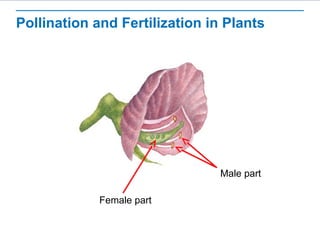
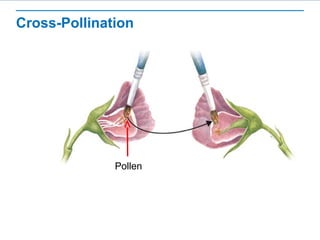
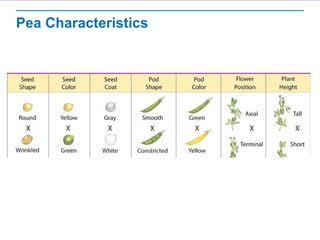
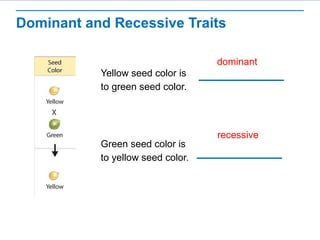
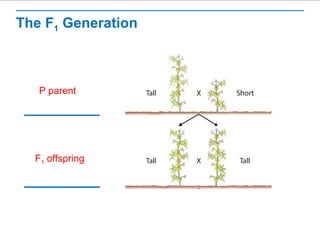
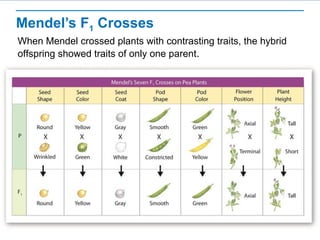
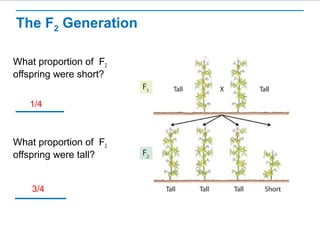
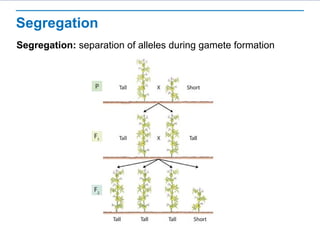
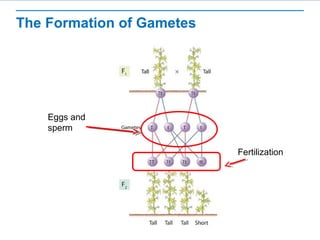
Gregor Mendel conducted experiments with pea plants to study inheritance of traits. He found that (1) when he crossed plants with contrasting traits, the hybrid offspring only showed traits of one parent, (2) in the next generation, the traits separated and were expressed in a 3:1 ratio, with the dominant trait appearing more often. His findings supported that inheritance is determined by discrete units (genes and alleles) that are transmitted from parents to offspring and can be dominant or recessive.