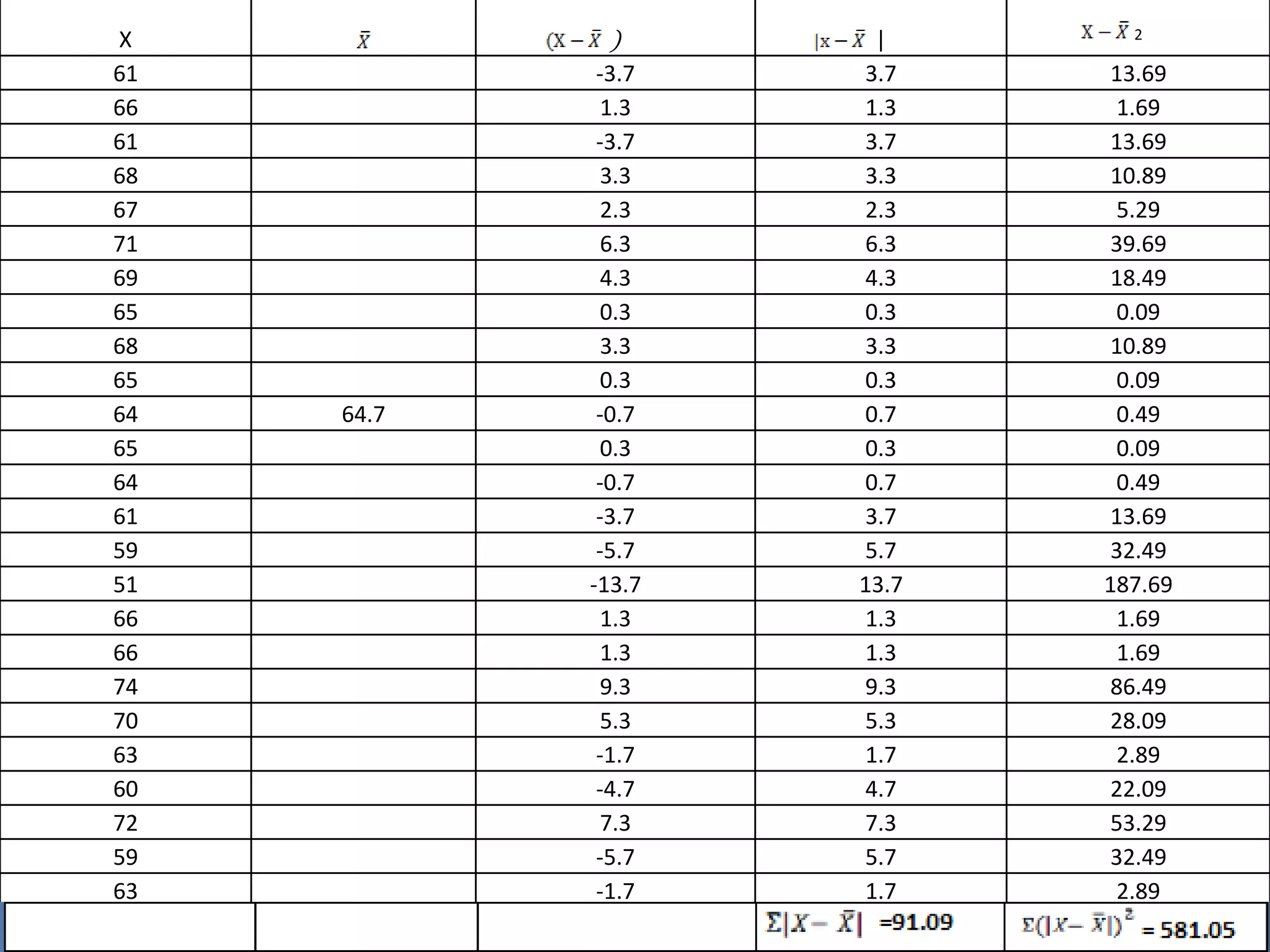
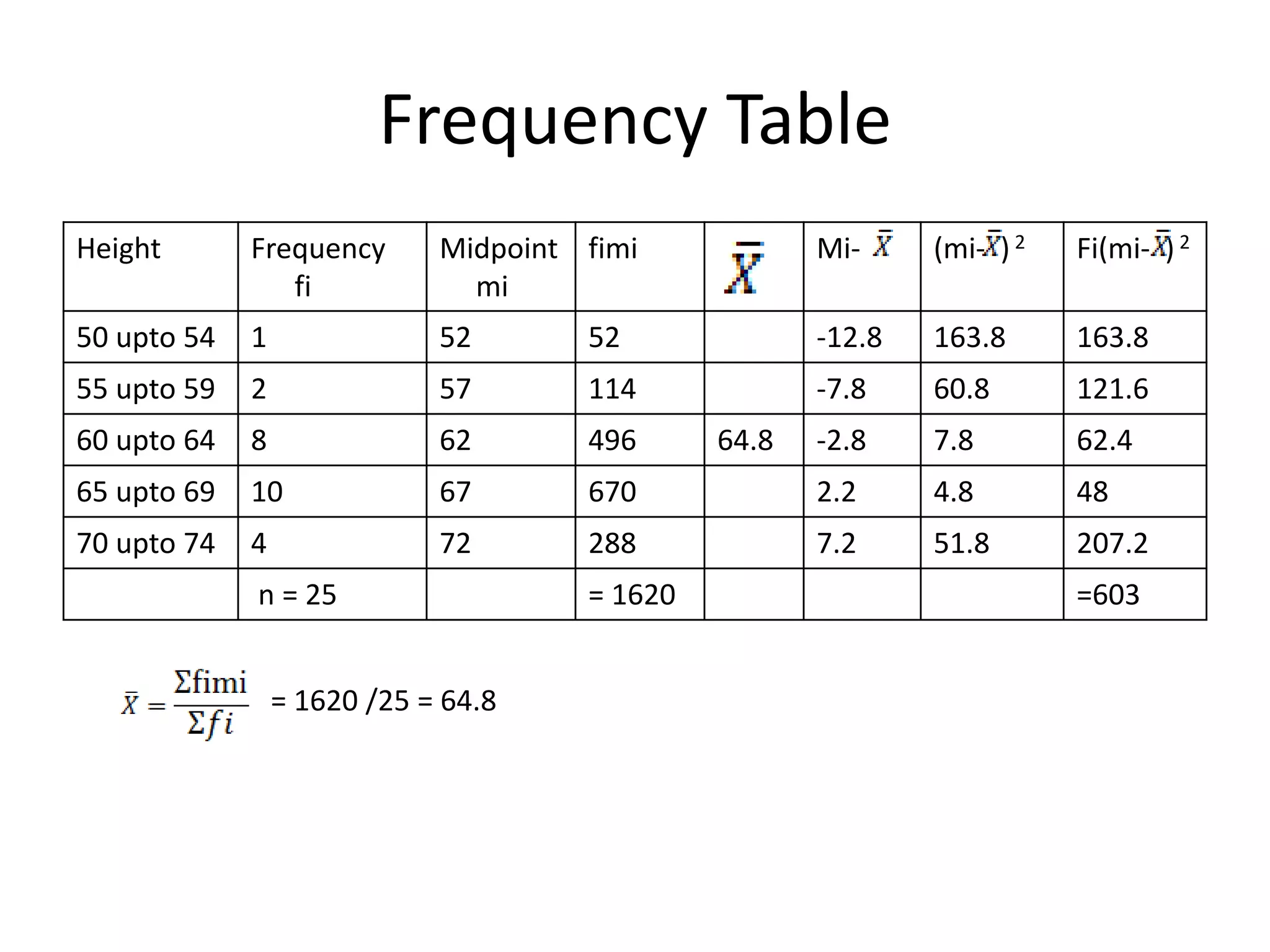
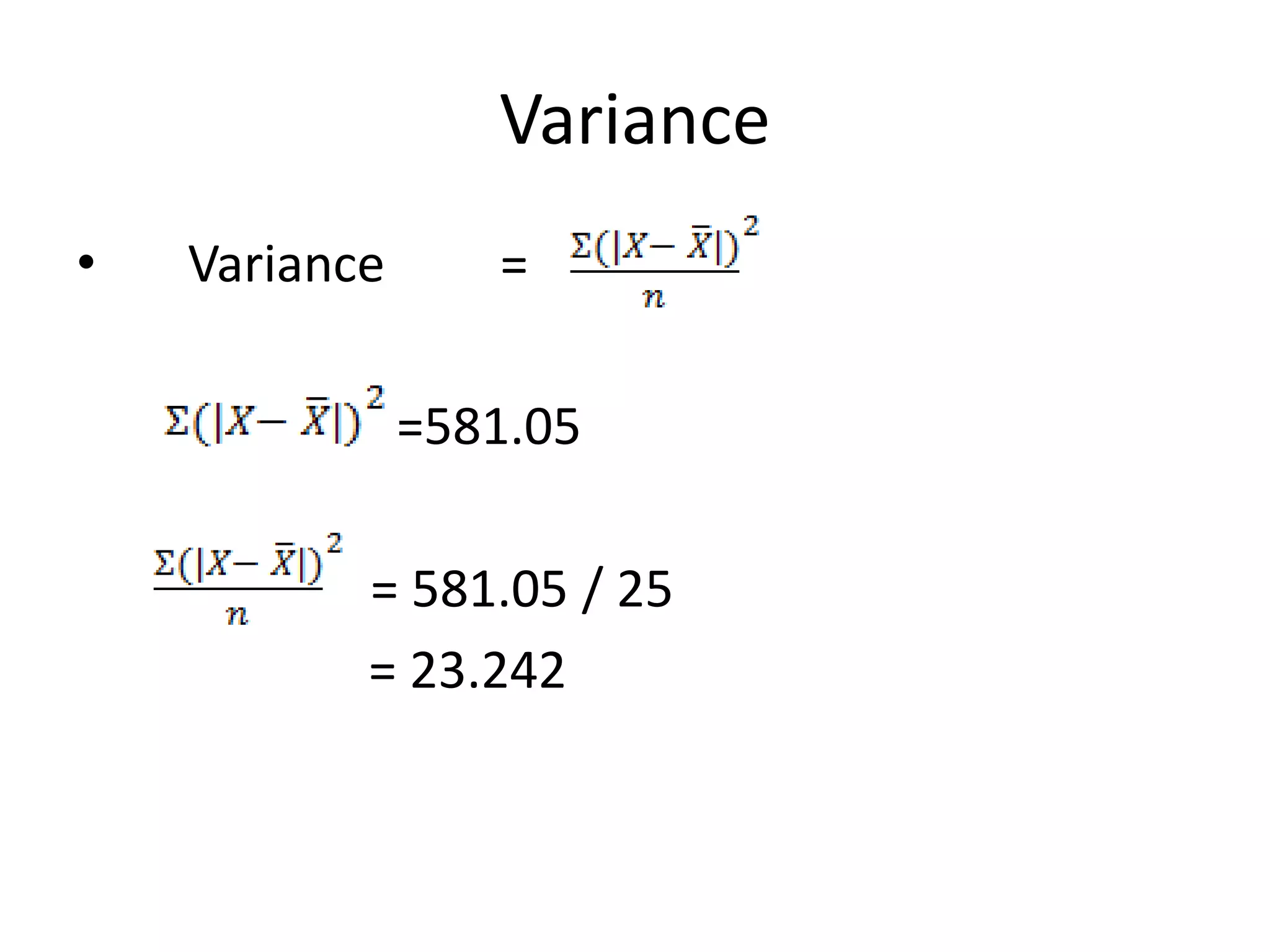This document presents information on measures of dispersion used to analyze student height data. It defines measure of dispersion as the average deviation from a central value to describe data spread. Formulas are provided for range, coefficient of range, mean deviation, variance, and standard deviation. Raw height data for 25 students is analyzed, finding a range of 23 inches, mean of 64.7 inches, and standard deviation of approximately 5 inches. Measures of dispersion are used to understand data homogeneity, mean reliability, and distribution comparisons.