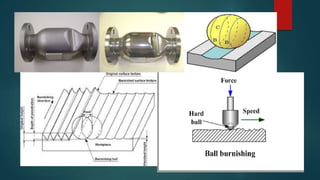
This document discusses methods for reducing the stair step effect in additively manufactured surfaces. It begins with an introduction to rapid prototyping and additive manufacturing processes. It then discusses common form errors in additive manufacturing, including flatness/straightness errors, cylindricity errors, and stair step errors. The document focuses on stair step errors, explaining that they occur due to the layered manufacturing process approximating surfaces. It then discusses several methods for reducing stair step errors, including adaptive slicing to vary layer thicknesses based on geometry, and ball burnishing as a post-processing technique to smooth layer edges through plastic deformation. Finally, it discusses factors that influence the effectiveness of ball burnishing, such as ball diameter, rolling pressure, and