The document outlines operational techniques in the operating room (OR) as presented by Ame Mehadi from Haramaya University. It covers essential OR design principles, necessary equipment, aseptic techniques, and the roles of personnel, emphasizing infection prevention and patient care before, during, and after surgical procedures. Key sections also define areas within the OR and highlight the importance of environmental factors like lighting, ventilation, and temperature control for optimal surgical outcomes.

























![December 2024 © Haramaya University, CHMS,
Department of Emergency and Critical Care Nursing
Operation Room Technique
By Ame Mehadi (EMCCN, Assistant Professor)
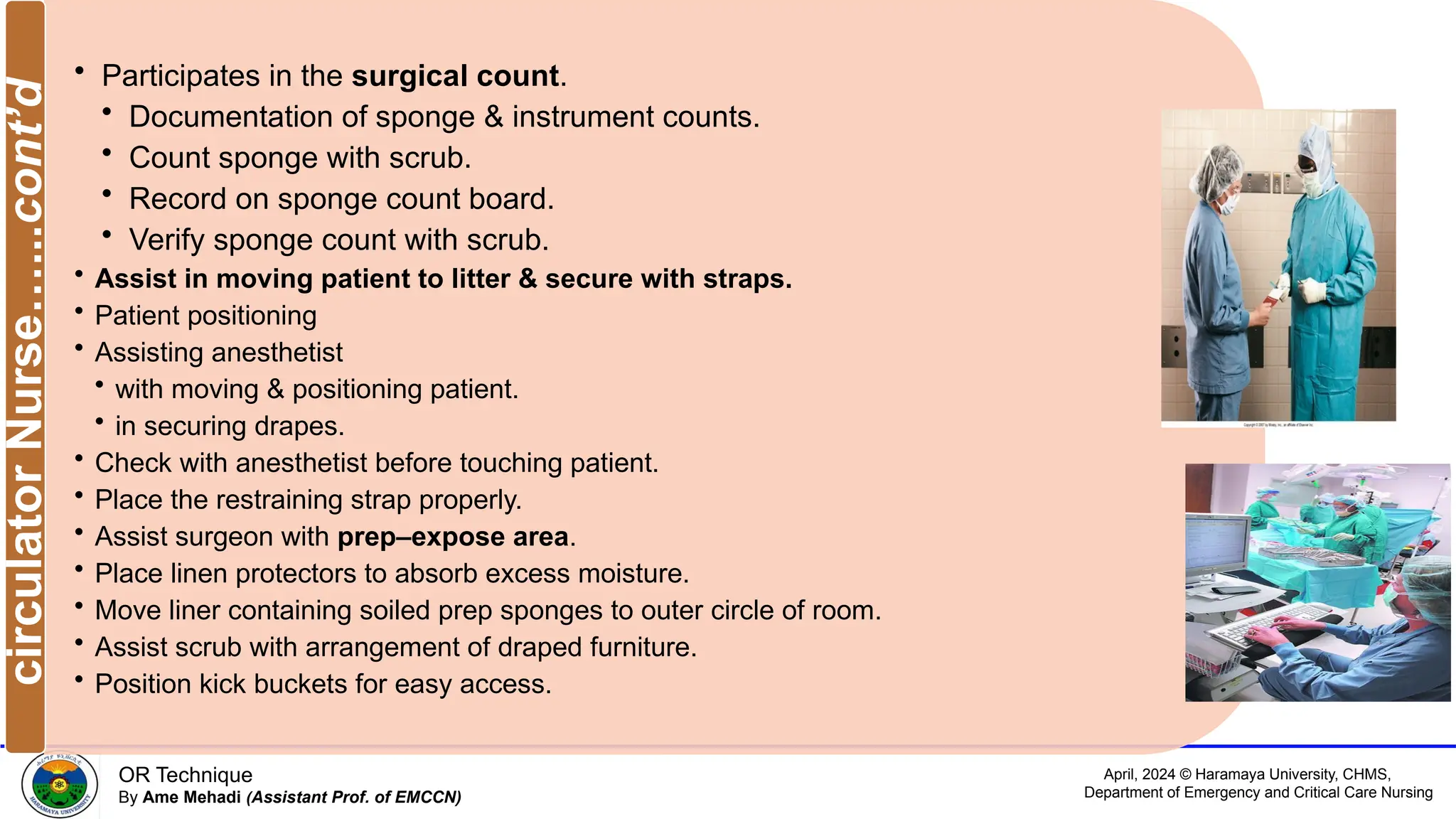
Materials required in RR
Emergency drugs
• Adrenaline
• Analgesics like morphine
• Anti-emetic drugs
• Chlorpromazine
• Promethazine
• Anticholinergic drugs like atropine
• decrease secretion, increase HR
• Sodium bicarbonate –for acidosis
IV fluids
• Crystalloids – are fluids with lower
molecular weight.
• e.g.
• 5% DW [sugar + water]
• 0.9% NS [salt + water]
• 5% DNS [sugar + salt]
• R/L [water + electrolytes-k, Ca, Mg
etc.
• Colloids – are fluids with higher
molecular weight
• Are plasma expanders –used for
hemorrhagic (bleeding) pts.
• e.g. Dextran, plander, plasmin.
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-250129125239-9f2d0e04/75/1-Introduction-to-Operation-Theatre-Nursing-35-2048.jpg)




















![December 2024 © Haramaya University, CHMS,
Department of Emergency and Critical Care Nursing
Operation Room Technique
By Ame Mehadi (EMCCN, Assistant Professor)
• Nurses may be assigned to
• the scrub,
• the circulator,
• the recovery room,
• the workroom,
• the instrument room,
• the anesthesia section, or
• any other area within the surgical suite.
• function in various roles, including those of
• manager/director,
• clinical practitioner,
• e.g.,
• scrub,
• circulator,
• clinical nurse specialist,
• registered nurse first assistant [RNFA],
• educator, and
• researcher.
General
Responsibilities
of
Nurses
in
the
OR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-250129125239-9f2d0e04/75/1-Introduction-to-Operation-Theatre-Nursing-59-2048.jpg)