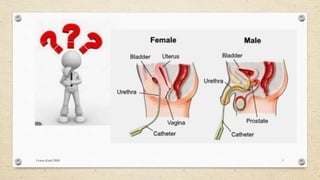
Catheterization is the process of drawing urine from the bladder using a catheter inserted through the urethra, performed with aseptic technique. It serves multiple purposes, including relieving urine retention, obtaining specimens, and facilitating urinary drainage in surgical patients. The document details types of catheterization, equipment needed, principles to follow, and specific procedures for both male and female patients.