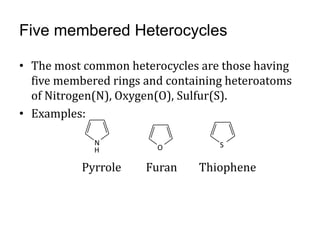
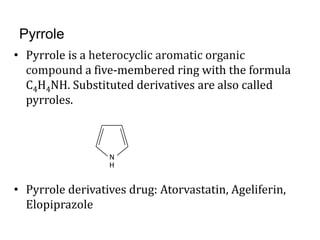
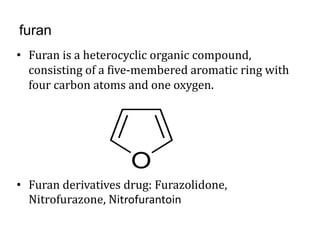
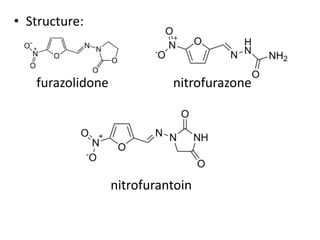
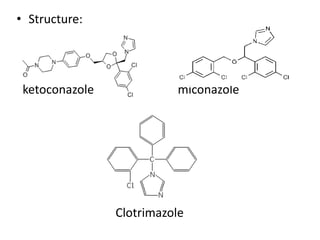
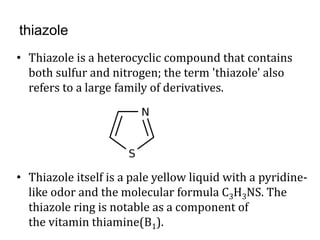
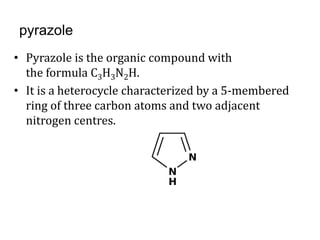
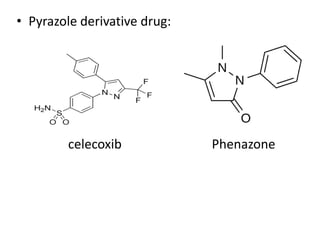
This document presents information on 5-membered heterocycles that are pharmaceutically important. It discusses heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and describes examples like pyrrole, furan, thiophene, imidazole, thiazole, pyrazole and oxazole. For each heterocycle, it provides structural examples of drug derivatives and their uses such as treatment of dyslipidemia, antibacterial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and muscle relaxant activities.