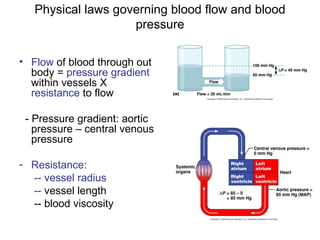
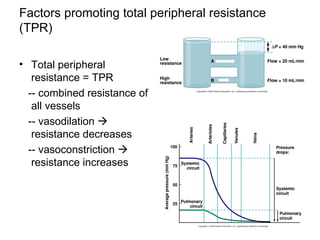
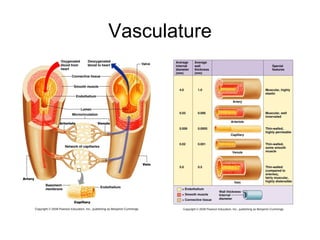
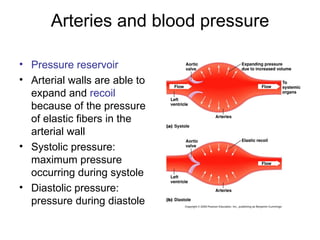
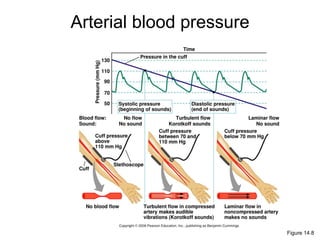
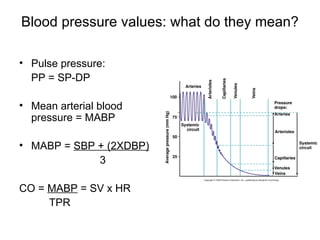
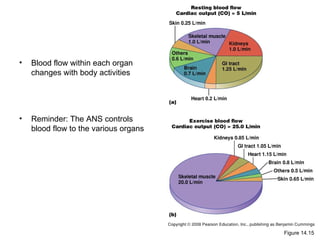
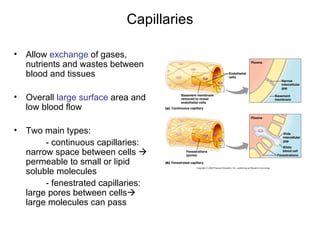
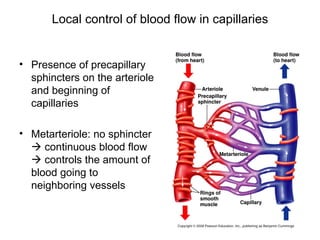
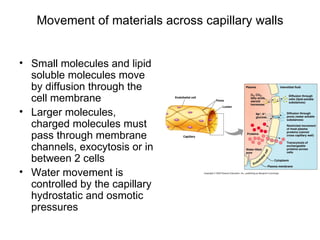
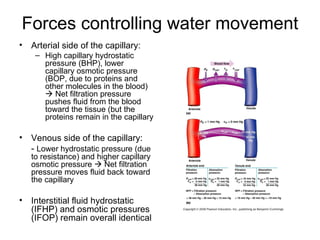
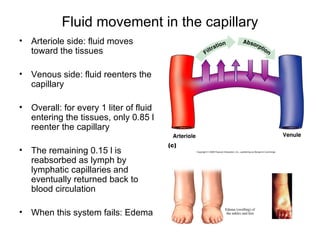
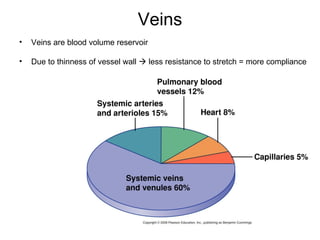
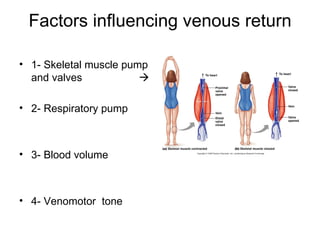
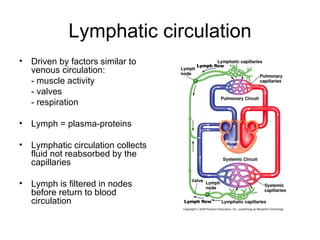
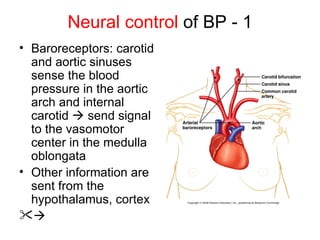
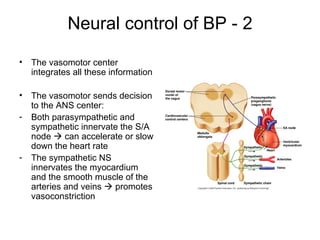
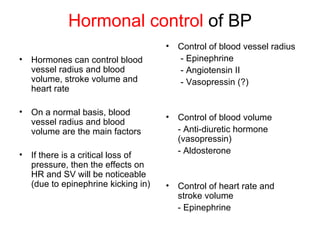
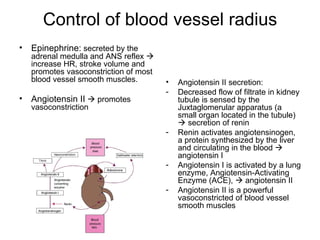
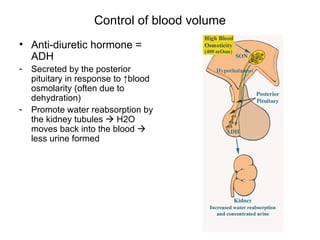
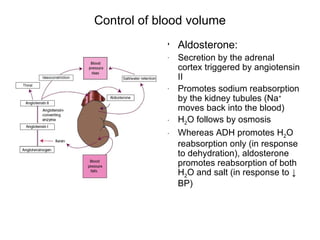
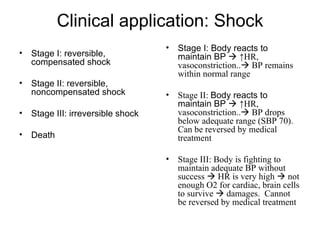
This document provides an outline and overview of the cardiovascular system, including blood flow, blood pressure, vasculature, arteries, capillaries, veins, and lymphatic circulation. It discusses the physical laws governing blood flow and pressure, factors that influence resistance and peripheral resistance. It also examines the regulation of blood flow and pressure through intrinsic controls like metabolic activity and stretch of arteries as well as extrinsic controls like neural and hormonal mechanisms. The goal is to explain how blood is circulated and pressure is maintained through the complex cardiovascular system.