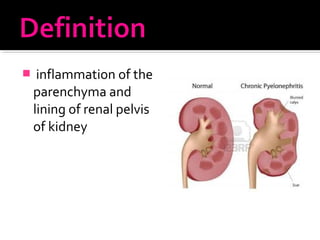
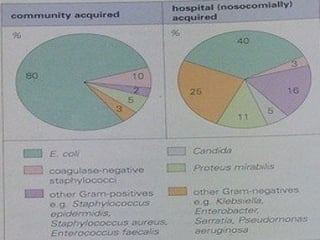
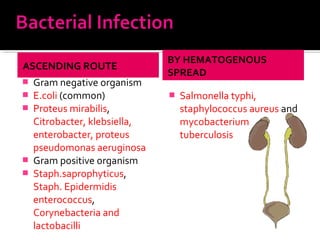
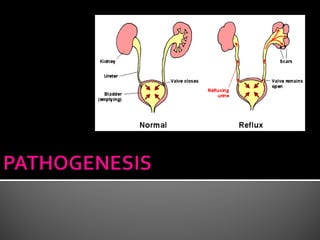
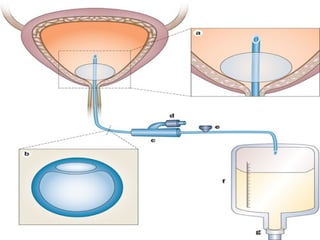
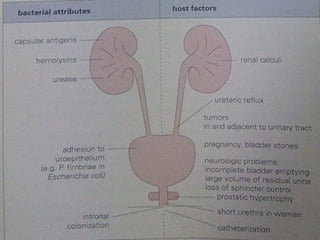
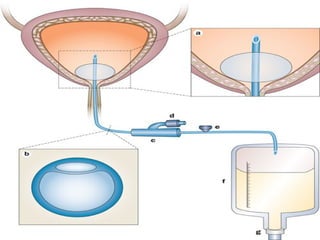
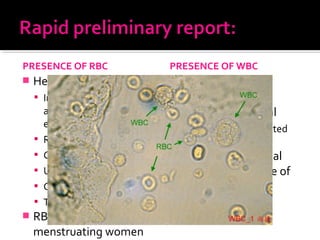
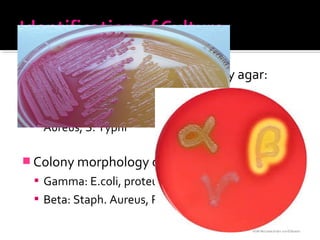
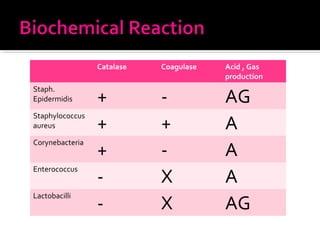
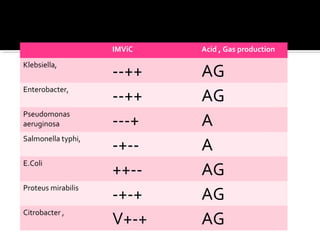
This document discusses urinary tract infections (UTIs), including pyelonephritis. It defines UTIs as inflammation of the renal pelvis and kidney parenchyma. E. coli is the most common causative organism, entering the urinary tract via the urethra or hematogenously. Risk factors include female anatomy, catheterization, neurological conditions, pregnancy, and diabetes. Symptoms range from asymptomatic to fever and flank pain. Diagnosis involves urine culture and microscopy. Treatment consists of antibacterial therapy and fluid intake. Prevention focuses on proper catheter care and hygiene.