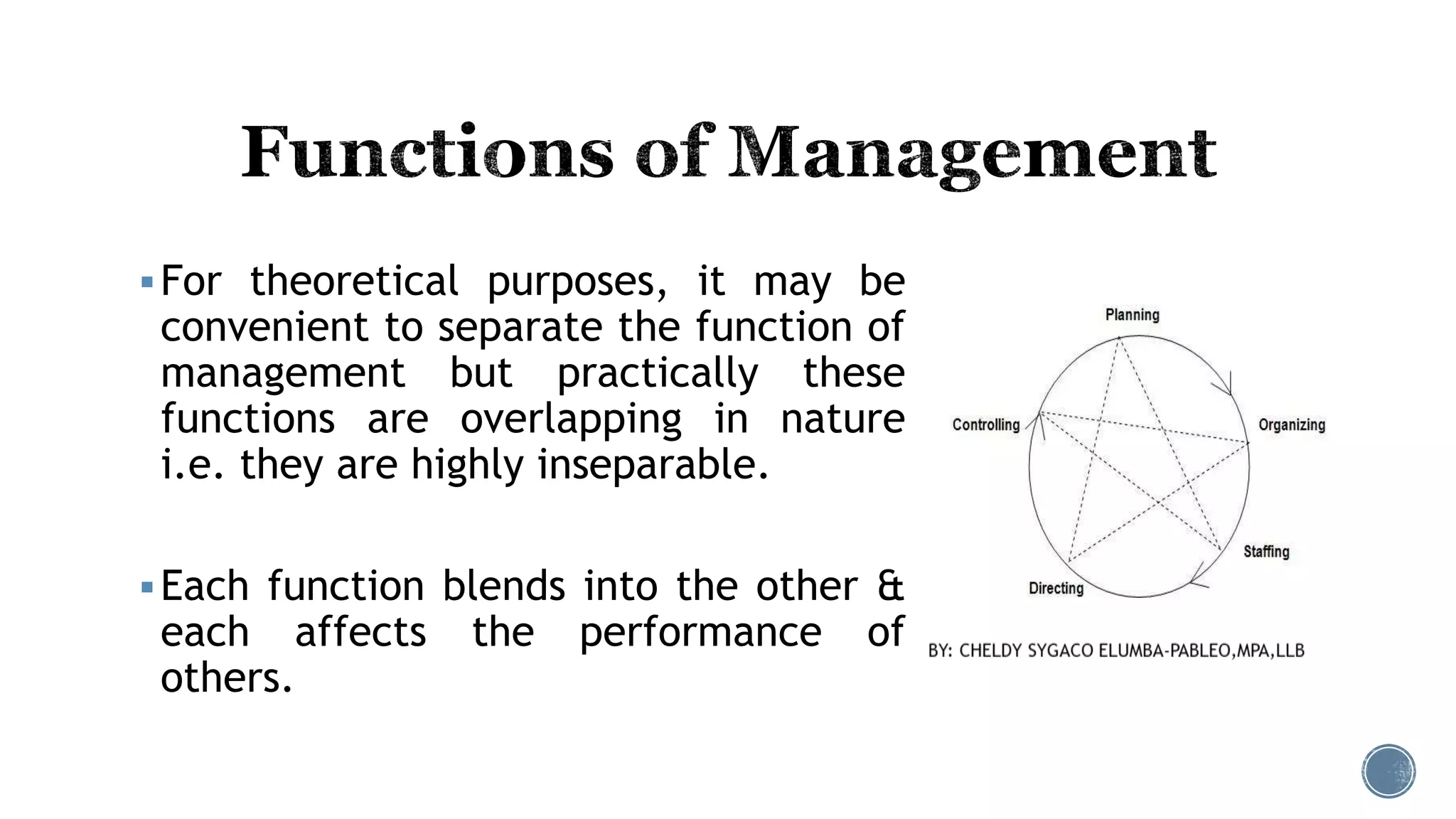
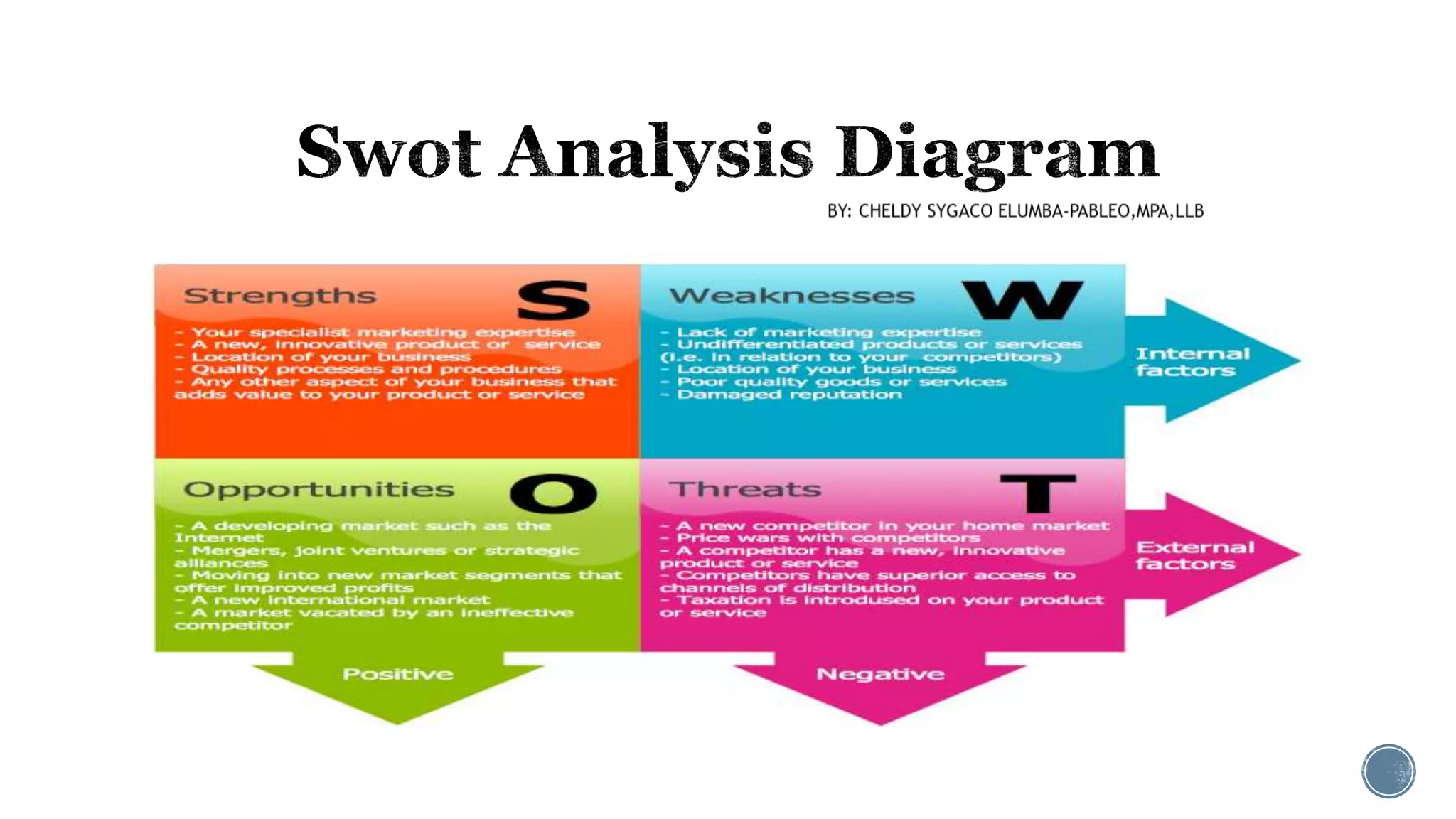
The document discusses the concept of media as a communication tool and the related field of media management, which involves tasks like processing and tracking media files. It outlines the four fundamental functions of management: planning, organizing, directing, and controlling, emphasizing their interrelated nature and continuous process. Additionally, it describes the levels of management within an organization, detailing the responsibilities and roles of top, middle, and lower-level management.