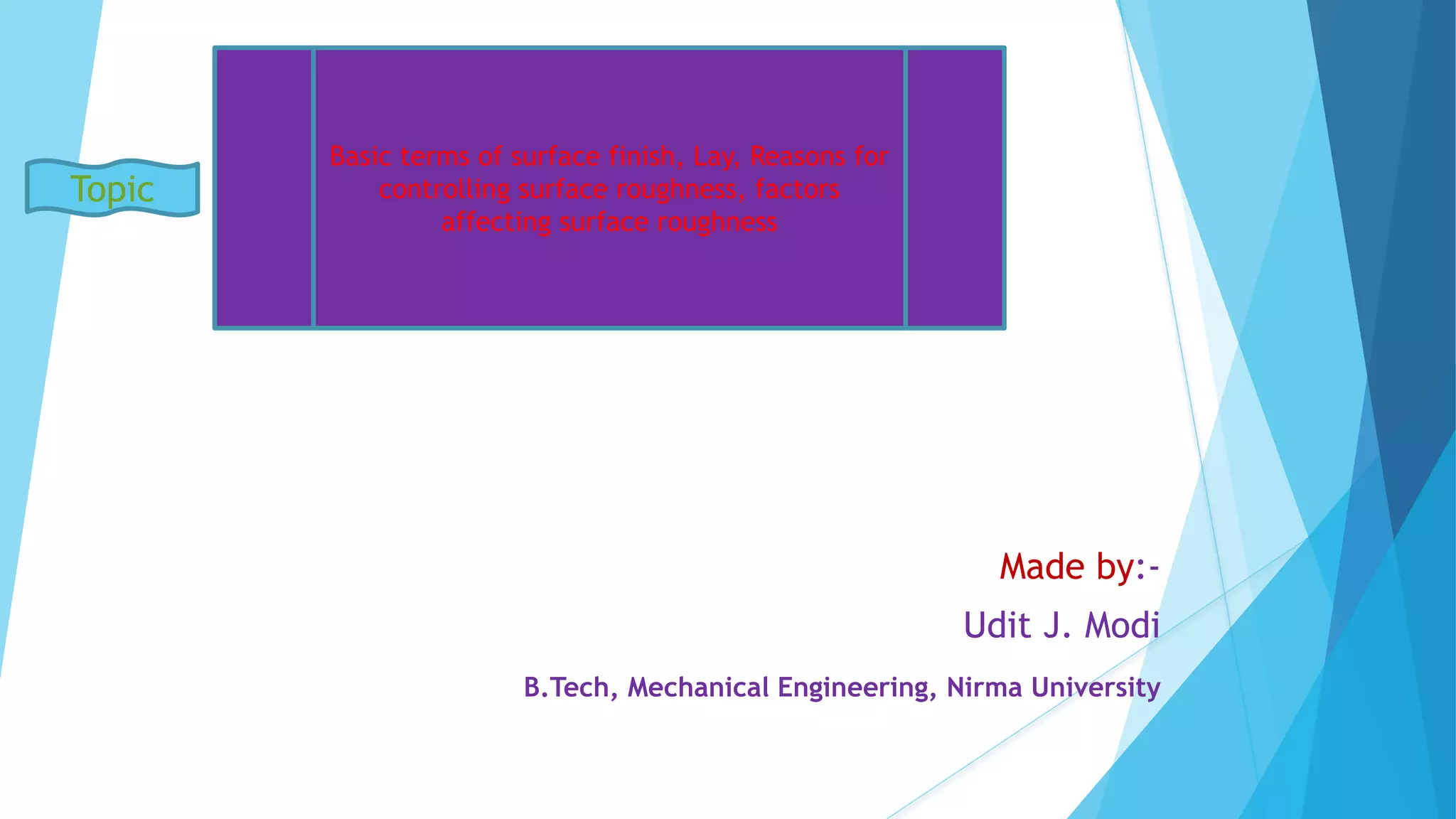
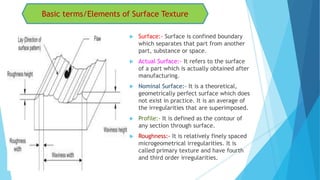
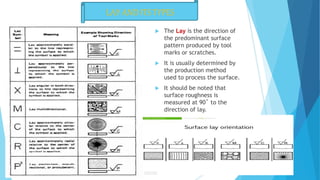
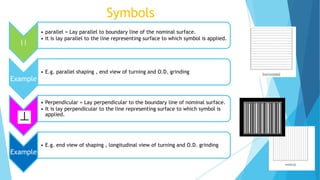
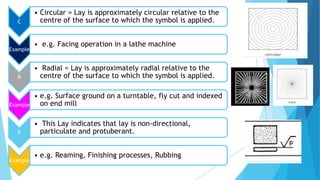
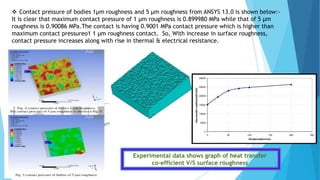
The document provides an overview of surface finish concepts in mechanical engineering, detailing terms such as surface, roughness, waviness, and flaws. It discusses the importance of controlling surface texture for improving performance, durability, and aesthetic appeal while identifying factors affecting surface roughness, including machining conditions and cutting tool characteristics. Additionally, it explores specific examples of how surface texture impacts functionality in various applications.