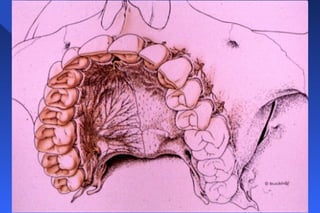
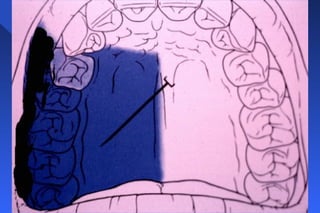
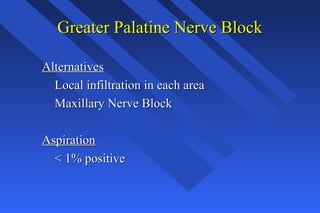
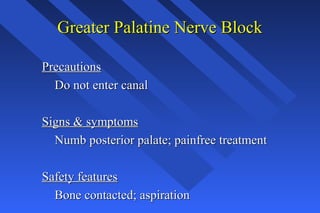
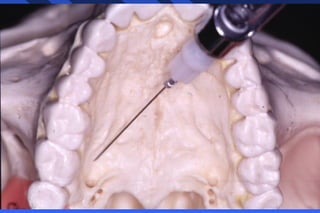
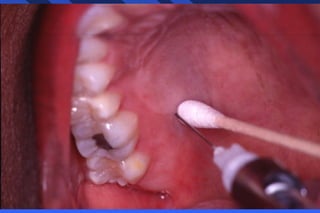
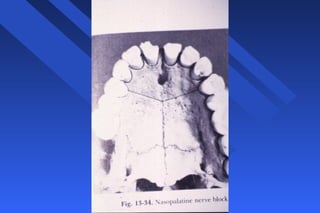
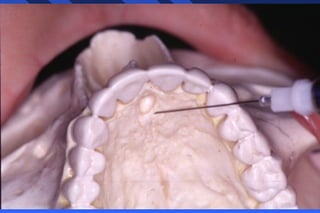
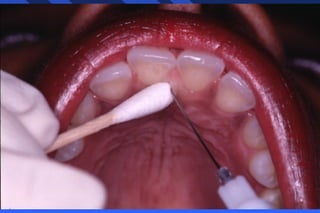
This document provides information on palatal anesthesia techniques, including greater palatine and nasopalatine nerve blocks. It describes the indications, contraindications, advantages, disadvantages, alternatives, landmarks, precautions, techniques, potential failures, and complications for each nerve block. The goal of these techniques is to provide pain control in the hard and soft tissues of the posterior or anterior palate for dental procedures by injecting a small volume of local anesthetic near the targeted nerve.