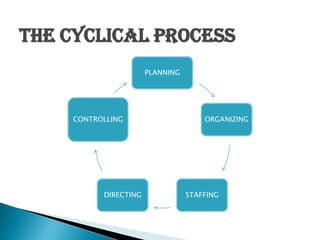
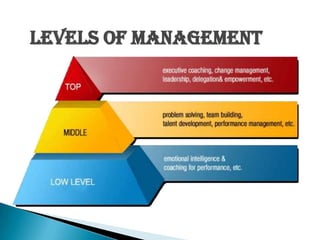
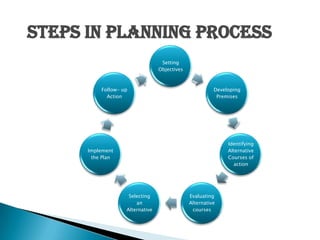
Management involves planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling to accomplish organizational goals through a group of people. It is a continuous social process that coordinates work activities. Effective management utilizes resources to develop innovations, integrate interests, and provide stability. Over time, management evolved from a strict, top-down approach to focus more on strategic planning, quality, technology, and human factors through various theories. Managers require technical, human, and conceptual skills to fulfill interpersonal, informational, and decision-making roles within legal and ethical boundaries.