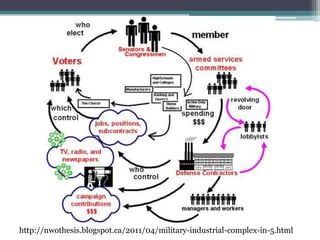
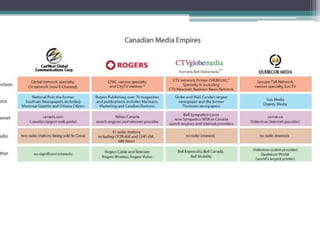
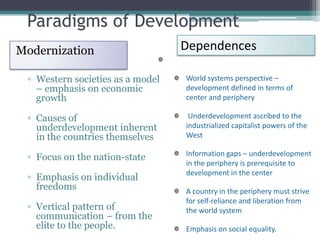
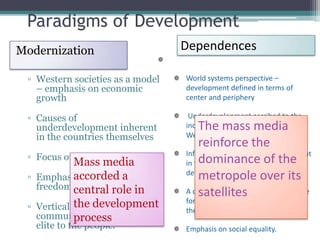
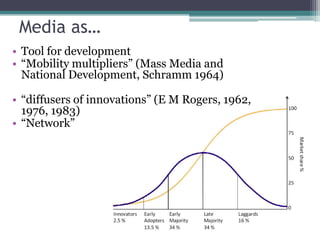
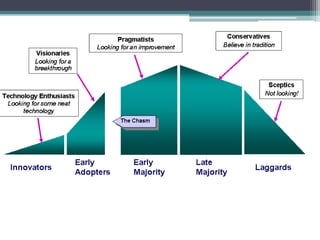
This document discusses changing conceptions of development and the role of media. It explores how views of development have shifted from modernization theories focusing on economic growth to more critical dependency and participatory paradigms. The document also examines how assumptions about media's role in development have changed from thinking media could drive development to recognizing its more limited effects and the need for audience participation. It notes increasing concerns about media concentration and calls for a more democratic, participatory media order.