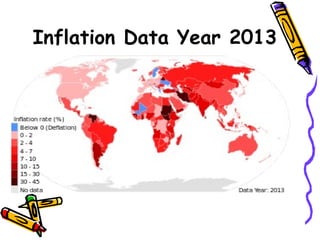
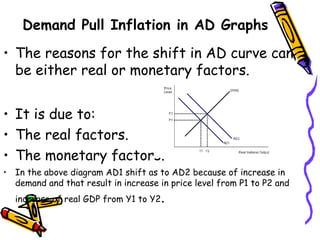
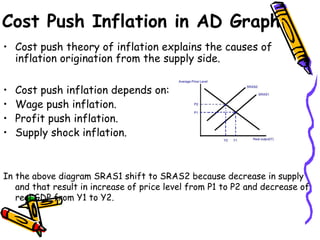
This presentation discusses macroeconomic topics including inflation, consumption, savings, investment, and unemployment. It focuses on defining inflation and exploring different types of inflation such as demand-pull, cost-push, and structural inflation. The presentation is given by a team of 5 students who are introduced. In particular, it examines inflation in developing countries like Bangladesh, outlining effects such as discouraging investment and savings, adding inefficiencies, causing budgeting difficulties, demanding rapid wage increases, and risking hyperinflation.