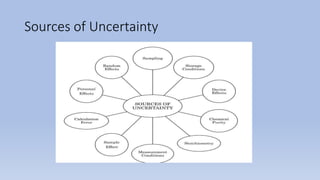
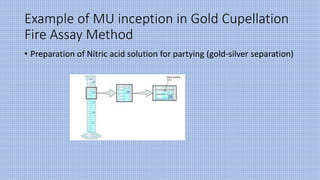
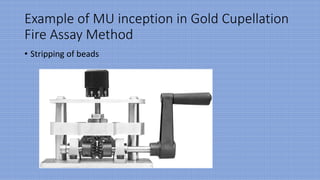
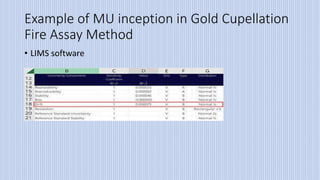
The document discusses measurement uncertainty (mu) in testing laboratories, particularly in the context of gold fire assay, highlighting the definitions, sources, and types of errors involved. It emphasizes the importance of accuracy and precision, as well as the necessity of following ISO 17025:2017 standards for evaluating measurement uncertainty. The document also outlines seven basic steps for determining mu and includes a general formula for its calculation.













![General formula for calculation of mu
• Measurement Uncertainty (MU) = √ [∑ (xi – μ)2 / (n * (n-1))]
• Where xi is reading(measured value)
μ is mean
n is number of tests](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/measurementuncertaintytestinglabs-231125081734-5a0c7455/85/MEASUREMENT-UNCERTAINTY-Gold-testing-labs-pptx-18-320.jpg)


