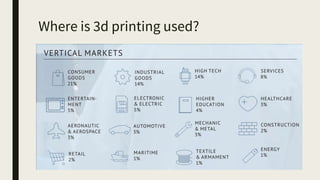
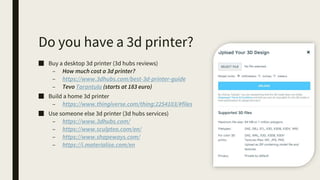
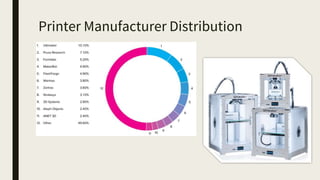
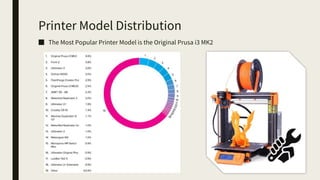
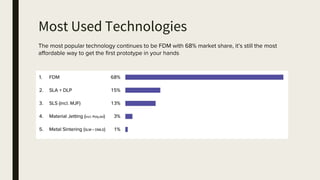
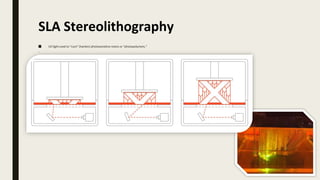
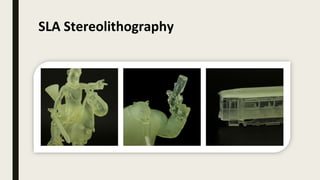
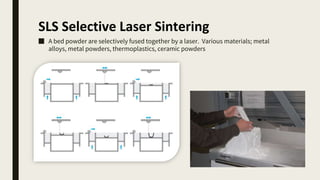
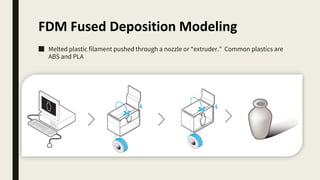
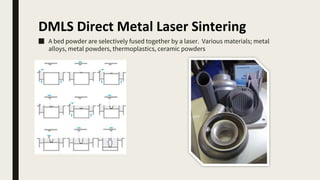
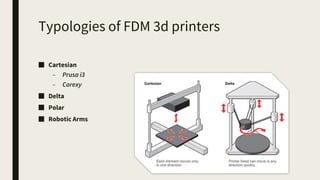
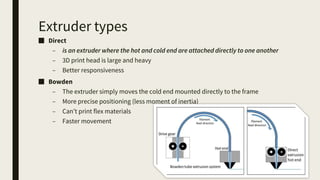
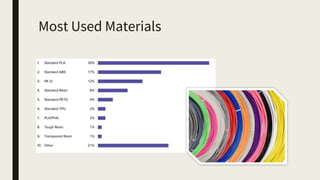
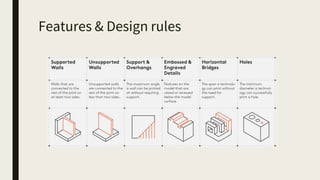
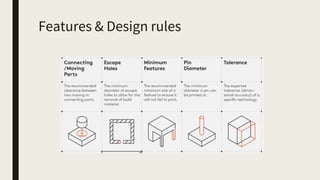
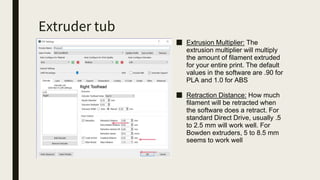
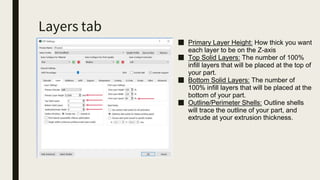
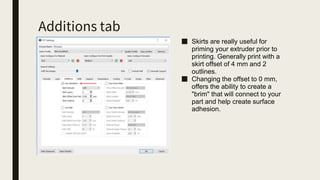
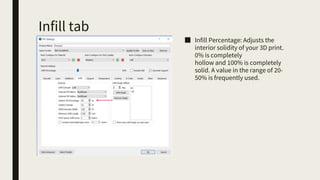
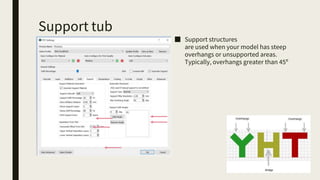
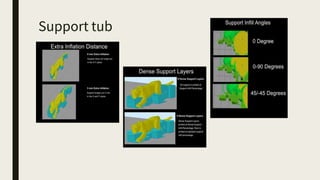
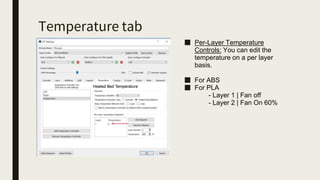
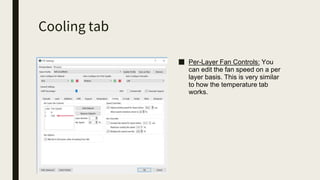
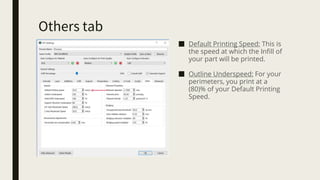
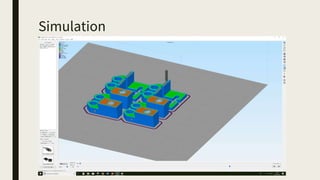
3D printing involves using computer-controlled layering to create 3D objects from digital files. The most common technologies are Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). To get started with 3D printing, you need a 3D printer, filament or resin, a CAD program, 3D model files, and a slicer program to prepare files for printing. Popular desktop 3D printers start around $183, or you can access printers through services like 3D Hubs. Common materials include PLA, ABS, and resins for SLA printers.