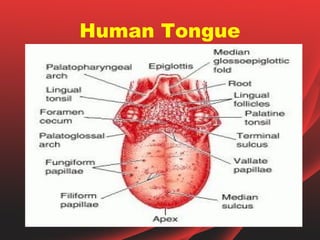
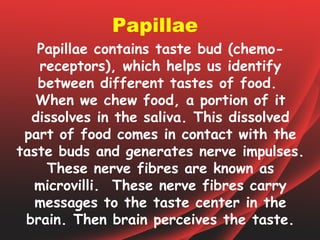
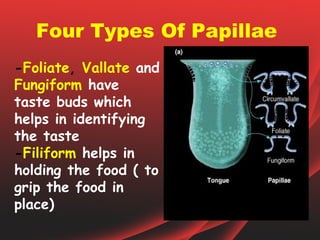
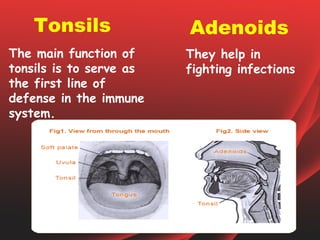
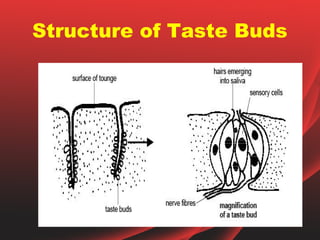
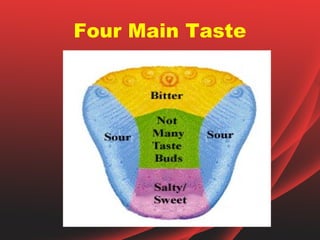
The document provides an overview of the human tongue, describing its structure, function, and the role of taste buds in perceiving flavors. It also outlines various diseases affecting the tongue, such as oral candidiasis and leukoplakia, along with their symptoms and treatment options. Key sections include the types of papillae and their functions, as well as the immune functions of the tonsils associated with the tongue.