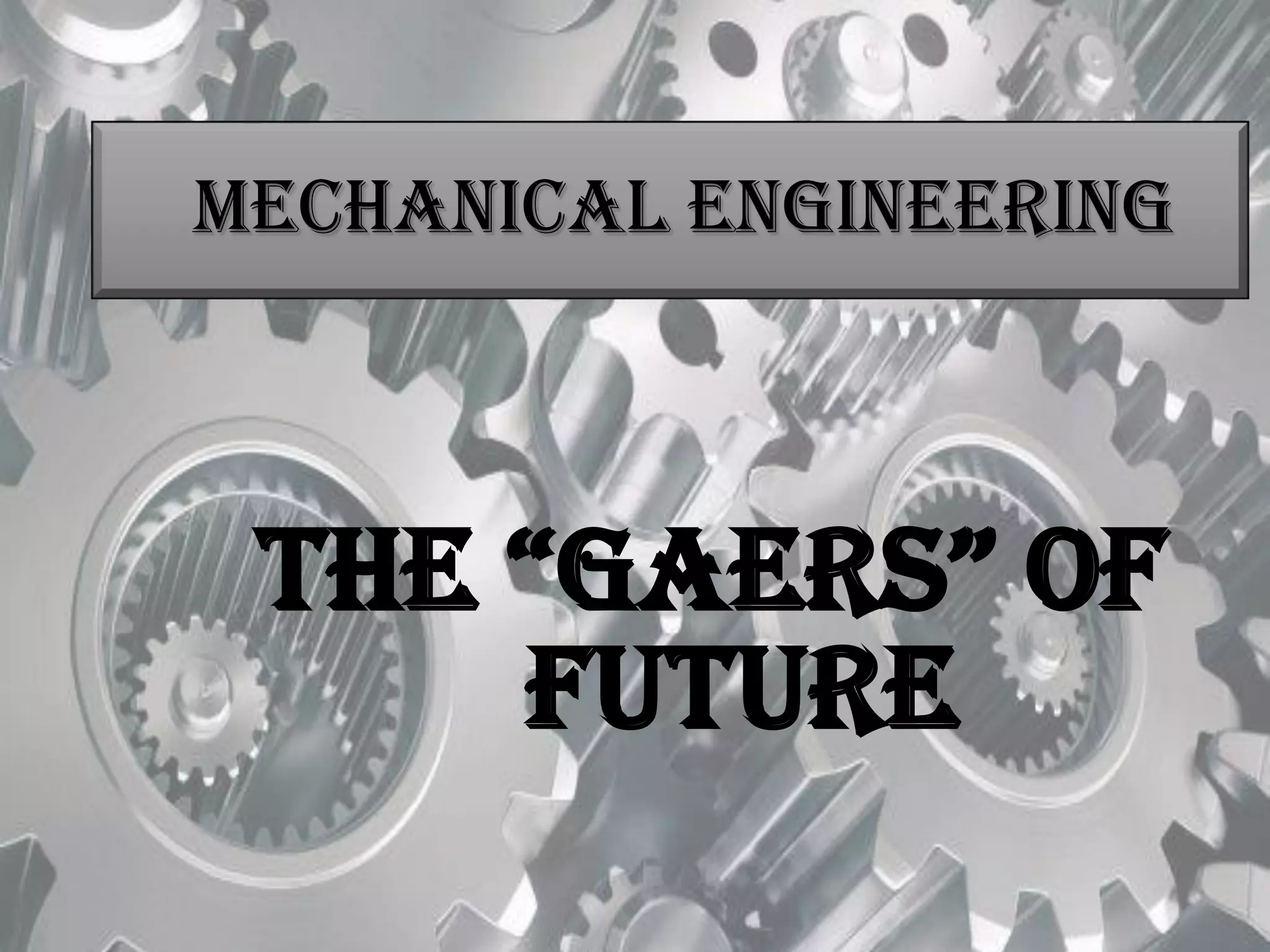
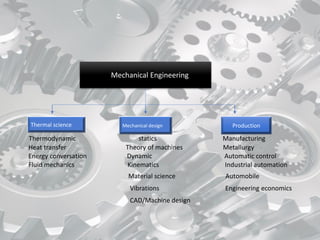
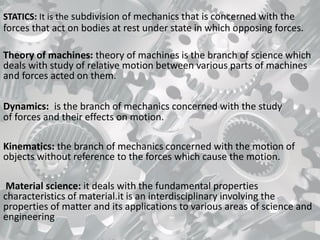
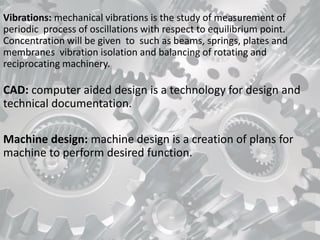
Mechanical engineering is a broad field that applies principles of physics, mathematics, and materials science to design, analyze, manufacture, and maintain mechanical systems. It touches many aspects of modern life as it deals with objects and systems in motion, including the human body. Some key areas of mechanical engineering include thermodynamics, heat transfer, fluid mechanics, dynamics, materials science, manufacturing, and design. Mechanical engineering involves tasks like analyzing energy usage and conversion, modeling fluid flow and thermal energy transfer, designing mechanical components, and overseeing manufacturing processes. It is one of the broadest and oldest of the engineering disciplines.