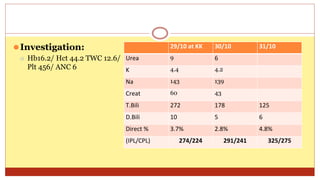
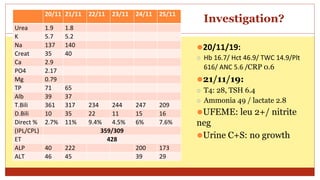
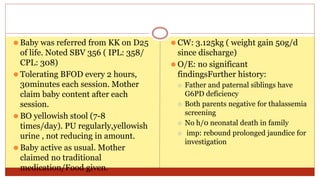
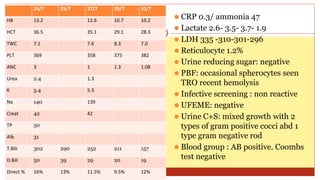
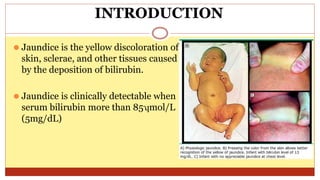
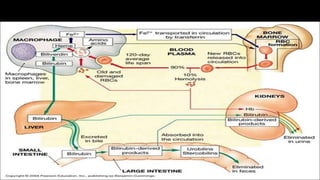
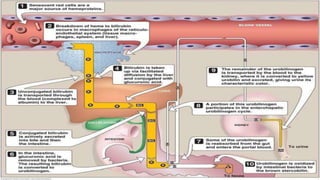
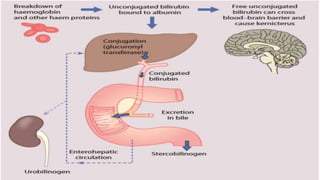
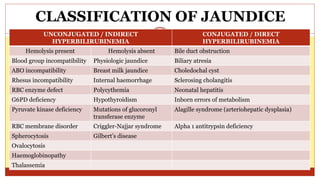
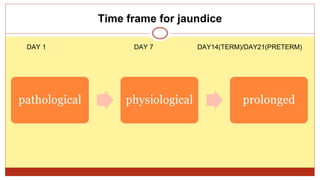
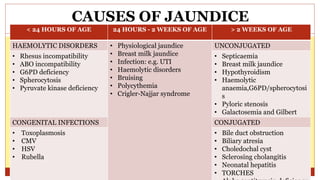
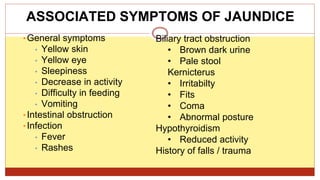
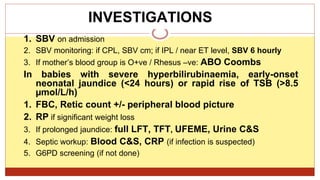
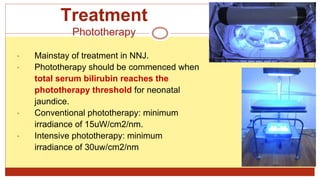
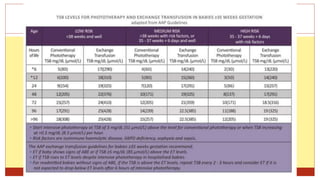
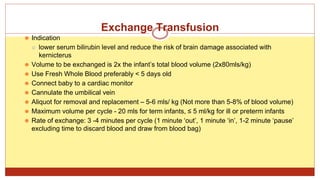
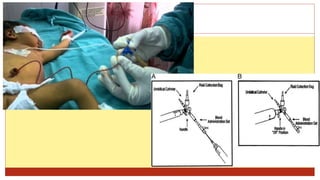
- This document presents 3 case scenarios of neonatal jaundice. The first case involves a 2-day old female infant with a serum bilirubin of 272 referred for poor breastfeeding and phototherapy. The second case involves a 10-day old male infant referred for jaundice and weight loss with a bilirubin of 310. The third case involves a 25-day old male infant with a history of jaundice and admissions with a current bilirubin of 356.