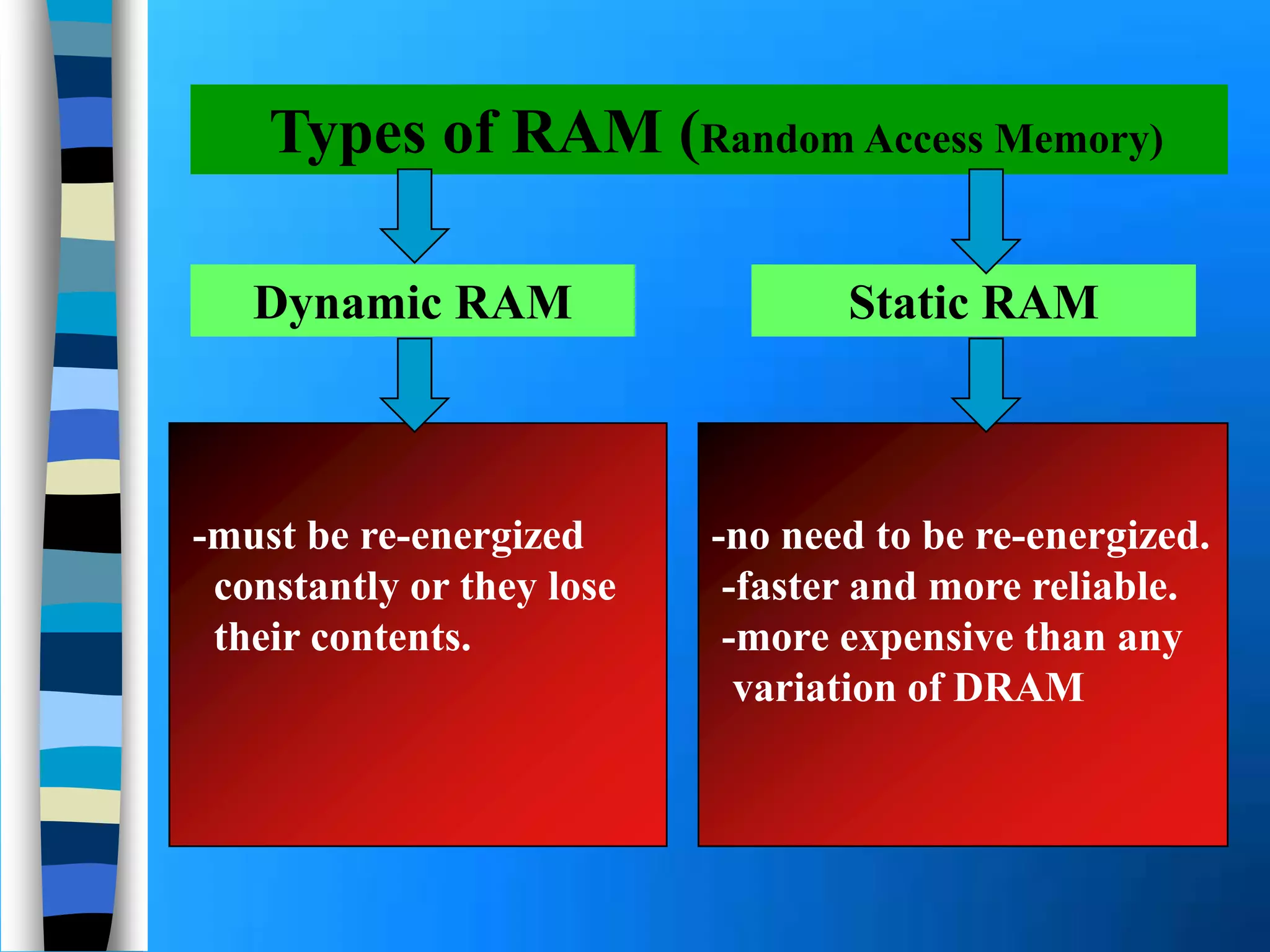
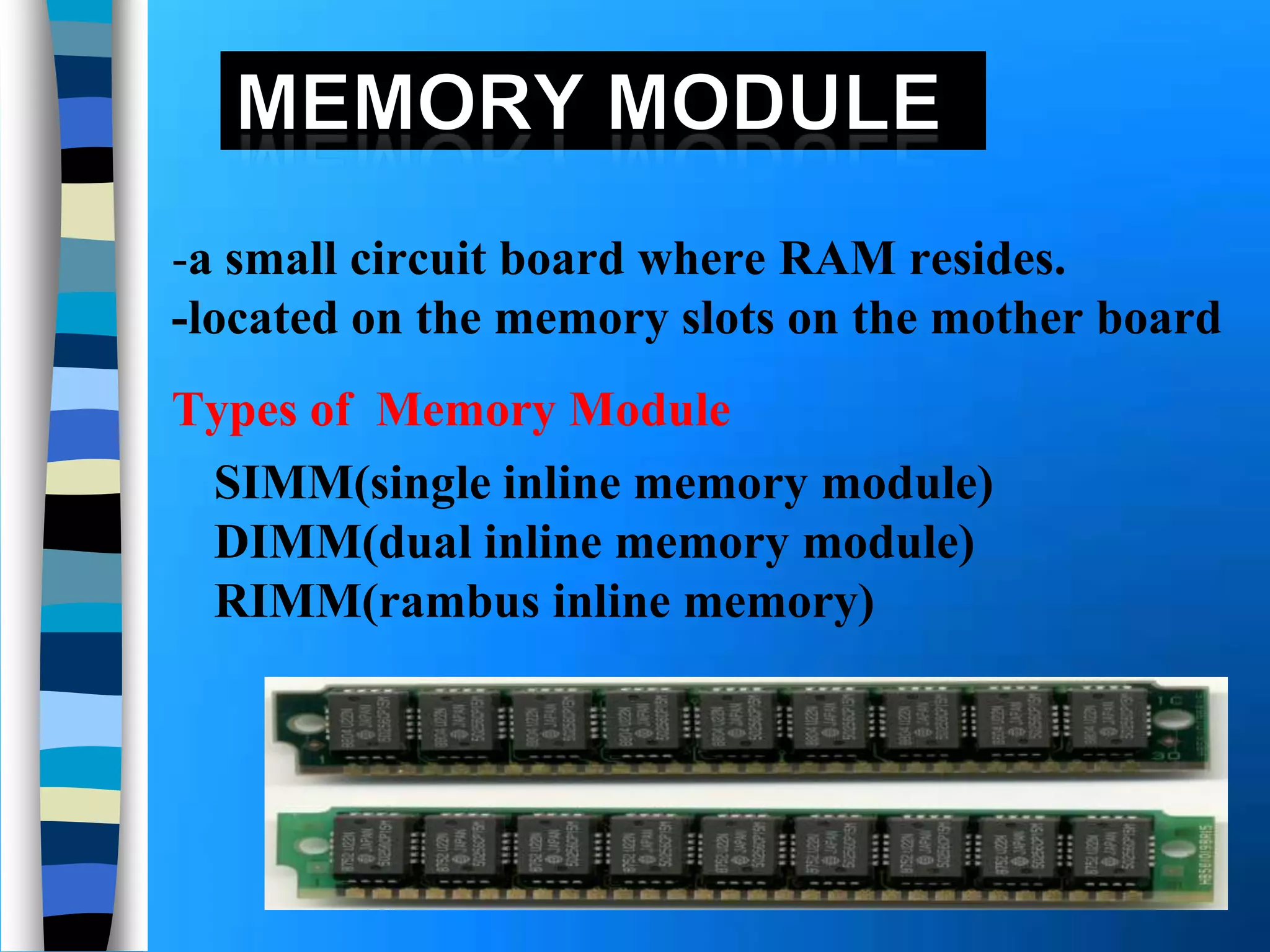
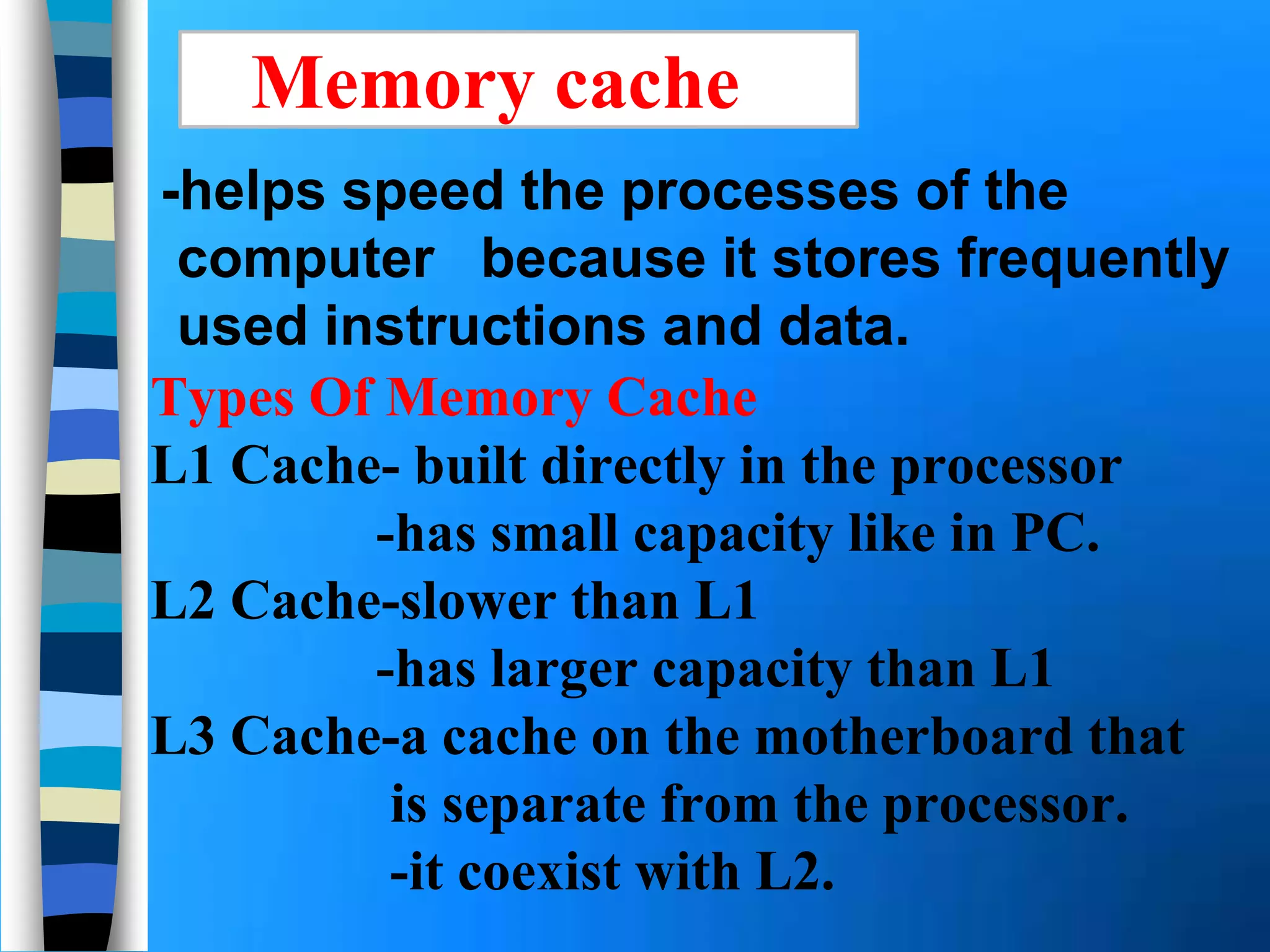
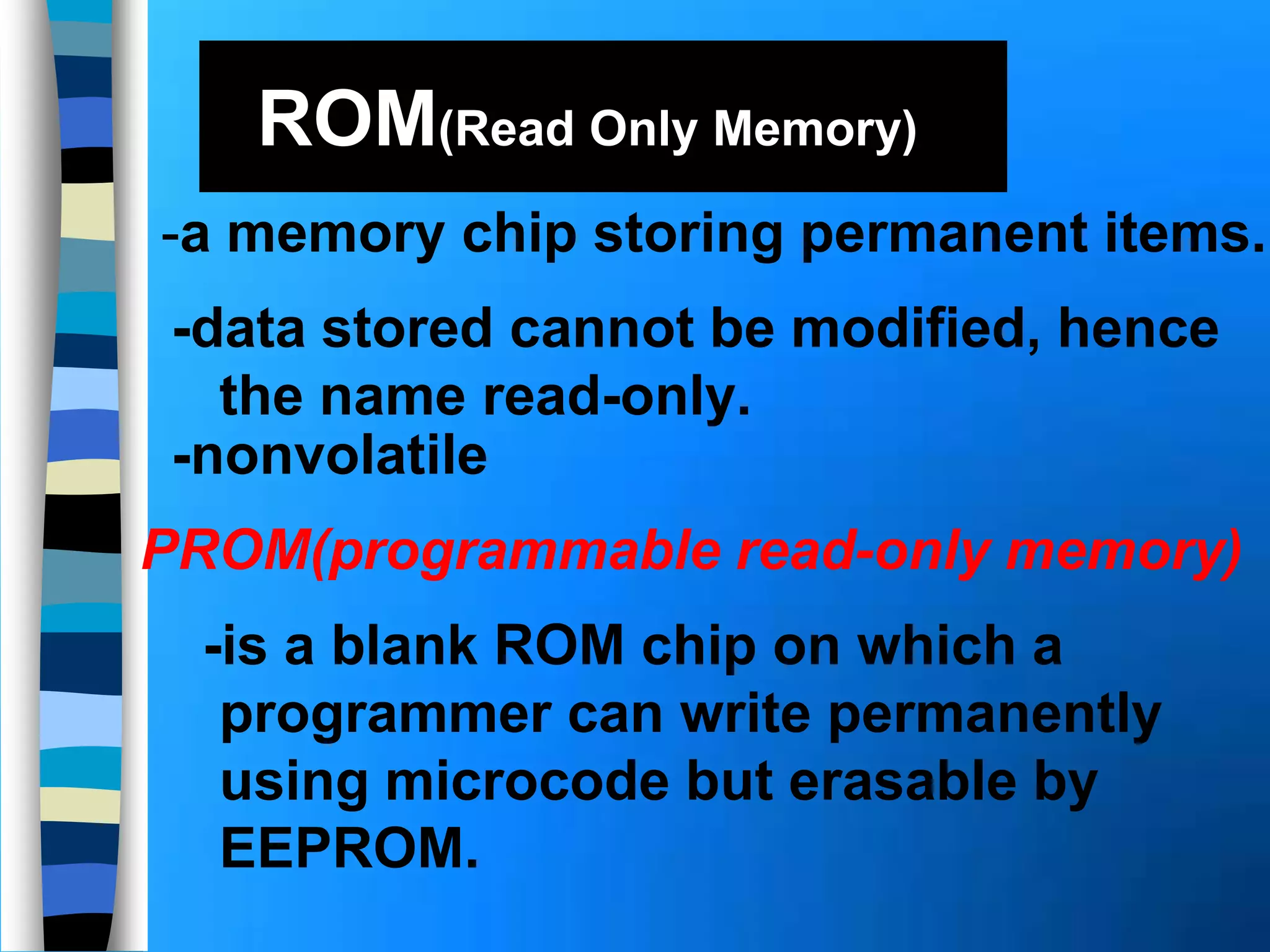
Memory holds instructions, data, and results and comes in different types. Volatile memory like RAM loses contents when powered off but allows for fast reading and writing. Nonvolatile memory like ROM retains contents when powered off but does not allow rewriting. Caches like L1, L2, and L3 improve processing speed by storing frequently used instructions and data closer to the processor. Memory can be upgraded by adding modules like SIMMs, DIMMs, or RIMMs.