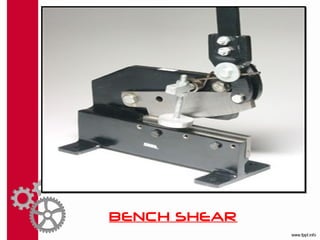
Mechanical cutting involves splitting a workpiece into two by removing a thin slice of material. The key processes are sawing using hacksaws, bandsaws, and circular saws. Hand shears use one hand to snip and collect while long blades make them versatile. Bench shears are mounted and have a lever mechanism to increase force but cannot do delicate work. Guillotines use a heavy sliding blade for beheading. Shear machines cut stock without chips using straight or curved blades for sheet metal. Nibblers cut sheet metal with minimal distortion using punch and die or scissor-like mechanisms. Bench shears can normally cut up to 0.5mm thick mild steel.